Nomenclature
Short Name:
LRRK1
Full Name:
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 1
Alias:
- EC 2.7.11.1
- KIAA1790
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
TKL
Family:
LRRK
SubFamily:
NA
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
225,150 (partial)
# Amino Acids:
# mRNA Isoforms:
2
mRNA Isoforms:
225,393 Da (2015 AA; Q38SD2); 28,848 Da (264 AA; Q38SD2-2)
4D Structure:
NA
1D Structure:
Subfamily Alignment
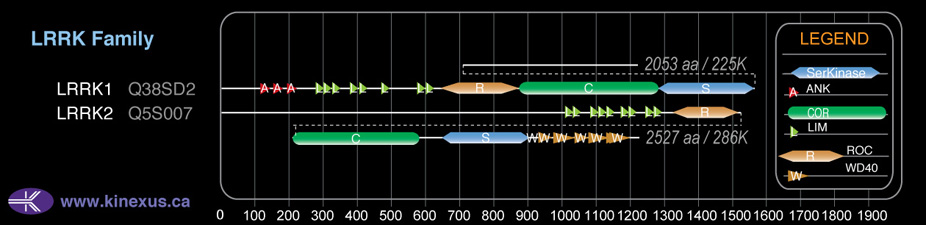
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K1276, K1278.
Serine phosphorylated:
S182, S337, S360, S1064, S1100, S1103, S1104, S1241, S1246, S1855, S1858.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T30, T175, T358, T1628.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y183, Y971, Y1063, Y1098, Y1258, Y1430-.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 100
100
799
16
1075
 4
4
28
8
22
 30
30
236
3
179
 36
36
290
42
514
 66
66
527
14
525
 3
3
22
37
12
 6
6
49
15
27
 68
68
542
17
668
 34
34
270
10
242
 5
5
36
35
66
 6
6
51
14
92
 94
94
749
65
590
 11
11
84
14
106
 4
4
35
6
20
 18
18
143
11
248
 2
2
19
7
11
 8
8
64
76
51
 13
13
104
8
133
 5
5
40
39
70
 62
62
492
56
535
 7
7
56
10
80
 10
10
76
12
65
 19
19
154
4
143
 13
13
106
8
52
 11
11
84
10
117
 72
72
573
24
630
 10
10
80
17
81
 13
13
107
8
94
 14
14
112
8
131
 21
21
169
14
80
 45
45
361
18
262
 81
81
647
27
1309
 13
13
100
44
260
 97
97
778
26
647
 9
9
74
22
65
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 94.9
94.9
96
98 96.1
96.1
97
97 -
-
-
89 -
-
-
- 66.4
66.4
69.5
91 -
-
-
- 87.8
87.8
92.1
89 86.8
86.8
91.8
88 -
-
-
- 49
49
55.3
- -
-
-
78 -
-
-
68 56.2
56.2
71.3
60 -
-
-
- 20.1
20.1
35.4
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | RIMS1 - Q86UR5 |
| 2 | LYZ - P61626 |
| 3 | EXOSC7 - Q15024 |
Regulation
Activation:
Binding of GTP stimulates kinase activity.
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
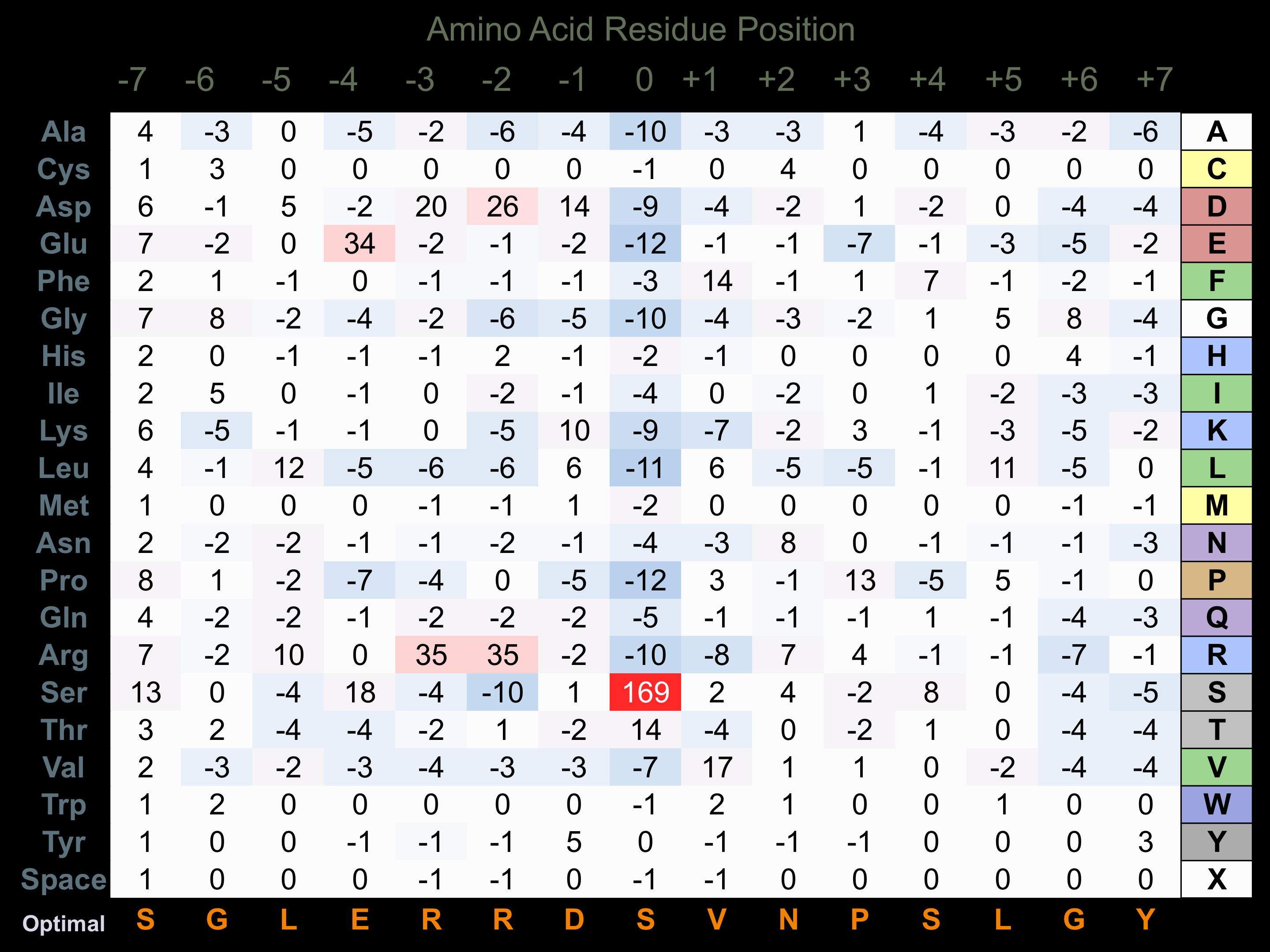
Matrix Type:
Predicted from the application of the Kinexus Kinase Substrate Predictor Version 2.0 algorithm, which was trained with over 10,000 kinase-protein substrate pairs and 8,000 kinase-peptide substrate pairs.
Domain #:
1
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Neurological disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Parkinson's disease (PD)
Comments:
LRRK1 has been implicated as a susceptibility gene for the development of Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative movement disorder, characterized by the degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the midbrain. Synptoms of PD include trembling of hands, arms, legs, and face, stiffness in the arms and legs, bradykinesia, and poor coordination and balance. Mutations in the closely related LRRK2 gene are the most common genetic causes of familial and sporadic PD. LRRK1 is thought to act as a modifier of the disease pathology through the formation of heterodimers with LRRK2 and regulate aspects of LRRK2 activity. Additionally, a missense substitution mutation (L416M) was identified in the LRRK2 protein that correlated with on average a 6.2 year younger age at time of PD onset compared to those without the mutation. Therefore, LRRK1 may affect the age of PD onset through the regulation of LRRK2 in heterodimers. Sequencing of the LRRK1 gene in 95 families with autosomal dominant PD revealed four non-synonymous amino acid substitution mutations in the coding seqeunce. Two of these substitutions were found in the WD40 domain of the LRRK1 protein (P1796H, R1850C), a domain critical for protein-protein interaction, specifically the formation of heterodimers. The other two mutations were observed in the ankyrin repeat region and COR domain. Therefore, LRRK1 is a plausible candidate gene for the development of PD through its influence on LRRK2 activity.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Classical Hodgkin lymphomas (%CFC= +103, p<0.026); Large B-cell lymphomas (%CFC= +105, p<0.001); Ovary adenocarcinomas (%CFC= +161, p<0.002); and Prostate cancer - metastatic (%CFC= -49, p<0.0001).
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis. LRRK1 autophosphorylation can be inhibited by either L1269Y or K1270W substitution mutations in the ATP-binding domain of the protein. Binding of GTP/GDP to LRRK1 can be inhibited with a K651A mutation. LRRK1 phosphotransferase activity can also be inhibited K746G, F1022C or I1412T mutations.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.06 % in 24453 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is -14% lower than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.26 % in 1229 large intestine cancers tested; 0.23 % in 569 stomach cancers tested; 0.20 % in 864 skin cancers tested; 0.19 % in 603 endometrium cancers tested; 0.125 % in 273 cervix cancers tested; 0.097 % in 1608 lung cancers tested; 0.08 % in 125 biliary tract cancers tested; 0.08 % in 947 upper aerodigestive tract cancers tested; 0.06 % in 1512 liver cancers tested; 0.06 % in 1289 breast cancers tested; 0.058 % in 2031 central nervous system cancers tested; 0.05 % in 807 ovary cancers tested; 0.05 % in 710 oesophagus cancers tested; 0.05 % in 1437 pancreas cancers tested; 0.05 % in 1253 kidney cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: R1924C (6); R1924H (3).
Comments:
Eleven deletions, 1 insertion and 1 complex mutation are noted on the COSMIC website.

