Nomenclature
Short Name:
MAST4
Full Name:
Microtubule-associated serine-threonine-protein kinase 4
Alias:
- EC 2.7.11.1
- KIAA0303
- Microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase family member 4
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
AGC
Family:
MAST
SubFamily:
NA
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
284,378
# Amino Acids:
2626
# mRNA Isoforms:
5
mRNA Isoforms:
284,378 Da (2626 AA; O15021); 266,119 Da (2444 AA; O15021-3); 265,354 Da (2434 AA; O15021-4); 264,762 Da (2429 AA; O15021-1); 25,702 Da (250 AA; O15021-2)
4D Structure:
NA
1D Structure:
Subfamily Alignment
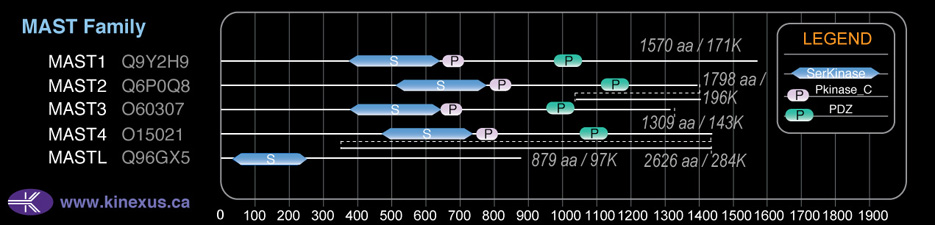
Domain Distribution:
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Methylated:
R1640, R1641.
Serine phosphorylated:
S32, S114, S166, S206, S213, S266, S268, S270, S288, S356, S358, S360, S867, S905, S906, S917, S948, S962, S964, S969, S976, S1245, S1278, S1286, S1293, S1299, S1373, S1380, S1387, S1400, S1418, S1422, S1435, S1441, S1470, S1526, S1595, S1782, S1789, S1825, S1841, S1848, S1849, S1850, S1858, S1863, S1912, S1919, S1950, S2000, S2066, S2134, S2135, S2234, S2238, S2246, S2395, S2399, S2443, S2445, S2523, S2555, S2616.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T211, T301, T726, T727, T946, T967, T1238, T1385, T1389, T1393, T1425, T1589, T1772, T1909, T1915, .
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y686, Y690, Y873, Y2382.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 100
100
1306
65
1015
 11
11
145
22
119
 12
12
156
3
100
 29
29
373
235
805
 82
82
1069
69
615
 19
19
252
155
352
 15
15
193
84
435
 63
63
823
61
2414
 41
41
534
21
370
 22
22
284
193
301
 6
6
77
39
67
 67
67
876
267
700
 5
5
62
36
47
 12
12
163
13
179
 7
7
88
30
90
 8
8
111
43
109
 19
19
248
413
1534
 10
10
134
12
99
 8
8
105
168
95
 67
67
877
266
741
 7
7
95
27
101
 6
6
72
33
73
 8
8
98
6
71
 10
10
134
11
98
 18
18
241
27
297
 90
90
1169
139
2326
 7
7
89
36
72
 12
12
159
11
110
 15
15
198
13
234
 13
13
171
84
119
 29
29
385
30
412
 52
52
679
71
1361
 14
14
179
134
482
 57
57
747
182
653
 67
67
880
98
3261
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 34
34
39.6
99 85.4
85.4
86.4
- -
-
-
83 -
-
-
- 44.2
44.2
45.9
88 -
-
-
- 81.7
81.7
86.2
83 34.6
34.6
43.7
82 -
-
-
- 41
41
45.6
- -
-
-
69 37.2
37.2
44.2
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
41 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | SMAD1 - Q15797 |
Regulation
Activation:
NA
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
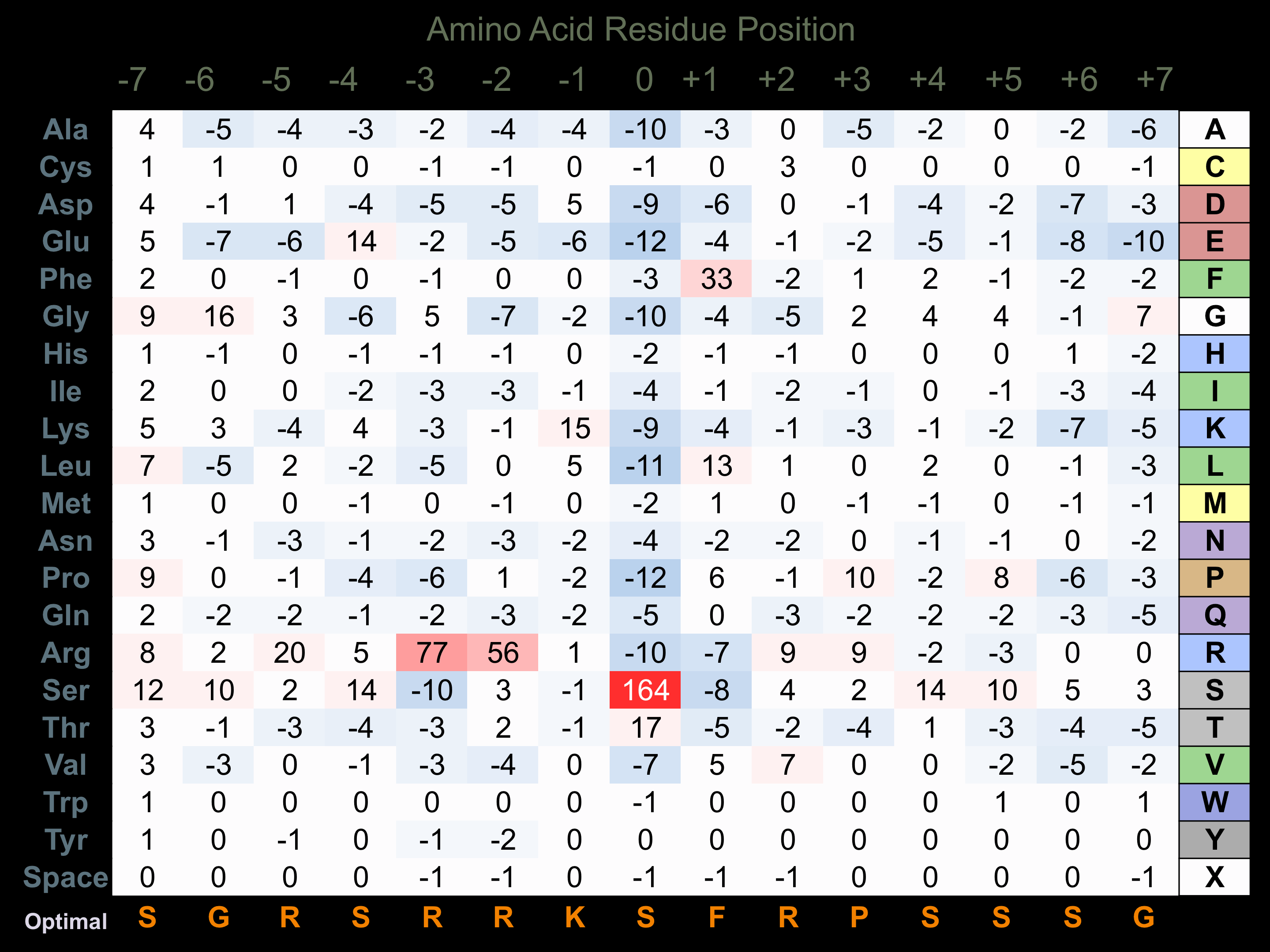
Matrix Type:
Predicted from the application of the Kinexus Kinase Substrate Predictor Version 2.0 algorithm, which was trained with over 10,000 kinase-protein substrate pairs and 8,000 kinase-peptide substrate pairs.
Domain #:
1
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer
Specific Cancer Types:
Cystic Lymphangioma
Comments:
MAST4 may be a tumour requiring protein (TRP), since it displays extremely low rates of mutation in human cancers. MAST4 has been linked to Cystic lymphangiomas, which is the growth of a soft mass in the head or neck area of a fetus or neonate. This rare condition may be a sign of chromosomal rearrangement and it can affect tissues including testes, pancreas, and the colon.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Barrett's esophagus epithelial metaplasia (%CFC= -52, p<0.043); Bladder carcinomas (%CFC= +68, p<0.006); Cervical epithelial cancer (%CFC= +62, p<0.008); Cervical cancer stage 1B (%CFC= +67, p<0.03); Cervical cancer stage 2A (%CFC= +70, p<0.098); Classical Hodgkin lymphomas (%CFC= +77, p<0.014); Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (cRCC) stage I (%CFC= +307, p<0.005); Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) (%CFC= -65, p<0.0001); Skin melanomas (%CFC= -55, p<0.056); Skin melanomas - malignant (%CFC= -91, p<0.001); Uterine fibroids (%CFC= +48, p<0.096); and Uterine leiomyomas from fibroids (%CFC= +91, p<0.02).
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.03 % in 24433 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is -62 % lower than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general. Such a low frequency of mutation in human cancers is consistent with this protein kinase playing a role as a tumour requiring protein (TRP).
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.16 % in 864 skin cancers tested; 0.14 % in 555 stomach cancers tested; 0.1 % in 1229 large intestine cancers tested; 0.06 % in 273 cervix cancers tested; 0.05 % in 1253 kidney cancers tested; 0.04 % in 1512 liver cancers tested; 0.03 % in 942 upper aerodigestive tract cancers tested; 0.03 % in 710 oesophagus cancers tested; 0.03 % in 238 bone cancers tested; 0.03 % in 1437 pancreas cancers tested; 0.02 % in 548 urinary tract cancers tested; 0.02 % in 2030 central nervous system cancers tested; 0.01 % in 881 prostate cancers tested; 0.01 % in 382 soft tissue cancers tested; 0.01 % in 1982 haematopoietic and lymphoid cancers tested; 0.01 % in 1608 lung cancers tested; 0.01 % in 1289 breast cancers tested; 0 % in 807 ovary cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: N75K (8).
Comments:
Nine deletions, 4 insertions, and no complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

