Nomenclature
Short Name:
MER
Full Name:
Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase MER
Alias:
- C-mer
- C-mer proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase
- MERTK
- Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase MER precursor
- Receptor tyrosine kinase MerTK
- RP38
- EC 2.7.10.1
- Kinase Mer
- MGC133349
- MERK
Classification
Type:
Protein-tyrosine kinase
Group:
TK
Family:
Axl
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
110249
# Amino Acids:
999
# mRNA Isoforms:
1
mRNA Isoforms:
110,249 Da (999 AA; Q12866)
4D Structure:
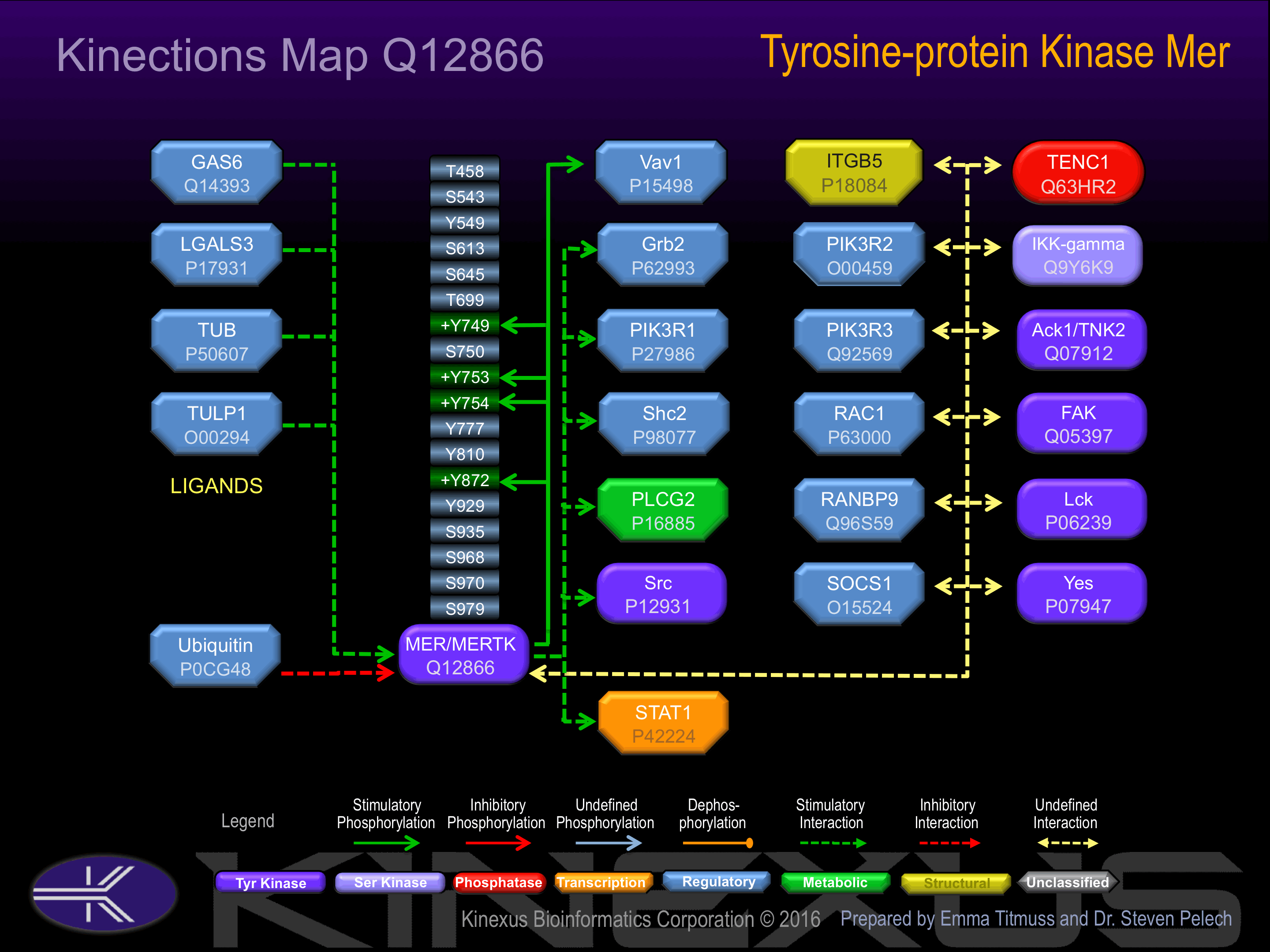
Interacts (upon activation) with TNK2; stimulates TNK2 autophosphorylation.
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
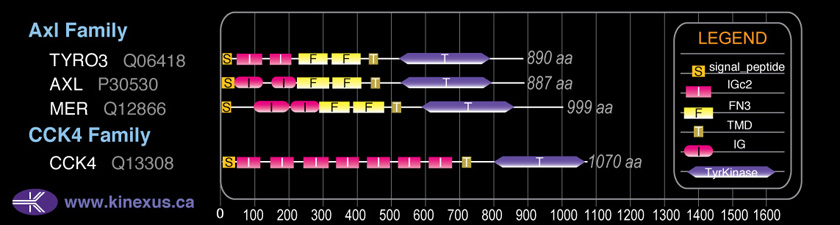
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Methylated:
R775.
N-GlcNAcylated:
N114, N170, N207, N215, N234, N294, N316, N329, N336, N354, N389, N395, N442, N454.
Serine phosphorylated:
S543, S613, S645, S750, S935.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T458, T699.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y549, Y749+, Y753+, Y754+, Y929.
Ubiquitinated:
K552, K591, K622, K765, K856, K923.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 100
100
1447
48
1842
 11
11
154
23
120
 9
9
127
13
105
 16
16
235
154
346
 40
40
576
46
509
 8
8
120
128
443
 13
13
193
57
422
 45
45
658
55
1242
 22
22
325
24
225
 6
6
93
149
66
 5
5
79
43
60
 41
41
594
250
562
 5
5
69
47
84
 5
5
67
18
41
 4
4
61
23
39
 12
12
171
28
194
 16
16
235
222
2386
 4
4
61
27
51
 4
4
53
145
37
 22
22
325
190
328
 7
7
106
31
95
 12
12
175
36
181
 10
10
140
24
96
 14
14
199
26
220
 5
5
77
31
67
 38
38
544
94
572
 4
4
51
50
45
 5
5
79
27
82
 8
8
115
26
145
 13
13
194
56
118
 21
21
306
30
364
 44
44
639
56
1174
 7
7
100
90
378
 40
40
579
109
531
 7
7
108
61
87
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 80.2
80.2
80.7
99 95.6
95.6
97.2
96 -
-
-
82 -
-
-
- 82.1
82.1
87.3
86 -
-
-
- 81.2
81.2
87.8
82 80.6
80.6
88.5
81 -
-
-
- 21.8
21.8
23.7
- 37.9
37.9
55.1
63 37.3
37.3
54.1
56.5 37.2
37.2
54.5
51 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | VAV1 - P15498 |
| 2 | GRB2 - P62993 |
| 3 | GAS6 - Q14393 |
| 4 | TNK2 - Q07912 |
| 5 | BMPR2 - Q13873 |
| 6 | LMO4 - P61968 |
Regulation
Activation:
Phosphorylation of Tyr-749, Tyr-753 and Tyr-754 increases phosphotransferase activity.
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| MER (MERTK) | Q12866 | Y749 | FGLSKKIYSGDYYRQ | + |
| MER (MERTK) | Q12866 | Y753 | KKIYSGDYYRQGRIA | + |
| MER (MERTK) | Q12866 | Y754 | KIYSGDYYRQGRIAK | + |
| MER (MERTK) | Q12866 | Y872 | RNQADVIYVNTQLLE | + |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
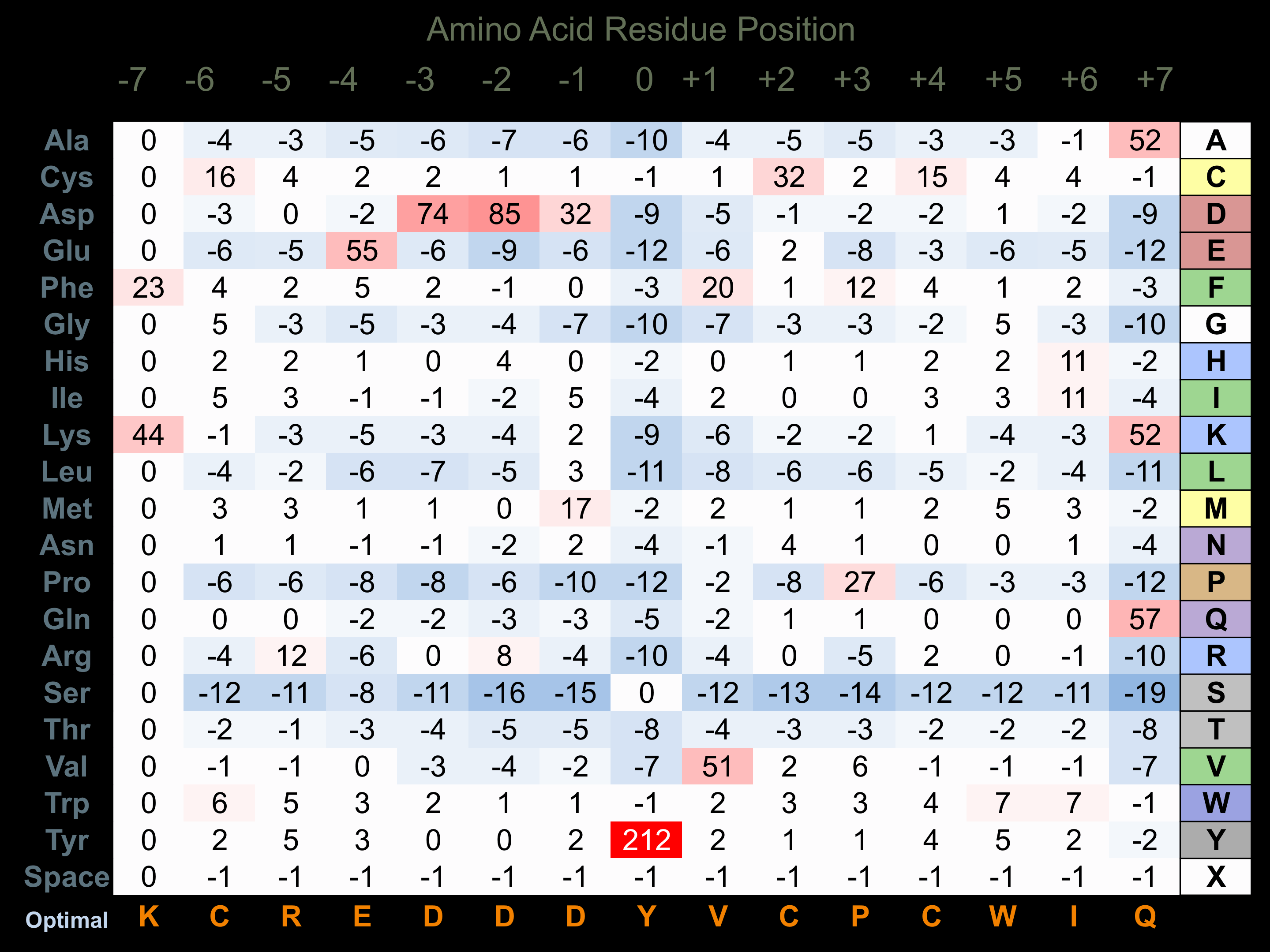
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 3 known protein substrate phosphosites and 55 peptides phosphorylated by recombinant MER in vitro tested in-house by Kinexus.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Eye disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
MERTK-related retinitis pigmentosa; Leber congenital amaurosis; Retinitis pigmentosa 38
Comments:
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is an inherited degenerative eye disease characterized by the progressive loss of photoreceptor cells and/or the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) of the retina and the aberrant deposition of retinal pigment. Affected individuals often display defective light-to-dark or dark-to-light adaptation, night blindness (nyctalopia), and peripheral visual field vision loss (tunnel vision). Leber congenital amaurosis is an eye disease that predominately affects the retina. Affected individuals display severe visual defects, photophobia, nystagmus (involuntary eye movement), and far-sightedness. MER also plays a role in the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) in the regulation of phagocytotic activity, which mainly functions to prevent the aberrant accumulation of fragments shed by the rod outer segments. Several mutations in the MER gene have been observed in patients with RP, including a 5-bp deletion mutation (2070delAGGAc) resulting in a frameshift, a splice site mutation in the intron 10 splice acceptor site, termination mutations (R651X, R775X), a truncating transversion mutation (1289+1G-T), a 9-kb deletion mutation encompassing exon 8 and part of intron 7 and 8, and a 91-kb deletion encompassing exons 1-7 of the gene. These mutations observed in RP patients are associated with a loss-of-function of MER phosphotransferase activity. In animal studies, a small inactivating deletion mutation in the MER gene was found in a rat model of inherited retinal degeneration characterized by the failure of the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) to phagocytose fragments shed by the outer segments, resulting in photoreceptor cell death. Furthermore, mice lacking MER expression displayed inefficient clearance of apoptotic debris by macrophages in the RPE, leading to the aberrant accumulation of rod fragments. Sub-retinal injection of an adenovirus carrying MER into the retina of rats with retinal degeneration was sufficient to correct the retinal dystrophy phenotype, resulting in the preservation of photoreceptor cells and restoring efficient phagocytosis capability to the RPE. Therefore, loss-of-function mutations in the MER gene are suggested to be the underlying cause of various forms of retinal degeneration, such as that seen in RP.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Bladder carcinomas (%CFC= +54, p<0.053); Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (cRCC) stage I (%CFC= +177, p<0.001); Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) (%CFC= +63, p<0.016); and Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (%CFC= -58, p<0.001). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for MERTK in diverse human cancers of 445, which is close to the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 0 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 100% lower than the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.08 % in 25518 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is very similar (+ 8% higher) to the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.58 % in 805 skin cancers tested; 0.41 % in 1093 large intestine cancers tested; 0.34 % in 502 urinary tract cancers tested; 0.18 % in 602 endometrium cancers tested; 0.13 % in 1941 lung cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
None > 5 in 20,801 cancer specimens
Comments:
Only 2 deletions, and no insertions or complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.