Nomenclature
Short Name:
PLK4
Full Name:
Serine-threonine-protein kinase PLK4
Alias:
- EC 2.7.11.21
- Serine/threonine protein kinase Sak
- Serine/threonine-protein kinase 18
- STK18
- PLK-4
- Polo-like kinase 4
- Sak
- Serine,threonine-protein kinase 18
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
Other
Family:
PLK
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
108,972
# Amino Acids:
970
# mRNA Isoforms:
3
mRNA Isoforms:
108,972 Da (970 AA; O00444); 105,253 Da (938 AA; O00444-2); 104,636 Da (929 AA; O00444-3)
4D Structure:
Homodimer
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
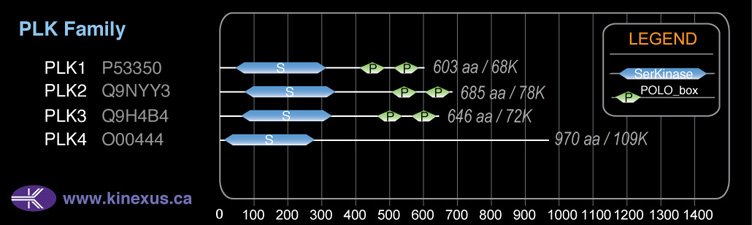
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y177, Y377, Y394, Y420, Y495, Y582.
Acetylated:
K538.
Serine phosphorylated:
S22, S255, S257, S258, S266, S282, S291, S297, S298, S301, S303, S305, S330, S378, S401, S406, S421, S499, S551, S589, S592, S665, S671, S749, S817, S821.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T170+, T174, T289, T292, T295, T300, T323, T345, T547, T591, T751.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 62
62
1053
42
1725
 0.6
0.6
10
21
14
 7
7
121
18
125
 16
16
277
134
690
 25
25
429
32
331
 1.5
1.5
25
112
33
 12
12
200
47
418
 53
53
900
58
2146
 19
19
321
24
255
 1.4
1.4
24
128
44
 3
3
54
46
102
 25
25
417
257
462
 3
3
59
51
107
 0.6
0.6
11
18
8
 3
3
45
37
77
 0.5
0.5
8
23
9
 0.9
0.9
16
218
43
 3
3
59
31
111
 1.2
1.2
21
132
51
 20
20
340
162
389
 3
3
52
34
76
 2
2
35
39
64
 6
6
102
29
111
 39
39
659
30
835
 23
23
393
35
535
 47
47
795
83
2101
 4
4
61
54
80
 4
4
70
31
119
 5
5
78
30
97
 2
2
32
42
25
 26
26
448
30
546
 100
100
1697
51
3359
 52
52
889
118
1211
 36
36
603
83
593
 66
66
1117
48
1840
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 98.9
98.9
99.4
99 97.3
97.3
98.9
97 -
-
-
90 -
-
-
- 88.8
88.8
93.7
89 -
-
-
- 78.9
78.9
86.9
83 79
79
86.6
82 -
-
-
- 30.6
30.6
40.4
- -
-
-
69 60.3
60.3
74.1
- 52.2
52.2
67.1
56 -
-
-
- 29
29
45.3
47 35
35
50.7
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | FAM46C - Q5VWP2 |
| 2 | MTUS2 - Q5JR59 |
| 3 | SFN - P31947 |
| 4 | SMAD4 - Q13485 |
| 5 | TGFBR1 - P36897 |
Regulation
Activation:
NA
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
Down-regulated in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells, leading to aberrant centrioles composed of disorganized cylindrical microtubules and displaced appendages. Down-regulated by p53/TP53.
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
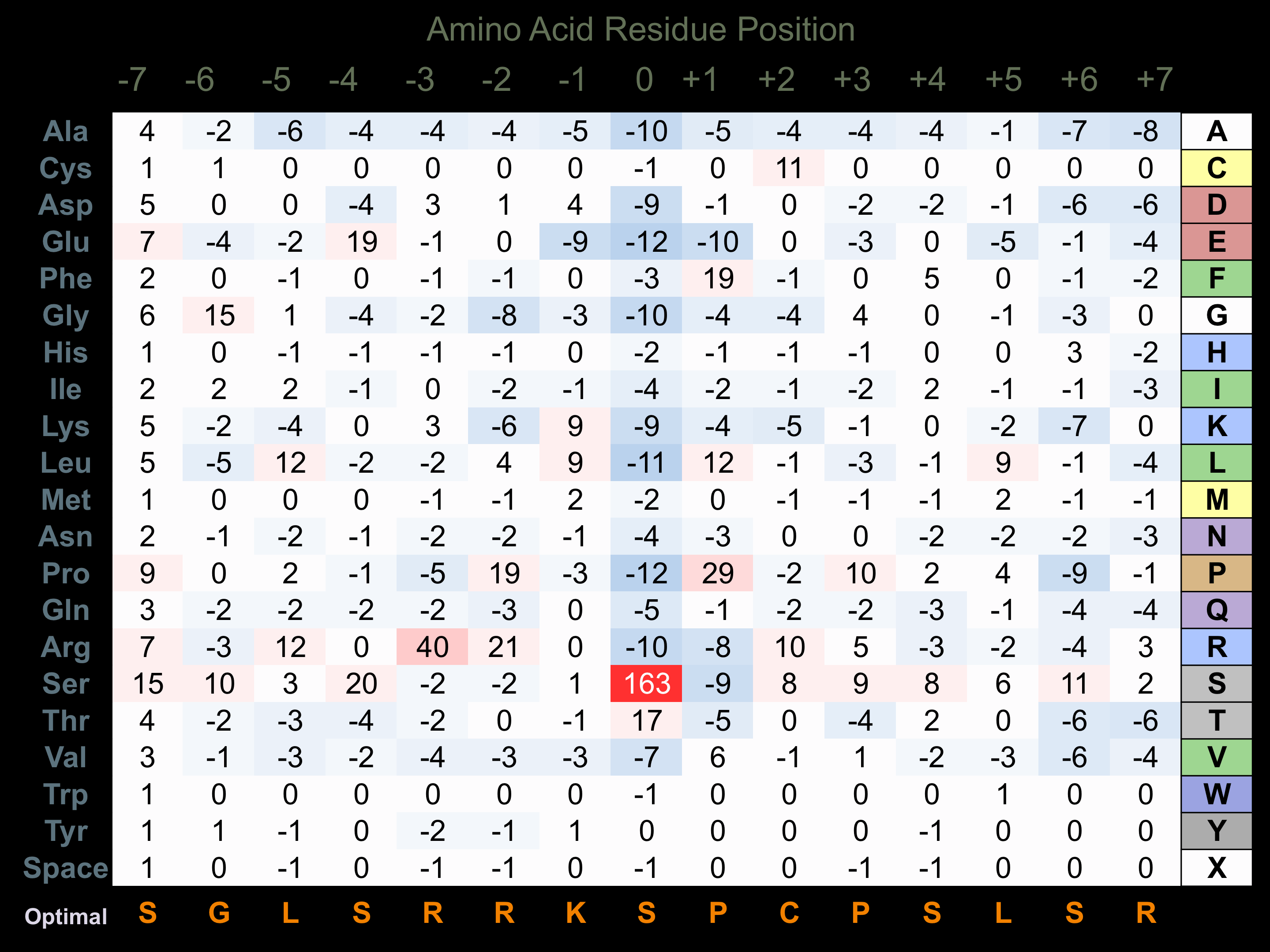
Matrix Type:
Predicted from the application of the Kinexus Kinase Substrate Predictor Version 2.0 algorithm, which was trained with over 10,000 kinase-protein substrate pairs and 8,000 kinase-peptide substrate pairs.
Domain #:
1
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, Developmental disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Microcephaly; Retinopathy
Comments:
Microcephaly is a development disease characterized by a reduced brain size. This disease is autosomal recessive and may be congenital or may develop over the first few post-natal weeks. The life expectancy and brain function of affected individuals is poor. Centrosome aberrations have been implicated in human microcephaly and growth disorders, thus implicating Plk4 as a potential microcephaly suceptibility gene. Mutations in the Plk4 gene have been observed in patients with microcephaly. The c.2811-5C>G mutation was predicted to create a novel splice site, resulting in the abnormal splicing of the Plk4 mRNA leading to premature truncation of one of the polo-box domains of the protein. The c.1299_1303delTAAAG mutation is located in exon 5 of the Plk4 gene and causes a frameshift mutation that produces an inactive truncated Plk4 protein. Therefore, loss-of-function of the Plk4 gene is thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of microcephaly and other growth disorders, possibly through effects on cell growth or proliferation. In animal studies, Plk4 knockdown in zeB-Rafish embryos resulted in reduced body size, stemming from a reduced cell number, not a reduced cell size. The phenotype of these mutants closely resembled that of several human growth and developmental disorders, including microcephaly, further implicating the Plk4 gene in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Specific Cancer Types:
Gallbladder carcinomas
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Brain oligodendrogliomas (%CFC= -61, p<0.034); Breast sporadic basal-like cancer (BLC) (%CFC= +55, p<0.0001); Cervical cancer (%CFC= -59, p<0.0002); Cervical cancer stage 1B (%CFC= -77); Colon mucosal cell adenomas (%CFC= +118, p<0.0001); and Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) (%CFC= +134, p<0.0004). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for PLK4 in diverse human cancers of 447, which is close to the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 17 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 0.3-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.05 % in 24726 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only -29 % lower than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.32 % in 1093 large intestine cancers tested; 0.21 % in 602 endometrium cancers tested; 0.18 % in 805 skin cancers tested; 0.1 % in 1619 lung cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
None > 3 in 20,009 cancer specimens
Comments:
Only 6 deletions, and no insertions or complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

