Nomenclature
Short Name:
BRD4
Full Name:
Bromo domain-containing protein 4
Alias:
- Bromodomain containing 4
- CAP
- Chromosome-associated protein
- HUNK1
- HUNKI
- MCAP
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
Atypical
Family:
BRD
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
152,219
# Amino Acids:
1362
# mRNA Isoforms:
3
mRNA Isoforms:
152,219 Da (1362 AA; O60885); 88,289 Da (794 AA; O60885-3); 80,463 Da (722 AA; O60885-2)
4D Structure:
Associated with chromosomes during mitosis
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
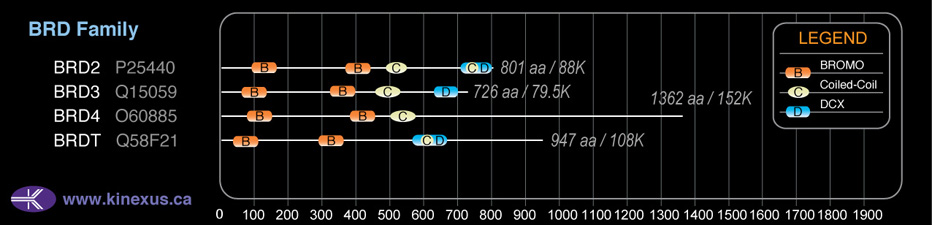
Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 75 | 147 | BROMO |
| 368 | 440 | BROMO |
| 502 | 567 | Coiled-coil |
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Serine phosphorylated:
S324, S325, S338, S469, S470, S484, S488, S492, S494, S498, S499, S503, S578, S579, S581, S584, S601, S619, S673, S705, S858, S1045, S1051, S1064, S1070, S1074, S1083, S1100, S1117, S1126, S1201, S1204, S1223.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T103, T109, T299, T315, T316, T942, T1080, T1211, T1212.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y65+, Y599, Y1054.
Acetylated:
K111, K333, K346, K362, K367, K368, K726, K727, K1111, K1114.
Methylated:
K404, K406.
O-GlcNAcylated:
S1215.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 65
65
1304
53
1162
 6
6
130
24
133
 45
45
904
13
1247
 23
23
469
201
792
 44
44
891
64
647
 84
84
1689
118
6002
 11
11
229
78
410
 83
83
1665
59
3027
 29
29
580
20
615
 12
12
235
192
251
 17
17
336
45
594
 39
39
787
220
741
 28
28
560
35
1194
 4
4
87
18
124
 19
19
374
37
750
 9
9
180
36
204
 18
18
360
368
1598
 17
17
338
27
591
 10
10
209
185
422
 39
39
779
224
697
 14
14
280
37
502
 24
24
488
41
1047
 33
33
661
15
979
 25
25
494
27
921
 21
21
423
37
832
 63
63
1263
131
2091
 18
18
360
41
711
 15
15
295
27
503
 21
21
431
27
834
 69
69
1392
84
1494
 40
40
808
36
576
 100
100
2011
62
4750
 23
23
462
112
684
 46
46
920
156
726
 27
27
551
105
1229
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 77.2
77.2
78.8
96.5 31.2
31.2
41.3
- -
-
-
96 -
-
-
95 51.8
51.8
52.3
89 -
-
-
- 93.1
93.1
94.1
93 31.8
31.8
41.4
93 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 29.4
29.4
39.9
81 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 28.2
28.2
37
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
23 -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | RFC2 - P35250 |
| 2 | RFC3 - P40938 |
| 3 | ATP6V0A1 - Q93050 |
| 4 | RFC4 - P35249 |
| 5 | RFC1 - P35251 |
| 6 | RFC5 - P40937 |
| 7 | CRK - P46108 |
| 8 | GRB2 - P62993 |
| 9 | PIK3R1 - P27986 |
| 10 | PRPF40A - O75400 |
| 11 | NCK1 - P16333 |
| 12 | TBP - P20226 |
Regulation
Activation:
NA
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
| Lestaurtinib | Kd = 570 nM | 126565 | 19654408 |
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer
Specific Cancer Types:
Breast cancer
Comments:
Nuclear protein in testis (NUT) midline carcinoma (NMC) is an unusual group of carcinomas characterized by chromosomal rearrangements involving the NUT gene on chromosome 15. These cancers are found in the midline structures of adults and children and are undifferentiated or poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinomas. The majority of NMCs are thought to be caused by the fusion of the entire coding region of the NUT gene onto the 3' end of BRD4 or BRD3, leading to the creation of oncogenic chimeric fusion proteins. A rare, but highly aggressive and lethal form of cancer caused by BRD4 arises from a BRD-NUT fusion. BRD4 binding to acetylated histones could be prevented with a N140A or a N433A mutation. CK2 phosphorylation and binding to acetylated histones occurs with S492A+S494A, S498A+S499A+T500A, and S503A mutations. In a breast cancer sample, Twist (transcription activator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition) was reported to utilize BRD4 to bind to acetylated H4.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Breast epithelial cell carcinomas (%CFC= +56, p<0.063); Ovary adenocarcinomas (%CFC= +94, p<0.002); Prostate cancer - primary (%CFC= +50, p<0.0004); Skin melanomas - malignant (%CFC= +253, p<0.0001); and Skin squamous cell carcinomas (%CFC= +108, p<0.082). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for BRD4 in diverse human cancers of 634, which is 1.4-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 124 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 2.1-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.04 % in 25525 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is -50 % lower than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general. Such a low frequency of mutation in human cancers is consistent with this protein kinase playing a role as a tumour requiring protein (TRP).
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.23 % in 1270 large intestine cancers tested; 0.16 % in 864 skin cancers tested; 0.15 % in 589 stomach cancers tested; 0.12 % in 603 endometrium cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
None > 5 in 20,517 cancer specimens
Comments:
Only 1 insertion, and no deletions or complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

