Nomenclature
Short Name:
PKACb
Full Name:
cAMP-dependent protein kinase, beta-catalytic subunit
Alias:
- cAPKb
- PKA-b
- EC 2.7.11.11
- KAPB
- KAPB1
- KAPCB
- PKA C-beta
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
AGC
Family:
PKA
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
40623
# Amino Acids:
351
# mRNA Isoforms:
10
mRNA Isoforms:
46,236 Da (398 AA; P22694-2); 41,395 Da (358 AA; P22694-9); 41,296 Da (357 AA; P22694-6); 41,046 Da (355 AA; P22694-7); 40,947 Da (354 AA; P22694-5); 40,623 Da (351 AA; P22694); 39,477 Da (339 AA; P22694-3); 39,379 Da (338 AA; P22694-4); 36,979 Da (321 AA; P22694-10); 29,696 Da (257 AA; P22694-8)
4D Structure:
A number of inactive tetrameric holoenzymes are produced by the combination of homo- or heterodimers of the different regulatory subunits associated with two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits.
1D Structure:
Subfamily Alignment
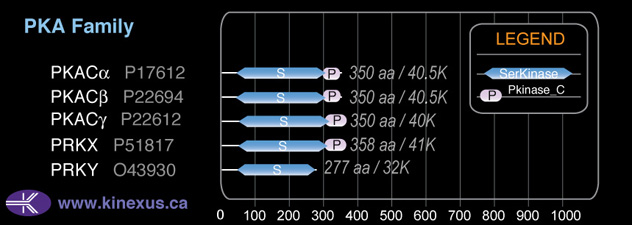
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
N267 (N6).
Methylated:
K47, K267, K280.
Myristoylated:
G2.
Serine phosphorylated:
S11, S15, S54, S260, S264, S322, S326, S339+.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T6, T49, T52, T89, T196+, T198+, T202-, T325, T341.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y69, Y70, Y205, Y331.
Ubiquitinated:
K17, K24, K30, K73, K84, K93, K267, K280, K286.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 76
76
1201
35
1083
 7
7
114
16
111
 23
23
360
11
169
 100
100
1576
121
1377
 52
52
827
35
725
 35
35
553
91
1615
 56
56
883
41
925
 50
50
793
48
1537
 45
45
709
17
637
 9
9
145
110
142
 7
7
111
34
108
 45
45
715
182
715
 19
19
306
33
182
 5
5
79
12
68
 8
8
124
18
146
 12
12
188
20
265
 41
41
647
191
3580
 32
32
506
20
480
 7
7
104
104
123
 36
36
572
137
558
 46
46
726
26
616
 19
19
304
30
262
 20
20
321
21
267
 6
6
100
20
136
 22
22
344
26
324
 42
42
663
76
656
 16
16
246
36
172
 9
9
148
20
121
 11
11
179
20
150
 5
5
85
42
60
 54
54
849
36
310
 47
47
736
35
760
 46
46
726
115
1113
 75
75
1180
83
822
 6
6
101
66
158
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 97.2
97.2
98
100 47.9
47.9
54.1
100 -
-
-
98.5 -
-
-
- 98.9
98.9
99.2
98 -
-
-
- 92
92
95.2
92.5 96.9
96.9
98
97 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 35.6
35.6
54.6
90 35.3
35.3
55.1
94 34.4
34.4
54.3
92 -
-
-
- 82.2
82.2
89.8
83 -
-
-
- 66.3
66.3
77.5
84 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
35 46.3
46.3
65.8
51 -
-
-
55
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | NGFR - P08138 |
| 2 | PRKAR2A - P13861 |
| 3 | PRKAR2B - P31323 |
| 4 | PKLR - P30613 |
Regulation
Activation:
Activated by binding of two cAMP molecules to each of the two associated regulatory subunits in the PKA holoenzyme. Binding of cAMP induces dissociation of the two active catalytic subunits. Phosphorylation of Thr-198 increases phosphotransferase activity. Phosphorylation of S339 may play a role in stabilizing PKA.
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
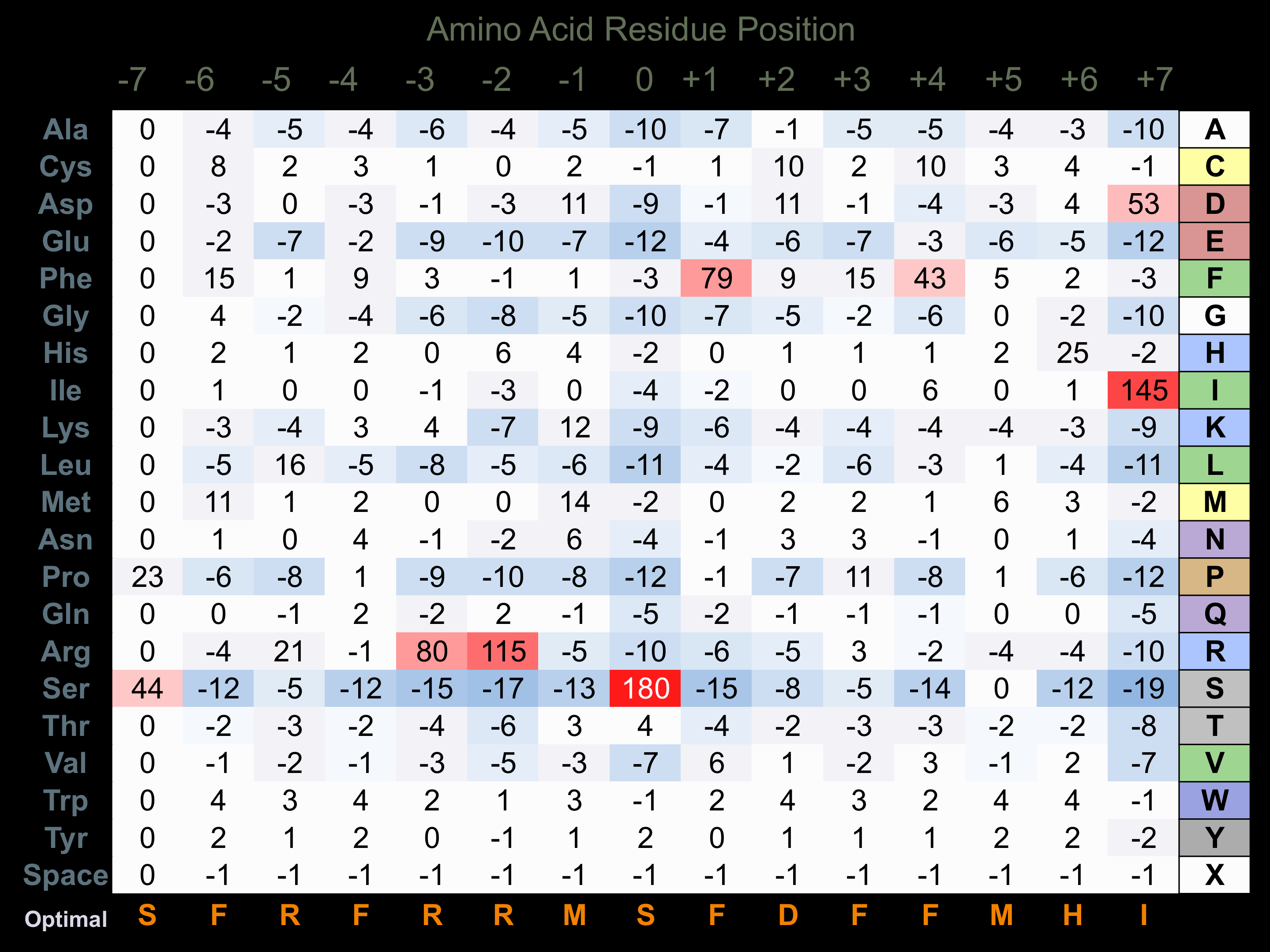
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 3 known protein substrate phosphosites and 37 peptides phosphorylated by recombinant PKACb in vitro tested in-house by Kinexus.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Endocrine disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease (PPNAD)
Comments:
Primary Pigmented Nodular Adrenocortical Disease (PPNAD) is a rare endocrine disorder which can be related to Cushing’s syndrome and carney complex. PPNAD can affect the cortex, adrenal cortex, and adrenal gland tissues.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Cervical cancer (%CFC= -47, p<0.005); Cervical cancer stage 2A (%CFC= -51, p<0.015); Cervical cancer stage 2B (%CFC= -48, p<0.047); Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (cRCC) stage I (%CFC= -79, p<(0.0003); Gastric cancer (%CFC= -52, p<0.004); Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) (%CFC= +81, p<0.004); Ovary adenocarcinomas (%CFC= -62, p<0.017); and Prostate cancer - primary (%CFC= +78, p<0.0001). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for PKACb in diverse human cancers of 344, which is 0.7-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 29 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 0.5-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.1 % in 25455 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only 27 % higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.36 % in 1093 large intestine cancers tested; 0.35 % in 805 skin cancers tested; 0.31 % in 1941 lung cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
None > 5 in 20,738 cancer specimens
Comments:
Only 5 deletions, 1 insertion and 1 complex mutation are noted on the COSMIC website.

