Nomenclature
Short Name:
ATR
Full Name:
Serine-protein kinase ATR
Alias:
- EC 2.7.11.1
- FRAP-related protein
- FRP1
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
Atypical
Family:
PIKK
SubFamily:
ATR
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
301,367
# Amino Acids:
2644
# mRNA Isoforms:
3
mRNA Isoforms:
301,367 Da (2644 AA; Q13535); 297,479 Da (2610 AA; Q13535-3); 294,219 Da (2580 AA; Q13535-2)
4D Structure:
Forms an heterodimer with ATRIP. Binds to DNA, and to UV-damaged DNA with higher affinity. Interacts with RAD17, MSH2 and HDAC2. Present in a complex containing ATRIP and RPA-coated single-stranded DNA. Present in a complex containing CHD4 and HDAC2. Interacts with BCR-ABL after genotoxic stress. Interacts with EEF1E1. This interaction is enhanced by UV irradiation. Interacts with CLSPN and CEP164. Interacts with TELO2 AND TTI1.
1D Structure:
Subfamily Alignment
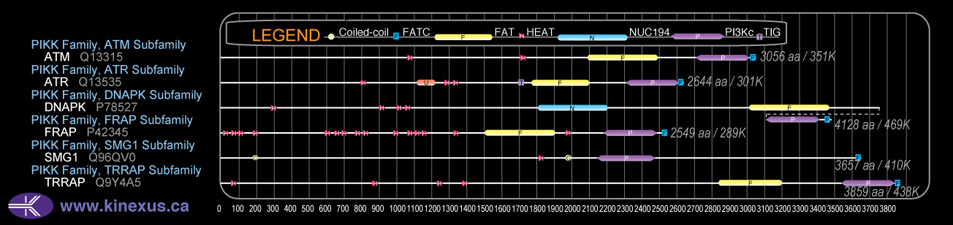
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K1173.
Serine phosphorylated:
S61, S428+, S435, S436, S437, S441, S919, S1007, S1140, S1333, S1645, S1871, S1876, S2186, S2313.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T533, T1275, T1566, T1578, T1589, T1989+, T2219.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y26, Y291, Y310, Y317, Y1122, Y2187.
Ubiquitinated:
K32, K442, K866, K1005, K1613, K1703, K1824, K2587, K2604.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 100
100
1303
35
1477
 6
6
84
16
72
 6
6
80
2
101
 21
21
273
103
370
 69
69
893
31
641
 6
6
81
89
66
 14
14
182
41
392
 78
78
1015
27
2019
 39
39
508
17
407
 5
5
59
97
58
 6
6
84
20
83
 47
47
608
169
586
 5
5
67
24
46
 5
5
71
12
61
 8
8
99
15
93
 7
7
92
20
81
 8
8
98
116
58
 3
3
35
11
27
 3
3
36
95
37
 47
47
606
137
629
 7
7
97
13
94
 10
10
129
17
151
 4
4
56
12
29
 8
8
98
11
78
 12
12
151
13
219
 54
54
709
62
651
 5
5
59
27
40
 4
4
54
11
45
 4
4
57
11
52
 3
3
33
42
34
 37
37
479
24
318
 38
38
499
47
609
 28
28
369
101
821
 67
67
874
83
779
 16
16
212
48
325
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 98.9
98.9
99.2
99.5 98.7
98.7
99.5
99 -
-
-
94 -
-
-
99 94.9
94.9
97.3
95 -
-
-
- 90.4
90.4
95.1
91 -
-
-
91 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
78 72.9
72.9
83.5
72 65.4
65.4
78.6
66 -
-
-
- 26.1
26.1
47.7
30 -
-
-
- -
-
-
24 43
43
60.8
- 27
27
46.1
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
45 26.5
26.5
46.1
32 22
22
41.7
24 -
-
-
28
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Regulation
Activation:
Activated by DNA. ; Slightly activated by ATRIP.
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| 4E-BP1 | Q13541 | S94 | DEPPMEASQSHLRNS | |
| Akt1 (PKBa) | P31749 | S473 | RPHFPQFSYSASGTA | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | S1981 | SLAFEEGSQSTTISS | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | S440 | SPLLMILSQLLPQQR | |
| ATRIP | Q8WXE1 | S68 | EELDTLASQALSQCP | |
| ATRIP | Q8WXE1 | S72 | TLASQALSQCPAAAR | |
| BLM | P54132 | T122 | PKEVVCTTQNTPTVK | |
| BLM | P54132 | T99 | NAPAGQETQRGGSKS | |
| BRCA1 | P38398 | S1423 | AVLEQHGSQPSNSYP | |
| BRCA1 | P38398 | S1457 | SEKAVLTSQKSSEYP | |
| BRCA1 | P38398 | S1524 | LQNRNYPSQEELIKV | |
| BRCA2 | P51587 | S2156 | IKVSPYLSQFQQDKQ | |
| Chk1 (CHEK1) | O14757 | S317 | ENVKYSSSQPEPRTG | + |
| Chk1 (CHEK1) | O14757 | S345 | LVQGISFSQPTCPDH | + |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S50 | TSTMPNSSQSSHSSS | |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | T26 | SQPHGSVTQSQGSSS | + |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| COPS1 | Q13098 | S454 | KSPPREGSQGELTPA | |
| CREB1 | P16220 | S121 | SVDSVTDSQKRREIL | |
| CTF18 | Q8WVB6 | S87 | PAASVGSSQGGARKR | |
| CUX1 (CUTL1) | P39880 | S1357 | ADTEEPKSQGEAERE | |
| Daxx | Q9UER7 | S424 | EGPSGMASQGCPSAS | |
| DBC-1 | Q8N163 | T454 | AAEAAPPTQEAQGET | |
| DNAPK (PRKDC) | P78527 | S2612 | MFVETQASQGTLQTR | ? |
| DNAPK (PRKDC) | P78527 | T2609 | LTPMFVETQASQGTL | + |
| DNAPK (PRKDC) | P78527 | T2647 | QQHDFTLTQTADGRS | - |
| E2F1 | Q01094 | S31 | ALRLLDSSQIVIISA | |
| FARSLA | Q9Y285 | S300 | QRVKRTHSQGGYGSQ | |
| FLJ23518 | Q8N4S0 | S154 | DDQEKHLSQEDNDLN | |
| IRS1 | P35568 | S270 | EFRPRSKSQSSSNCS | |
| MARCKSL1 | P49006 | S71 | AIEPAPPSQGAEAKG | |
| MCM2 | P49736 | S108 | DVEELTASQREAAER | + |
| MCM3 | P25205 | S535 | ATDDPNFSQEDQQDT | |
| MCM3 | P25205 | S728 | HTPKTADSQETKESQ | |
| MDC1 | Q14676 | S513 | PGIHLERSQASTTVD | |
| MDM2 | Q00987 | S407 | SSSIIYSSQEDVKEF | |
| NBS1 | O60934 | S615 | VPESSKISQENEIGK | |
| NOT2 | Q9NZN8 | S101 | PQLNRSLSQGTQLPS | |
| p53 | P04637 | S15 | PSVEPPLSQETFSDL | + |
| p53 | P04637 | S37 | NVLSPLPSQAMDDLM | + |
| PHF14 | O94880 | S294 | TNDSLTLSQSKSNED | |
| PSF2 | Q9Y248 | S182 | QPLESTQSQDF____ | |
| Rad17 | O75943 | S635 | ETWSLPLSQNSASEL | |
| Rad17 | O75943 | S645 | SASELPASQPQPFSA | |
| RBM21 | Q9H6E5 | S750 | HEAAQEWSQGEAGKG | |
| SFRS14 | Q8IX01 | T7 | _MAARRITQETFDAV | |
| Smc1 | Q14683 | S957 | ISQEEGSSQGEDSVS | |
| SUN2 | Q9UH99 | S12 | SQRLTRYSQGDDDGS | |
| UREB1 | Q7Z6Z7 | S2391 | DEAPSNLSQASTLQA | |
| VCP | P55072 | S784 | NQGGAGPSQGSGGGT | |
| WRN | Q14191 | S1141 | PEKAYSSSQPVISAQ | |
| WRN | Q14191 | S1292 | MTIGMHLSQAVKAGC | |
| XPA | P23025 | S173 | VKKNPHHSQWGDMKL | |
| XPA | P23025 | S196 | RSLEVWGSQEALEEA | |
| ZSCAN5A | Q9BUG6 | T422 | DVCQKQFTQKSYLKC |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
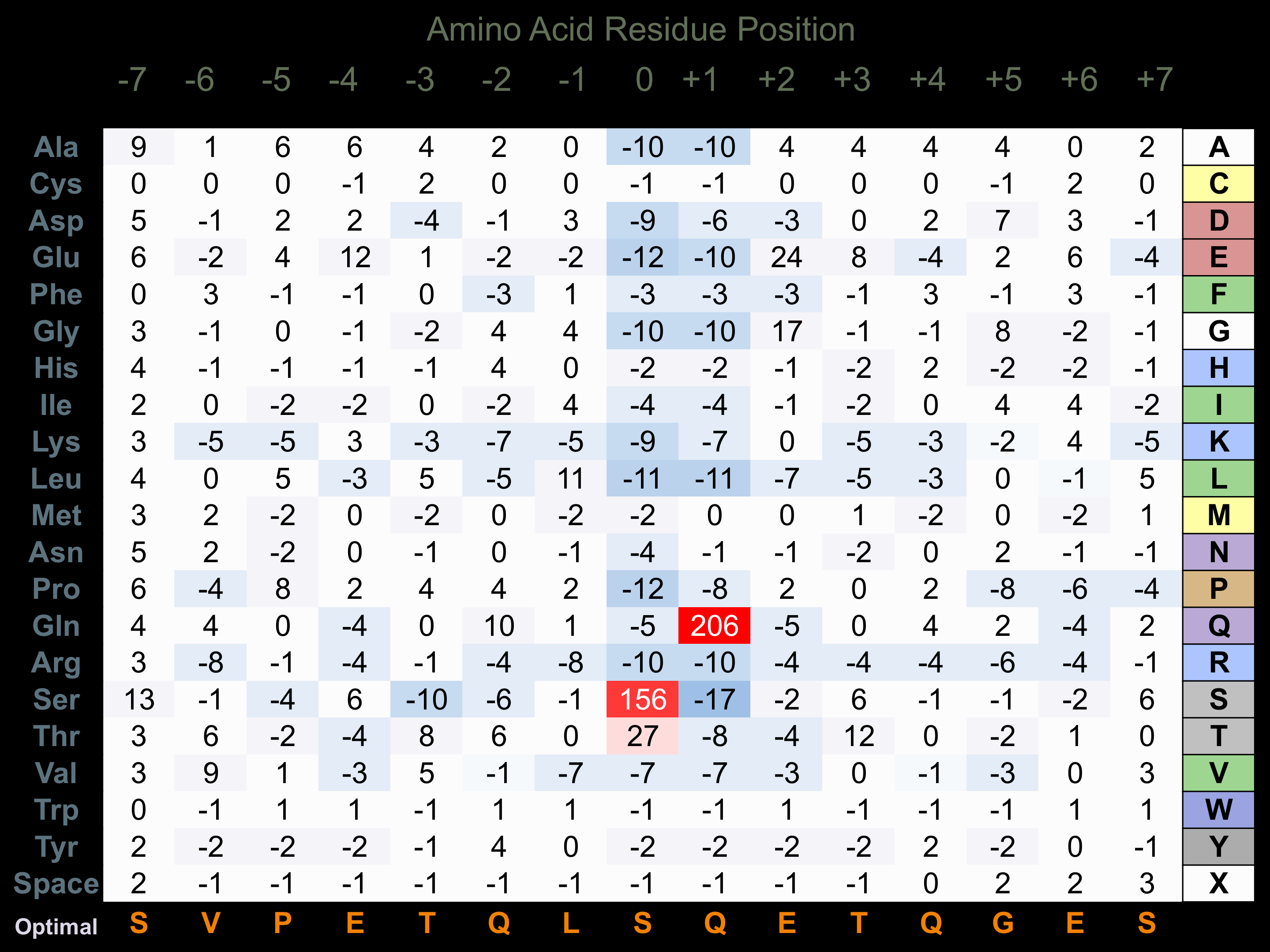
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 81 known protein substrate phosphosites.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, neurological disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Ataxia; Ataxia telangiectasia; Seckel syndrome; Cutaneous telangiectasia and cancer syndrome, familial; Alpha-thalassemia X-linked intellectual disability syndrome; Alpha-thalassemia X-linked intellectual disability syndrome linked to chromosome 16; Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection; Primary autosomal recessive microcephalies and Seckel syndrome spectrum disorders; Jawad syndrome; Seckel syndrome Type 1; Alpha-thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome; Gapo syndrome; Seckel syndrome Type 8
Comments:
Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) is a rare neurological disease characterized by the degeneration of the cerebellum leading to uncoordinated locomotion and speech patterns as well as problems with balance and hand dexterity. Seckel syndrome is a genetic disease characterized by stunted growth, microcephaly, mental retardation, and abnormal facial features (e.g. large eyes, a beak-like nose, and a narrow face). This disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. ATR is a member of the phosphatidylinositol kinase-related kinase (PIKK) family of large molecular weight kinases which have functions in cell cycle progression, DNA recombination, and detection of DNA damage. Specifically, ATR is an essential component of the DNA damage checkpoint that is critical for the detection and cellular response to DNA damage and replication stress. Loss-of-function mutations in the ATR gene result in impaired cellular detection and response to DNA damage and are associated with cell cycle abnormalities, aneuploidy, and aberrant cell growth. Several mutations in the ATR gene have been observed in patients with Seckel syndrome. For example, a synonymous single base substitution mutation (2101A-G) that resulted in the use of 2 cryptic splice sites in exon 9 of the gene resulting in premature termination and truncation of the protein, a D1879Y substitution mutation, a 540-kb deletion mutation encompassing the ATR gene, a M1159I substitution mutation at a highly conserved residue in the UME domain, and a C-to-G transversion mutation in intron 40 leading to premature termination (Val2300GlyfsTer75) of the protein. In animal studies, transgenic mice that are homozygous for the A-to-G transversion mutation in exon 9 of the ATR gene displayed severe dwarfism, microcephaly, and facial abnormalities. In addition, these mice showed reduced brain size, cyst formation, and corpus callosum agenesis, thus closely resembling the phenotype of Seckel syndrome in humans. In addition, mice heterozygous for this mutation displayed retinal and optic nerve degeneration at post-natal day 20 (P20) despite normal embryonic development, and possessed cilia that were ~40% shorter than those in wild-type mice. Therefore, loss-of-function of the ATR gene may play a role in the the pathology of ataxia-telangiectasia and Seckel syndrome.
Specific Cancer Types:
Hemangiomas, capillary infantile
Comments:
ATR appears to be a tumour suppressor protein (TSP). Cancer-related mutations in human tumours point to a loss of function of the protein kinase. The active form of the protein kinase normally acts to inhibit tumour cell proliferation. ATR levels are up-regulated 1.6-fold in human tumours compared to most other protein kinases. Loss-of-function mutations in ATR, which abolish the DNA damage detection ability of the protein, have been linked to hemangioma, a cancer that develops in the endothelial cells that line blood vessels of the cardiovascular system. Somatic mutations in the ATR gene are rarely observed in human cancer specimens, with the possible exception of sporadic stomach and endometrial cancers that display microsatellite instability. In animal studies, mice heterozygous for a loss-of-function mutation in the ATR gene exhibit similar survival times as wild-type mice, but have an increased occurence of tumour formation, which supports a role for the protein in the prevention of tumorigenesis. Caffeine is an inhibitor of ATR. Interestingly, caffeine exposure is known to sensitize tumours to ionizing radiation and other toxic agents, which is associated with the disruption of cell-cycle checkpoints.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Barrett's esophagus epithelial metaplasia (%CFC= +69, p<0.045); Bladder carcinomas (%CFC= +169, p<0.0004); Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (cRCC) stage I (%CFC= -67, p<0.0004); Colon mucosal cell adenomas (%CFC= +55, p<0.003); Malignant pleural mesotheliomas (MPM) tumours (%CFC= +89, p<0.045); Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) (%CFC= +103, p<0.0001); and Skin melanomas - malignant (%CFC= -47, p<0.022). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for ATR in diverse human cancers of 746, which is 1.6-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 123 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 2.1-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.06 % in 25343 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only -19 % lower than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.31 % in 1128 large intestine cancers tested; 0.25 % in 807 skin cancers tested; 0.18 % in 602 endometrium cancers tested; 0.16 % in 590 stomach cancers tested; 0.09 % in 1813 lung cancers tested; 0.07 % in 605 oesophagus cancers tested; 0.07 % in 1270 liver cancers tested; 0.05 % in 1380 breast cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: R256C (4).
Comments:
Only 4 deletions, 3 insertions, and 2 complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

