Nomenclature
Short Name:
BRD3
Full Name:
Bromo domain-containing protein 3
Alias:
- KIAA0043
- RING3L
- RING3-like protein
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
Atypical
Family:
BRD
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
79,542
# Amino Acids:
726
# mRNA Isoforms:
2
mRNA Isoforms:
79,542 Da (726 AA; Q15059); 60,942 Da (556 AA; Q15059-2)
4D Structure:
NA
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
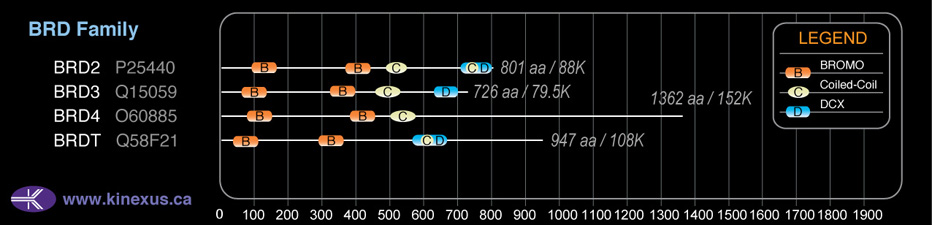
Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 51 | 123 | BROMO |
| 326 | 398 | BROMO |
| 453 | 524 | Coiled-coil |
| 645 | 684 | DUF755 |
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K304, K305, K655, K666.
Methylated:
K304, K305.
Serine phosphorylated:
S254, S259, S261, S263, S268, S281, S481, S558, S563, S609, S676, S680, S681, S682, S703, S705, S706, S707, S708, S710, S712, S716, S718, S719, S720, S722, S723, S725.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T85, T250, T257.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y561.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 94
94
1012
41
1035
 24
24
255
18
137
 32
32
350
12
247
 44
44
478
138
533
 87
87
938
32
759
 19
19
207
90
178
 39
39
420
49
563
 100
100
1081
59
1733
 67
67
720
17
490
 20
20
217
100
130
 16
16
176
39
194
 63
63
681
226
705
 21
21
226
34
168
 17
17
179
15
98
 14
14
150
33
175
 24
24
260
21
216
 48
48
521
377
3613
 18
18
190
23
149
 26
26
280
106
186
 72
72
779
132
711
 21
21
230
31
162
 19
19
210
35
160
 27
27
287
22
225
 17
17
189
23
126
 23
23
248
31
198
 77
77
837
90
999
 15
15
160
37
94
 20
20
211
23
137
 27
27
287
25
192
 7
7
80
28
95
 91
91
982
24
781
 59
59
640
41
678
 26
26
284
120
428
 88
88
952
83
827
 37
37
397
48
459
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 99.7
99.7
99.7
100 99
99
99.3
99 -
-
-
93 -
-
-
90 93.7
93.7
96.6
95 -
-
-
- 95.6
95.6
97.4
95 60.6
60.6
70.2
95 -
-
-
- 52.9
52.9
54.5
- 91.6
91.6
94.2
92 -
-
-
83.5 69.3
69.3
76.2
77 -
-
-
- 21.9
21.9
27.7
39 -
-
-
- -
-
-
29 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
28 20.9
20.9
38.7
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Regulation
Activation:
NA
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer
Specific Cancer Types:
Nuclear protein in testis (NUT) midline carcinomas (NMC)
Comments:
Nuclear protein in testis (NUT) midline carcinoma (NMC) is an unusual group of carcinomas characterized by chromosomal rearrangements involving the NUT gene on chromosome 15. These cancers are found in the midline structures of adults and children and are undifferentiated or poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinomas. The majority of NMCs are thought to be caused by the fusion of the entire coding region of the NUT gene onto the 3' end of BRD4 or BRD3, leading to the creation of oncogenic chimeric fusion proteins. The BRD3-NUT fusion protein contains two tandem repeat chromatin-binding BDs, an extra-terminal domain, and essentially the entirety of the NUT protein sequence. The function of the NUT gene is unknown. However, the protein contains a nuclear localization signal and export sequences that allow for nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling through leptomycin-sensitive mechanisms. Therefore, the oncogenic effects of the fusion protein may result from abnormal subcellular localization of the BRD3 and BRD4 proteins between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Knockdown of NUT-BRD3 expression by siRNA in NMC cancer cell lines resulted in reduced cell proliferation and growth, thus confirming an oncogenic role for the chimeric protein. It is predicted that the oncogenic fusion NUT-BRD proteins contribute to tumorigenesis by binding to chromatin and disrupting the differentiation and development of epithelial cells, leading to squamous cell carcinomas.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Brain glioblastomas (%CFC= +401, p<0.006); Gastric cancer (%CFC= +48, p<0.0006); and Uterine leiomyomas (%CFC= +51, p<0.043). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for BRD3 in diverse human cancers of 449, which is close to the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 139 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 2.3-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice support a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.06 % in 24857 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only -14 % lower than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.48 % in 629 stomach cancers tested; 0.32 % in 864 skin cancers tested; 0.3 % in 603 endometrium cancers tested; 0.27 % in 1270 large intestine cancers tested; 0.13 % in 548 urinary tract cancers tested; 0.1 % in 558 thyroid cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: R278Q (4).
Comments:
Nine deletion, 3 insertions and no complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

