Nomenclature
Short Name:
PINK1
Full Name:
Serine-threonine kinase PINK1, mitochondrial
Alias:
- PTEN induced putative kinase protein 1
- BRPK
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
Other
Family:
NKF2
SubFamily:
NA
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
62,769
# Amino Acids:
581
# mRNA Isoforms:
2
mRNA Isoforms:
62,769 Da (581 AA; Q9BXM7); 30,104 Da (274 AA; Q9BXM7-2)
4D Structure:
NA
1D Structure:
Subfamily Alignment

Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 156 | 511 | Pkinase |
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K262.
Serine phosphorylated:
S228, S402.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 35
35
856
29
782
 23
23
571
16
222
 12
12
288
9
249
 48
48
1184
91
644
 43
43
1045
25
720
 4
4
108
74
43
 21
21
520
35
604
 38
38
941
41
769
 32
32
787
17
558
 17
17
425
94
226
 14
14
351
31
254
 32
32
778
183
719
 6
6
148
31
101
 6
6
153
15
109
 8
8
204
19
103
 31
31
756
16
473
 14
14
336
205
2023
 12
12
304
18
281
 50
50
1231
97
967
 33
33
804
109
688
 20
20
502
24
490
 7
7
168
28
97
 11
11
261
11
219
 29
29
710
20
598
 7
7
161
24
129
 33
33
820
56
759
 7
7
170
34
132
 10
10
244
20
200
 9
9
219
20
176
 100
100
2457
28
1400
 29
29
721
24
657
 31
31
771
36
834
 7
7
168
34
58
 40
40
994
52
720
 96
96
2363
35
2042
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 67.8
67.8
69.5
100 97.2
97.2
97.9
97 -
-
-
87 -
-
-
91 -
-
-
87 -
-
-
- 81.4
81.4
87.4
82 -
-
-
79 -
-
-
- 21
21
30.6
- -
-
-
64 -
-
-
- 54.5
54.5
67.3
57.5 -
-
-
- 28.8
28.8
43
- 34
34
50.4
- 27.6
27.6
42.9
35.5 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 21.5
21.5
37.3
- 20.6
20.6
35.8
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | TRAP1 - Q12931 |
Regulation
Activation:
NA
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
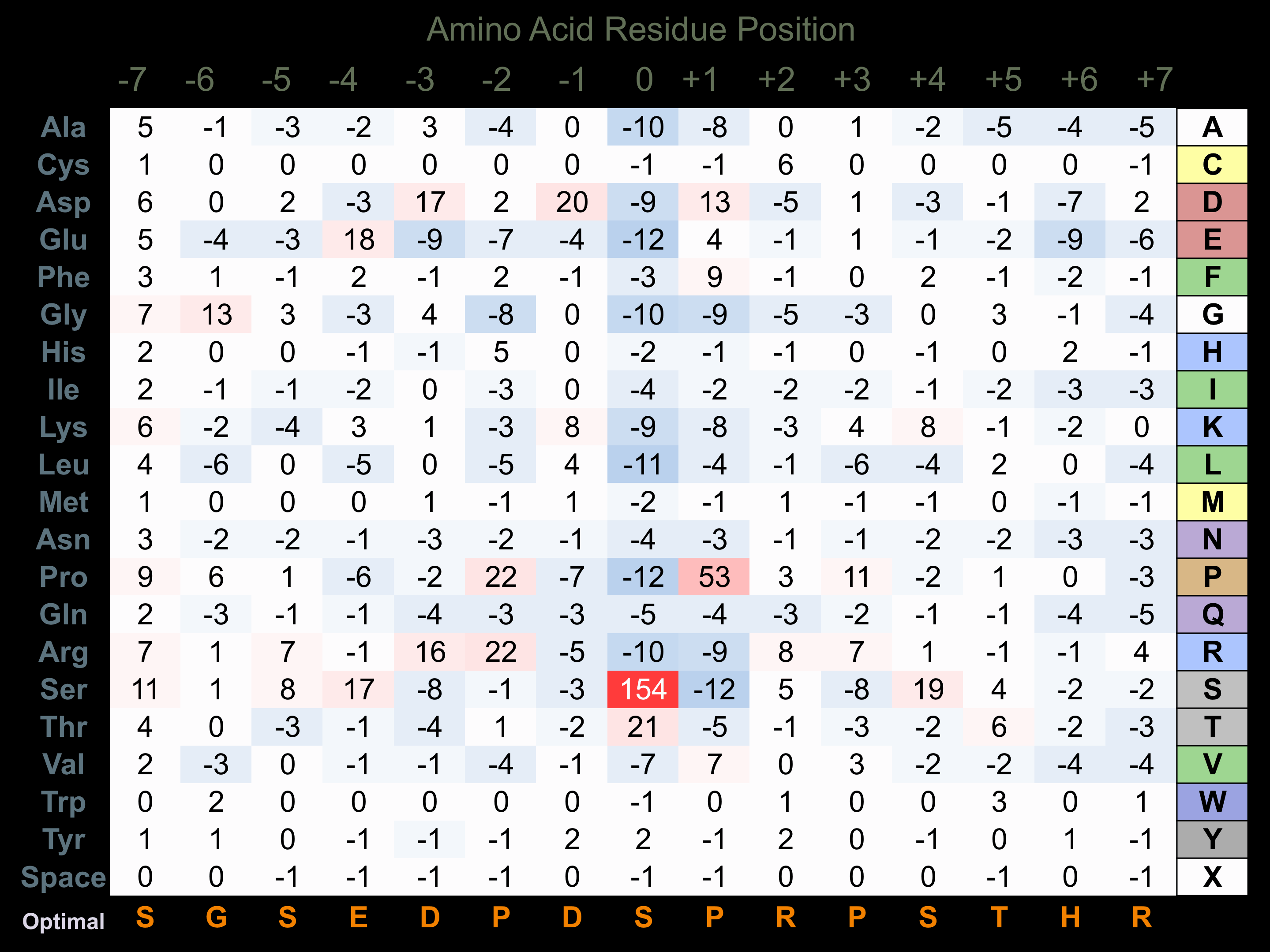
Matrix Type:
Predicted from the application of the Kinexus Kinase Substrate Predictor Version 2.0 algorithm, which was trained with over 10,000 kinase-protein substrate pairs and 8,000 kinase-peptide substrate pairs.
Domain #:
1
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Neurological disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
PINK1 Type of young-onset Parkinson's disease (PD); Parkinson disease 6, early onset; Parkinson's disease (PD); Parkinson disease 1
Comments:
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative movement disorder, characterized by the degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the midbrain. Symptoms of PD include trembling of hands, arms, legs, and face, stiffness in the arms and legs, bradykinesia, and poor coordination and balance. RNA-interference mediated knockdown of PINK1 in human and mouse neuronal cell cultures caused mitochondrial Ca2+ accumulation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and subsequent cell death. It has been suggested that PINK1 is essential to mitochondrial survival and function, specifically during cellular oxidative stress. Loss-of-function mutations in PINK1 are associated with Parkinson's disease, a movement disorder characterized by degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Mutations in the PINK1 gene have been observed in patients with PD, thus providing a direct link between mitochondrial dysfunction and the pathogenesis of PD. In animal models, mice lacking PINK1 expression display significantly increased levels of mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired neural activity, resembling the human PD phenotype.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for PINK1 in diverse human cancers of 288, which is 0.6-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 134 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 2.2-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.05 % in 24773 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only -35 % lower than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.25 % in 1093 large intestine cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
None > 3 in 20,056 cancer specimens
Comments:
Only 1 deletion, and no insertions or complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

