Nomenclature
Short Name:
MRCKb
Full Name:
Myotonic dystrophy kinase-related CDC42-binding kinase beta
Alias:
- CDC42BPB
- CDC42 binding protein kinase beta
- KIAA1124
- MRCK beta
- CDC42-binding protein kinase beta
- DMPK-like
- DMPK-like beta
- EC 2.7.11.1
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
AGC
Family:
DMPK
SubFamily:
GEK
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
194315
# Amino Acids:
1711
# mRNA Isoforms:
1
mRNA Isoforms:
194,315 Da (1711 AA; Q9Y5S2)
4D Structure:
Homodimer and homotetramer via the coiled coil regions. Interacts tightly with GTP-bound but not GDP-bound CDC42
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
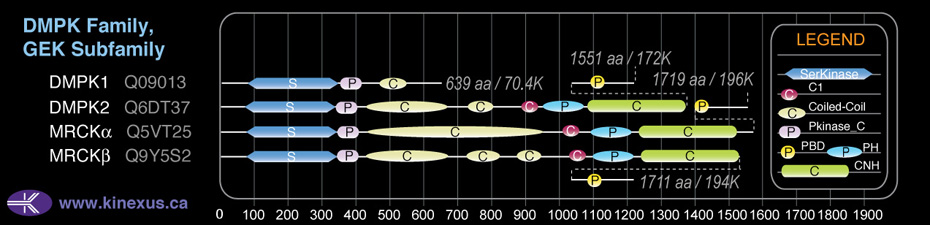
Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 76 | 342 | Pkinase |
| 343 | 413 | Pkinase_C |
| 431 | 665 | Coiled-coil |
| 726 | 817 | Coiled-coil |
| 877 | 939 | Coiled-coil |
| 1026 | 1075 | C1 |
| 1095 | 1214 | PH |
| 1240 | 1513 | CNH |
| 1583 | 1618 | PBD |
| 1583 | 1596 | CRIB |
| 878 | 939 | DMPK |
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K489.
Methylated:
R671.
Serine phosphorylated:
S304, S310, S363, S417, S421, S475, S481, S524, S641, S659, S707, S840, S851, S914, S1190, S1191, S1640, S1643, S1644, S1647, S1650, S1659, S1677, S1680, S1682, S1683, S1686, S1690, S1693.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T307, T423, T467, T676, T757, T843, T1196, T1652, T1678.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y954, Y1118, Y1355, Y1638.
Ubiquitinated:
K314, K337, K426, K665, K864.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 88
88
1211
22
1386
 21
21
288
9
295
 49
49
677
37
915
 34
34
462
105
465
 59
59
810
21
691
 9
9
119
53
235
 6
6
86
25
139
 45
45
611
57
723
 54
54
733
10
445
 14
14
189
35
132
 18
18
242
50
207
 62
62
855
107
619
 20
20
275
48
242
 20
20
279
6
245
 26
26
356
47
344
 15
15
205
12
198
 26
26
361
116
281
 23
23
318
42
314
 19
19
260
73
395
 45
45
622
79
520
 42
42
577
46
366
 22
22
295
48
210
 37
37
512
38
355
 26
26
359
42
246
 13
13
183
46
259
 39
39
533
78
500
 23
23
321
51
444
 24
24
329
42
270
 35
35
484
42
327
 1.5
1.5
20
14
19
 48
48
663
18
475
 100
100
1370
32
3012
 35
35
478
63
782
 70
70
955
52
788
 4
4
56
35
43
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 94.9
94.9
95.7
100 94.9
94.9
95.7
98 -
-
-
91 -
-
-
93 60
60
76.3
93 90
90
94
- -
-
-
92 91.8
91.8
96.5
92 92.1
92.1
96.4
- 83.4
83.4
89.7
- 83.4
83.4
89.7
84 -
-
-
80 73.6
73.6
85.7
74 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 43.1
43.1
62.8
- -
-
-
- 24.3
24.3
43.4
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | RPL35 - P42766 |
Regulation
Activation:
Agonist binding to the phorbol ester binding site disrupts this, releasing the kinase domain to allow N-terminus-mediated dimerization and kinase activation by transautophosphorylation.
Inhibition:
Maintained in an inactive, closed conformation by an interaction between the kinase domain and the negative autoregulatory C-terminal coiled-coil region.
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
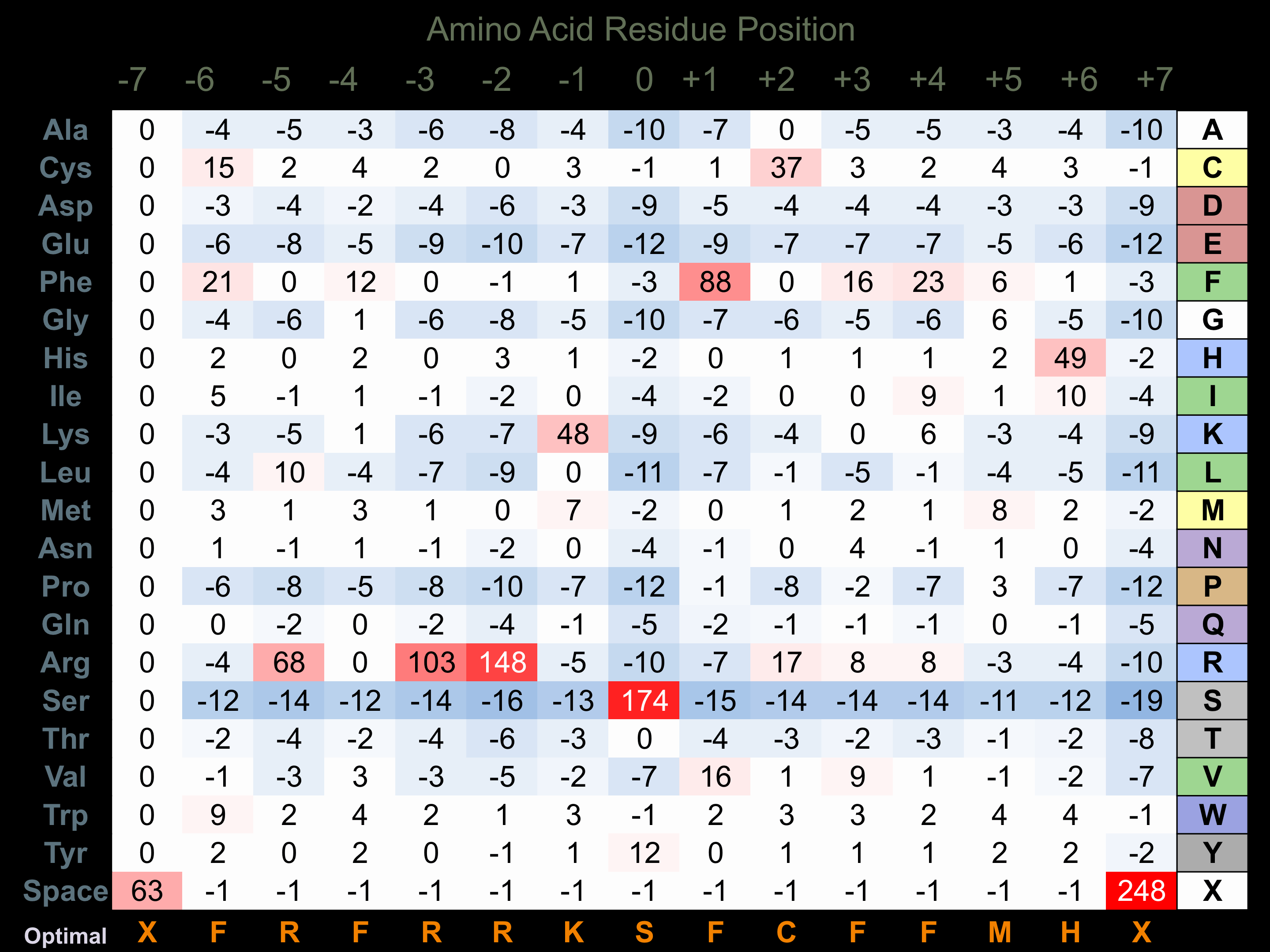
Matrix Type:
Derived from alignment of 31 peptides phosphorylated by recombinant MRCKb in vitro tested in-house by Kinexus.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Musculoskeletal disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Myotonic dystrophy
Comments:
Myotonic dystrophy is an inherited disease that affects multiple systems of the body. Symptoms include the wasting of the muscles (muscular dystrophy), cataracts, heart defects, endocrine dysfunction, and myotonia.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Bladder carcinomas (%CFC= +77, p<0.0002); Breast epithelial cell carcinomas (%CFC= +60, p<0.013); Pituitary adenomas (ACTH-secreting) (%CFC= +97); and Skin squamous cell carcinomas (%CFC= +124, p<0.021). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for MRCKb in diverse human cancers of 376, which is 0.8-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 325 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 5.4-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice support a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis. The MRCK-ß protein posesses many functional domains, including three independent coiled-coil (CC) domains involved in the dimerization that is critical for the activation of the protein, a cysteine-rich motif similar to that of protein kinase C (PKC), and potentially a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. Deletion of the two distal CC domains (CC2 and CC3; amino acid residues 658-930) results in a constitutively active kinase, indicating a role for these domains in the autoinhibition of the kinase catalytic domain of the protein.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.06 % in 24972 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only -18 % lower than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.24 % in 864 skin cancers tested; 0.22 % in 1272 large intestine cancers tested; 0.2 % in 589 stomach cancers tested; 0.18 % in 603 endometrium cancers tested; 0.15 % in 548 urinary tract cancers tested; 0.13 % in 273 cervix cancers tested; 0.12 % in 710 oesophagus cancers tested; 0.09 % in 127 biliary tract cancers tested; 0.08 % in 1822 lung cancers tested; 0.07 % in 238 bone cancers tested; 0.06 % in 1512 liver cancers tested; 0.06 % in 1372 breast cancers tested; 0.04 % in 942 upper aerodigestive tract cancers tested; 0.04 % in 833 ovary cancers tested; 0.04 % in 1276 kidney cancers tested; 0.03 % in 881 prostate cancers tested; 0.03 % in 2082 central nervous system cancers tested; 0.03 % in 1459 pancreas cancers tested; 0.01 % in 2009 haematopoietic and lymphoid cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
None > 3 in 20,256 cancer specimens
Comments:
Only 6 deletions, 2 insertions and no complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

