Nomenclature
Short Name:
BMPR1A
Full Name:
Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type IA
Alias:
- Activin receptor-like kinase 3
- ACVRLK3
- Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type IA precursor
- Bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IA
- CD292
- SKR5
- ALK3
- ALK-3
- BMR1A
- BMRA
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
TKL
Family:
STKR
SubFamily:
Type1
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
60,198
# Amino Acids:
532
# mRNA Isoforms:
1
mRNA Isoforms:
60,198 Da (532 AA; P36894)
4D Structure:
NA
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
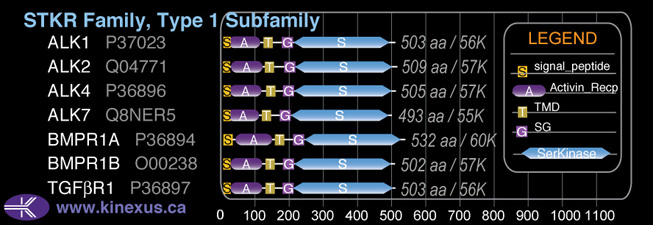
Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23 | signal_peptide |
| 37 | 138 | Activin_recp |
| 153 | 175 | TMD |
| 204 | 233 | GS |
| 234 | 525 | Pkinase |
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
N-GlcNAcylated:
N73.
Serine phosphorylated:
S215, S216, S218, S220.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y407-.
Ubiquitinated:
K531.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 85
85
800
29
863
 6
6
54
15
31
 33
33
309
15
275
 45
45
423
96
756
 97
97
916
25
716
 9
9
86
80
110
 28
28
263
31
456
 86
86
813
48
1358
 69
69
652
17
530
 9
9
87
75
50
 6
6
59
34
50
 73
73
690
168
656
 6
6
60
37
55
 8
8
75
12
43
 5
5
50
29
48
 10
10
96
15
31
 8
8
79
199
84
 13
13
125
24
138
 20
20
191
90
124
 74
74
703
109
687
 19
19
176
28
162
 7
7
65
30
63
 20
20
190
25
212
 7
7
67
24
60
 3
3
32
28
31
 90
90
854
64
755
 6
6
56
40
57
 14
14
135
24
121
 27
27
255
24
264
 5
5
50
28
43
 62
62
586
24
555
 100
100
944
36
2462
 15
15
142
71
385
 85
85
806
57
718
 7
7
66
35
62
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 99.6
99.6
99.8
100 99.6
99.6
99.6
100 -
-
-
98 -
-
-
- 97.4
97.4
98.5
99 -
-
-
- 97.9
97.9
98.5
98 97
97
98.3
97 -
-
-
- 94.5
94.5
97.2
- 69.7
69.7
79.9
91 32.9
32.9
49.3
83 76.5
76.5
85.2
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
50 53.4
53.4
66.2
- 31.3
31.3
49.5
33 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
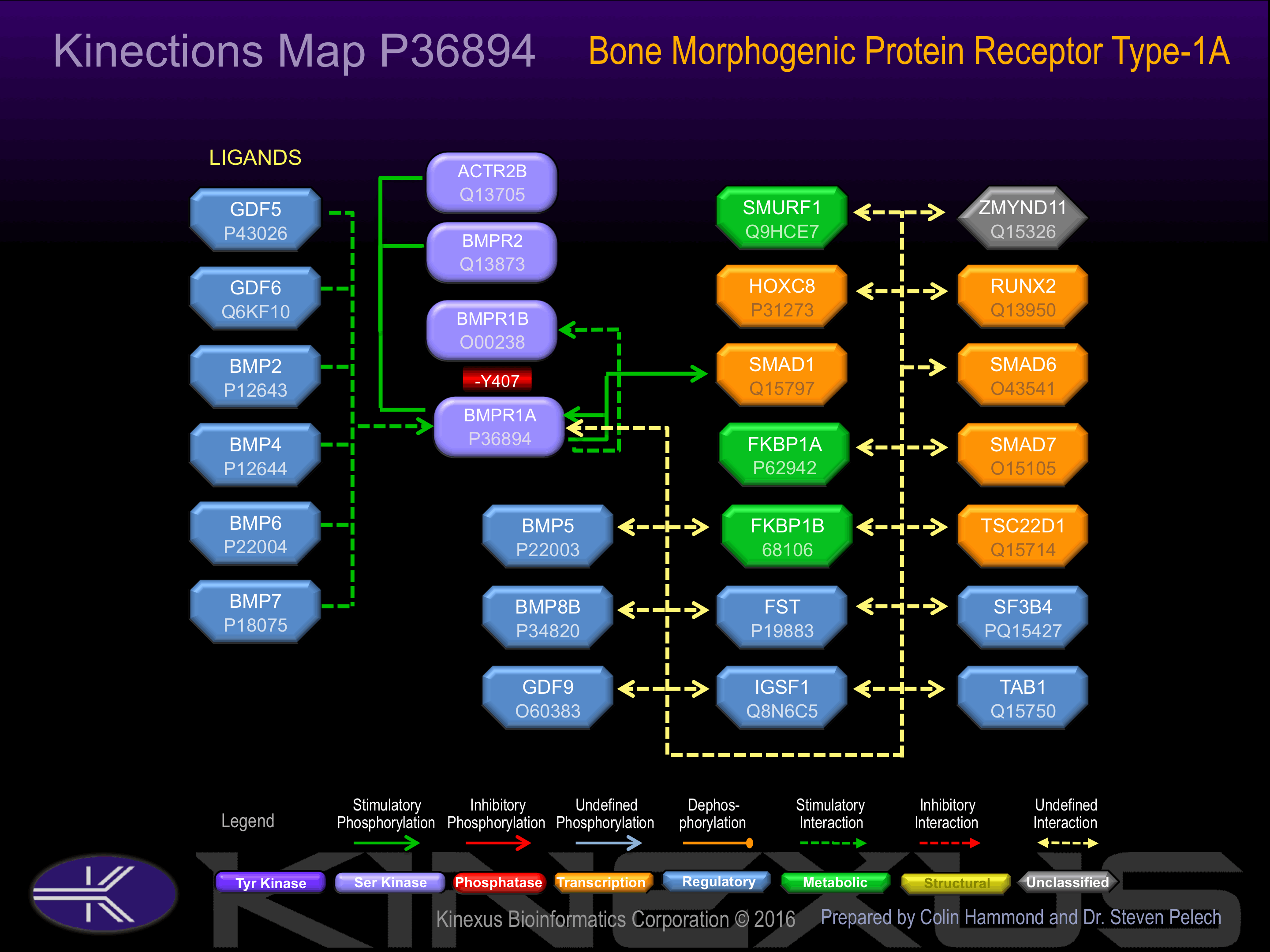
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | BMP4 - P12644 |
| 2 | BMP6 - P22004 |
| 3 | HOXC8 - P31273 |
| 4 | SMAD7 - O15105 |
| 5 | BMPR1B - O00238 |
| 6 | GDF9 - O60383 |
| 7 | SMAD1 - Q15797 |
| 8 | GDF6 - Q6KF10 |
| 9 | TAB1 - Q15750 |
| 10 | TGFBRAP1 - Q8WUH2 |
Regulation
Activation:
Activated by binding bone morphogenetic protein 2 and 4 (BMP-2, BMP-4), which appears to induce heterodimerization and autophosphorylation. Type II receptors phosphorylate and activate type I receptors which autophosphorylate, then bind and activate SMAD transcriptional regulators.
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
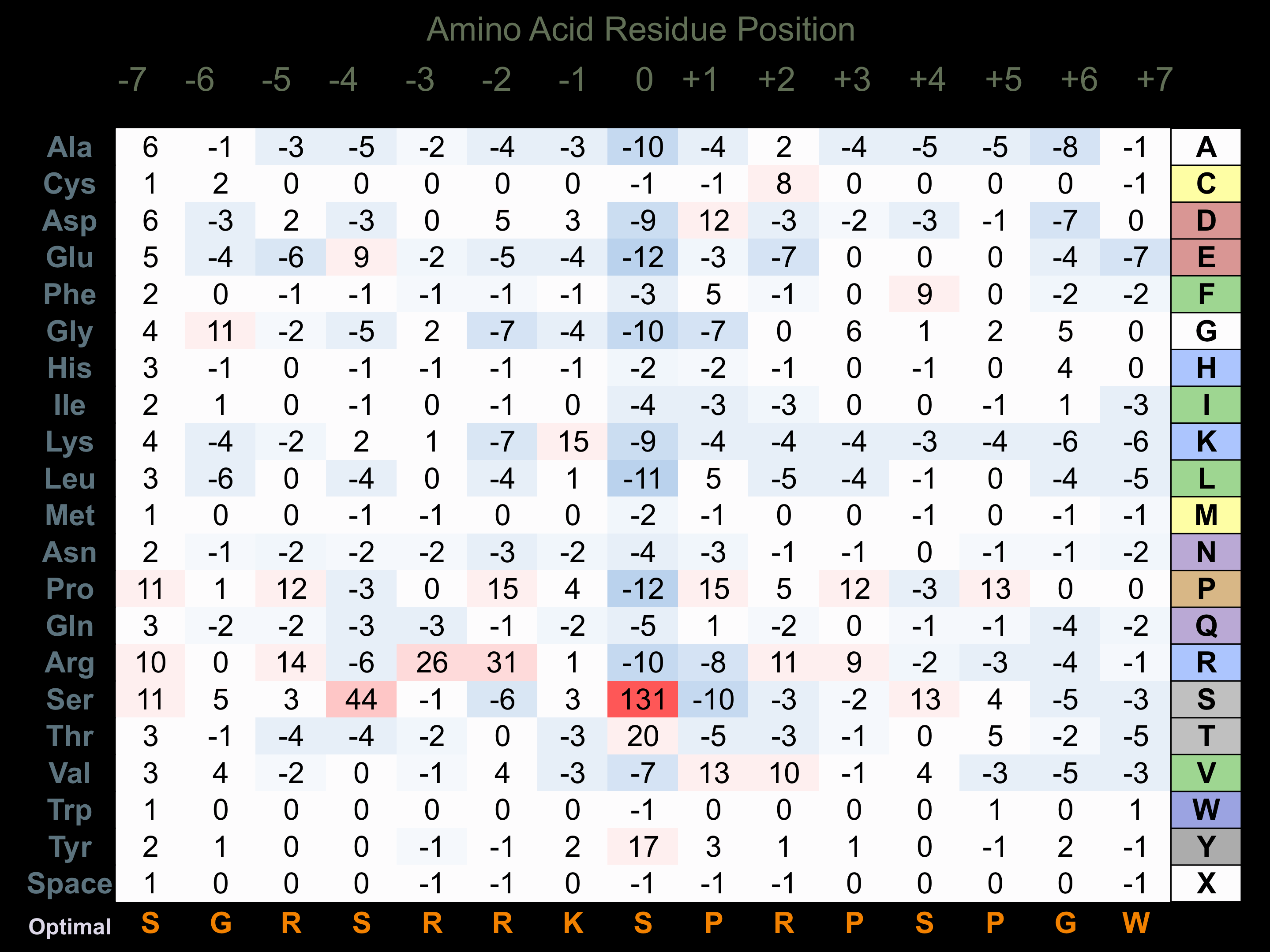
Matrix Type:
Predicted from the application of the Kinexus Kinase Substrate Predictor Version 2.0 algorithm, which was trained with over 10,000 kinase-protein substrate pairs and 8,000 kinase-peptide substrate pairs.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
| LDN193189 | IC50 = 40.7 nM | 25195294 | 513147 | 20020776 |
| PP242 | Kd = 64 nM | 25243800 | 22037378 | |
| SureCN7018367 | Kd < 150 nM | 18792927 | 450519 | 19035792 |
| NVP-TAE684 | Kd = 170 nM | 16038120 | 509032 | 22037378 |
| PD173955 | Kd = 170 nM | 447077 | 386051 | 22037378 |
| CHEMBL249097 | Kd < 400 nM | 25138012 | 249097 | 19035792 |
| Lestaurtinib | Kd = 950 nM | 126565 | 22037378 | |
| CHEMBL566515 | Kd = 1 µM | 44478401 | 566515 | 19788238 |
| WZ3146 | Kd > 1 µM | 44607360 | 20033049 | |
| WZ4002 | Kd > 1 µM | 44607530 | 20033049 | |
| Hesperadin | Kd < 1.25 µM | 10142586 | 514409 | 19035792 |
| SureCN5302803 | Kd > 1.25 µM | 24788740 | 19035792 | |
| KW2449 | Kd = 1.9 µM | 11427553 | 1908397 | 22037378 |
| Staurosporine | Kd = 3.7 µM | 5279 | 18183025 | |
| BMS-690514 | Kd < 4 µM | 11349170 | 21531814 |
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, growth disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Brachydactyly Type A2
Comments:
Brachydactyly Type A2 symptoms include clinodactyly (fifth finger), and short hand/brachydactyly. Important pathways in this syndrome are the mTOR and apopotosis pathways. Bone tissue may be affected in this condition. Loss of function of BMPR1A may induce Brachydactyly Type A2, as a reduction of growth and differentiation factor 5 (GDF5) interaction with BMPR1A also produced this disease.
Specific Cancer Types:
Juvenile polyposis syndrome; Juvenile polyposis syndrome, infantile Form; Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome; Ruvalcaba syndrome; Juvenile polyposis of Infancy; Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome 2; BMPR1A-related juvenile polyposis; Cowden disease; Colorectal cancer, Hereditary nonpolyposis, Type 1
Comments:
BMPR1A appears to be a tumour suppressor protein (TSP). Cancer-related mutations in human tumours point to a loss of function of the protein kinase. The active form of the protein kinase normally acts to inhibit tumour cell proliferation. Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome (JPS) can lead to polyp formation, often in the large bowel, and the disorder can lead to an increased risk of cancer. Multiple mutations in BMPR1A have been described in JPS patients. Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome is a rare disorder with mutations in PTEN, relates to Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome, and is characterized by macrocephaly, intestinal polyposis, lipomas, and pigmentation in the region of the glans penis. Tissues affected included skin, thyroid, and breast. Ruvalcaba Syndrome have mutations in pten, and are associated with an inositol metabolism pathway. Tissues affected in Ruvalcaba Syndrome include testes, skin, and kidneys. Cowden Disease is characterized by hamartoma growths (non-cancerous, tumour-like) but will also correlate with an increased risk of developing various cancers including breast, thyroid, and uterine endometrium. Cowden is from a mutation in the PTEN, SDHD, and KLLN genes and is associated with the cerebellum, breast, and thyroid. Mouse insertional mutagenesis experiments support BMPR1A as a cancer driver gene.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Brain oligodendrogliomas (%CFC= -95, p<0.064); Cervical cancer stage 2B (%CFC= -51, p<0.101); Colorectal adenocarcinomas (early onset) (%CFC= +46, p<0.08); Malignant pleural mesotheliomas (MPM) tumours (%CFC= +48, p<0.074); Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) (%CFC= +149, p<0.0001); Prostate cancer - primary (%CFC= -54, p<0.0001); and Skin squamous cell carcinomas (%CFC= -47, p<0.004). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for BMPR1A in diverse human cancers of 328, which is 0.7-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 130 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 2.2-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice support a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.08 % in 25763 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is the same as the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.51 % in 1243 large intestine cancers tested; 0.14 % in 1941 lung cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: R486L (6); R486Q (3); R486W (2);.
Comments:
Only 2 deletions, 1 insertion, and no complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.