Nomenclature
Short Name:
ZAP70
Full Name:
Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70
Alias:
- EC 2.7.10.2
- SRK
- Syk-related tyrosine kinase
- ZA70
- ZAP-70
Classification
Type:
Protein-tyrosine kinase
Group:
TK
Family:
Syk
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
69,872
# Amino Acids:
619
# mRNA Isoforms:
3
mRNA Isoforms:
69,872 Da (619 AA; P43403); 55,873 Da (493 AA; P43403-3); 35,647 Da (312 AA; P43403-2)
4D Structure:
Interacts with SLA2 when it is phosphorylated. Interacts with CD3Z and with phosphorylated NFAM1. Interacts with CBLB By similarity. Interacts with CBL and SLA when it is phosphorylated. The association with SLA (or SLA2) and CBL probably leads to its destruction. Interacts with SHB. Interacts with DEF6. Interacts (via SH2 domains) with RHOH By similarity. Interacts with FCRL3.
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
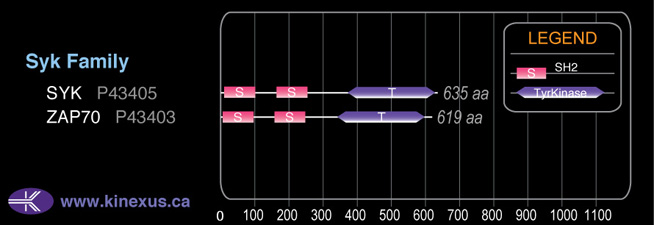
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K603 (N6).
Serine phosphorylated:
S166, S167, S179, S257, S258, S263, S289, S301, S313, S317, S320, S351, S491+, S520+, S534, S599.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T197, T278, T286, T293, T300, T312, T494, T611.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y12, Y46, Y69, Y87, Y126, Y164, Y178, Y198, Y204, Y209, Y211, Y221, Y248, Y292-, Y315+, Y319+, Y397, Y451, Y474+, Y492-, Y493+, Y506, Y535, Y569, Y597, Y598.
Ubiquitinated:
K25, K100, K132, K176, K193, K206, K217, K361, K362, K377, K455, K476, K484, K500, K538, K556, K603, K613.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 52
52
888
22
1076
 0.4
0.4
6
10
5
 1.3
1.3
22
1
0
 41
41
706
68
2517
 27
27
462
20
322
 1.1
1.1
18
46
15
 13
13
225
29
507
 100
100
1704
20
3213
 14
14
232
10
220
 4
4
76
44
120
 2
2
35
12
58
 33
33
570
100
569
 12
12
211
12
76
 0.7
0.7
12
8
16
 1.5
1.5
25
11
22
 0.6
0.6
10
12
10
 3
3
43
100
31
 0.9
0.9
16
7
15
 0.9
0.9
15
43
14
 17
17
291
79
269
 3
3
45
8
58
 14
14
244
12
341
 8
8
140
10
91
 0.9
0.9
15
8
20
 33
33
563
10
828
 92
92
1572
43
3386
 5
5
92
15
56
 1.1
1.1
18
8
21
 0.9
0.9
16
6
13
 8
8
131
14
60
 76
76
1291
30
441
 33
33
567
20
578
 21
21
364
61
563
 35
35
599
57
561
 4
4
76
35
52
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 99.8
99.8
100
100 97.6
97.6
98.4
98 -
-
-
94 -
-
-
94 53.6
53.6
70.4
90 -
-
-
- 93.5
93.5
96.1
94 53.7
53.7
70.9
93 -
-
-
- 57.7
57.7
62.7
- 22.7
22.7
35.6
77 24.3
24.3
39.1
74 25.3
25.3
37.4
67 -
-
-
- 25.1
25.1
40.9
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 34
34
49.5
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | LCK - P06239 |
| 2 | CBL - P22681 |
| 3 | SHC1 - P29353 |
| 4 | CD247 - P20963 |
| 5 | CD3E - P07766 |
| 6 | PTPN6 - P29350 |
| 7 | SH3BP2 - P78314 |
| 8 | CRK - P46108 |
| 9 | VAV1 - P15498 |
| 10 | LCP2 - Q13094 |
| 11 | SLC7A5P1 - Q8MH63 |
| 12 | SLC7A5 - Q01650 |
| 13 | SPNS1 - Q9H2V7 |
| 14 | CBLB - Q13191 |
| 15 | ACP1 - P24666 |
Regulation
Activation:
Phosphorylation of Ser-520 is required for priming ZAP70 binding to the plasma membrane where it can be activated. Phosphorylation of Tyr-315 induces association with CrkII. Phosphorylation of Tyr-319 increases phosphotransferase activity, PLC-g1+ Ras Activation and its serves as an Lck bindings site. Phosphorylation of Tyr-474 and Tyr-493 increases phosphotransferase activity.
Inhibition:
Phosphorylation of Tyr-292 inhibits ZAP-70 signalling and negulatively modulates the duration of activated TCR at the cell surface and functions as a docking site for Cbl. Phosphorylation of Tyr-492 inhibits phosphotransferase activity.
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| LCK | P06239 | Y292 | DTLNSDGYTPEPARI | - |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y292 | DTLNSDGYTPEPARI | - |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y315 | MPMDTSVYESPYSDP | + |
| ABL | P00519 | Y319 | TSVYESPYSDPEELK | + |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y319 | TSVYESPYSDPEELK | + |
| LCK | P06239 | Y474 | VLLVNRHYAKISDFG | + |
| LCK | P06239 | Y492 | ALGADDSYYTARSAG | - |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y492 | ALGADDSYYTARSAG | - |
| LCK | P06239 | Y493 | LGADDSYYTARSAGK | + |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y493 | LGADDSYYTARSAGK | + |
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| DUSP3 (VHR) | P51452 | Y138 | SPTLVIAYLMMRQKM | + |
| DUSP3 (VHR) | P51452 | Y38 | NEVTPRIYVGNASVA | |
| GAB2 | Q9UQC2 | Y614 | KSTGSVDYLALDFQP | |
| HIP55 (DBNL) | Q9UJU6 | Y334 | QAEEEAVYEEPPEQE | |
| HIP55 (DBNL) | Q9UJU6 | Y344 | PPEQETFYEQPPLVQ | |
| LAT | O43561 | Y156 | ADEDEDDYHNPGYLV | |
| LAT | O43561 | Y161 | DDYHNPGYLVVLPDS | |
| LAT | O43561 | Y200 | SMESIDDYVNVPESG | |
| LAT | O43561 | Y220 | SLDGSREYVNVSQEL | |
| LAT | O43561 | Y255 | EEEGAPDYENLQELN | |
| LCP2 | Q13094 | Y113 | SSFEEDDYESPNDDQ | + |
| LCP2 | Q13094 | Y128 | DGEDDGDYESPNEEE | + |
| LCP2 | Q13094 | Y145 | PVEDDADYEPPPSND | + |
| MUC1 | P15941 | Y1203 | IFPARDTYHPMSEYP | |
| p38a MAPK (MAPK14) | Q16539 | Y323 | DEPVADPYDQSFESR | + |
| PLCG1 | P19174 | Y1253 | EGSFESRYQQPFEDF | |
| PLCG1 | P19174 | Y783 | EGRNPGFYVEANPMP | + |
| SH3BP2 (3BP2) | P78314 | S225 | SDMPRAHSFTSKGPG | ? |
| SH3BP2 (3BP2) | P78314 | S278 | PATPRRMSDPPLSTM | ? |
| SH3BP2 (3BP2) | P78314 | Y174 | YPTDNEDYEHDDEDD | |
| SH3BP2 (3BP2) | P78314 | Y183 | HDDEDDSYLEPDSPE | + |
| SH3BP2 (3BP2) | P78314 | Y448 | GDDSDEDYEKVPLPN | + |
| Shc1 | P29353 | Y349 | EEPPDHQYYNDFPGK | + |
| Shc1 | P29353 | Y350 | EPPDHQYYNDFPGKE | + |
| Shc1 | P29353 | Y427 | ELFDDPSYVNVQNLD | ? |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y292 | DTLNSDGYTPEPARI | - |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y315 | MPMDTSVYESPYSDP | + |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y319 | TSVYESPYSDPEELK | + |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y492 | ALGADDSYYTARSAG | - |
| ZAP70 | P43403 | Y493 | LGADDSYYTARSAGK | + |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
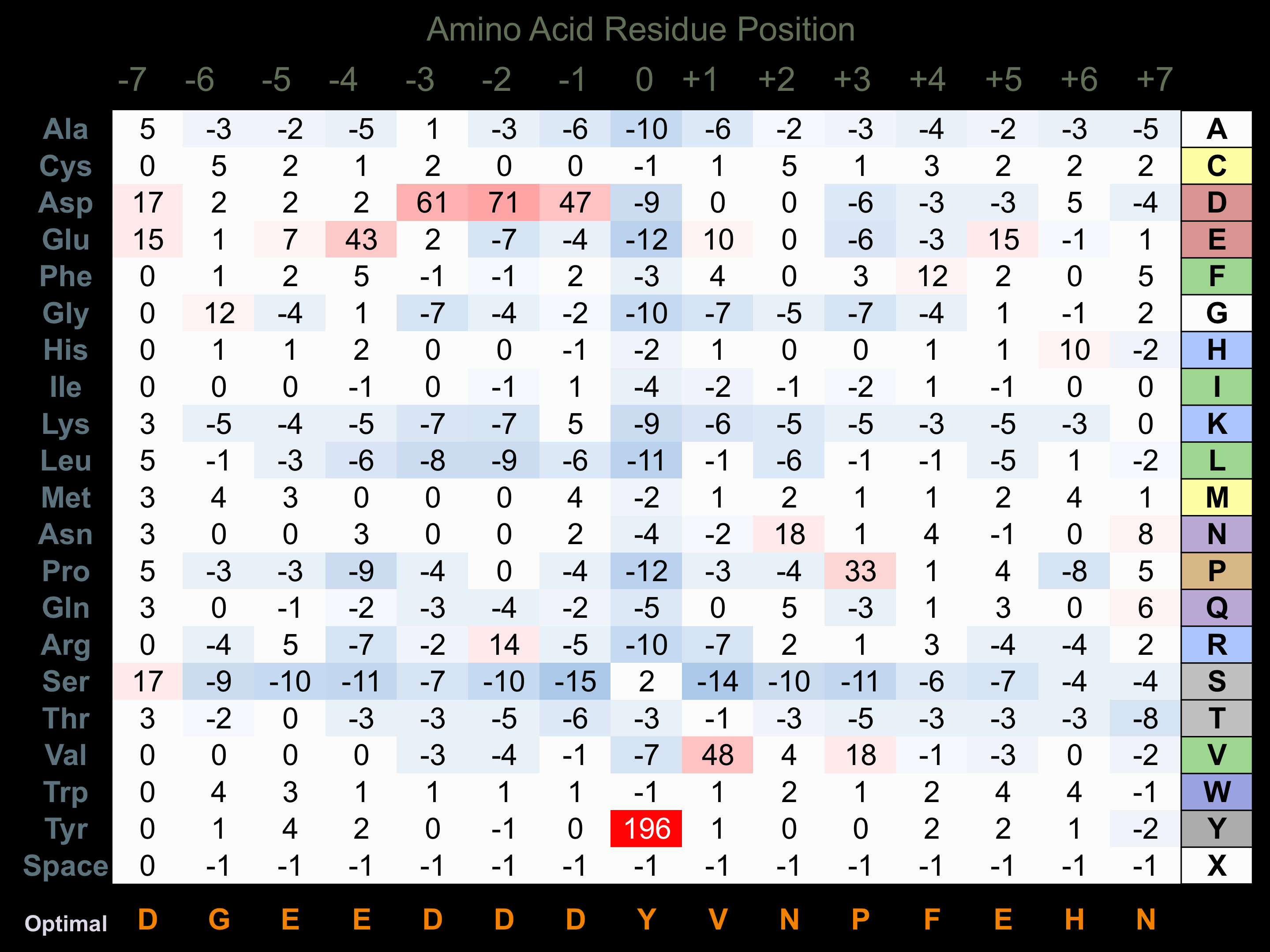
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 34 known protein substrate phosphosites and 72 peptides phosphorylated by recombinant ZAP70 in vitro tested in-house by Kinexus.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, immune disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
ZAP70-related severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID); ZAP-70 deficiency; Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID); Macroglobulinemia; Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
Comments:
Loss-of-function mutations in the ZAP70 gene that impair normal T-cell and B-cell development have been linked to Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and other immunodeficiency phenotypes. SCID is an inherited immune disease characterized by the abnormal development and function of both T-cells and B-cells. As a result, SCID patients have a significantly increased susceptibility to infections and commonly display ear infections, pneumonia, bronchitis, oral thrush, and diarrhea. Due to chronic infection, affected individuals do not display normal growth or weight gain (failure to thrive). SCID may be caused by mutations in several genes and is most commonly inherited in an X-linked manner, although autosomal recessive SCID has been reported as well. The most effective treatment for SCID is the transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells from the bone marrow of a healthy donor. >Several mutations in the ZAP70 gene have been identified in patients with immunodeficiency phenotypes, including an intronic point mutation that creates a new splice acceptor site, a 9-bp insertion mutation that results in the addition of a Leu-Glu-Gln amino acid sequence into the catalytic site, a substitution mutation (S518R) in the highly conserved S518 residue in the catalytic domain, a 13-bp deletion mutation involving nucleotides 1719-1731 causing a frame-shift after amino acid 503 and premature translational termination, and a R465H substitution mutation. Mutations at L377R, R465C, R465H, A507V, S518R, K541KLEQ, and C564R loci are associated selective T-cell defect (STCD), which a rare and atypical SCID with absent CD8+ T-cells. Family studies showed the homologous mutation in ZAP70, resulting in loss of the phosphotransferase activity of this kinase, were associated with STCD. However, the heterozygous genotypes produces unaffected phenotypes. >Macroglobulinemia is characterized by an increase in macroglobulins in blood and it can affect B cells, bone marrow, and bone tissues. Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia is a rare condition characterized by high immunoglobulin M antibody levels in blood leading to blood thickening, appetite loss, weight loss, and weakness. It can affect lymph node, bone marrow, and bone tissues. CD8 deficiency, familial is a rare disorder that is characterized by susceptibility to respiratory infections.
Specific Cancer Types:
Chronic lymphocytic leukemias (CLL); B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias (B-CLL); Malt lymphomas; Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas; Prolymphocytic leukemias (PLL); Cll/Sll
Comments:
ZAP70 may be an oncoprotein (OP). Gain-of-function mutations in the ZAP70 gene have been observed in several human cancer types, including particularly in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is a rare cancer of the blood involving the abnormal expansion of white blood cells that displace healthy blood cells. CLL can affect B cells, bone marrow, and bone tissues. In CLL patients, expression of ZAP70 was highly correlated with the disease progression, patient survival probability, and the mutation status of the immunoglobin heavy-chain variable region gene (an important prognostic factor in CLL). It was observed that CLL patients with greater than 20% ZAP70-positive leukemic cells had a more rapid disease progression and a significantly lower survival rate than patients with less than 20% ZAP70-positive leukemic cells. In aggressive CCL, the CCL cells usually express ZAP70 without mutated immunoglobulin heavy chains. Activation of ZAP70 is also linked with several other types of cancer. Malt Lymphoma is a rare condition and is a non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Malt Lymphoma is characterized by vomiting, increased sweating, and heartburn. Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma (JNA) is a rare condition related to familial adenomatous polyposis. Cll/sll is a chronic cancer characterized by immature lymphocytes in bone marrow, blood, or lymph nodes. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is a rare leukemia affecting B cells, T cells, and bone tissues.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Classical Hodgkin lymphomas (%CFC= +82, p<0.003); Colorectal adenocarcinomas (early onset) (%CFC= +85, p<0.016); Gastric cancer (%CFC= -63, p<0.007); Large B-cell lymphomas (%CFC= +127, p<0.005); and Malignant pleural mesotheliomas (MPM) tumours (%CFC= -50, p<0.038). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for ZAP70 in diverse human cancers of 271, which is 0.6-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 0 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 100% lower than the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis. ZAP70 can exhibit constitutive phosphotransferase activity with W131A, L133A, A141E, or V314A mutations. Constitutive phosphotransferase activity can occur with the combination of Y315A or Y315F with either Y319A or Y319F mutations. The Y319F mutation pair yields 80% loss of TCR-induced transcription factor NFAT and the Y315A mutation pair 75% loss of CD247/CD3Z binding with TCR stimulation, and loss of any Vav1 interaction. After activation via Lck phosphorylation, ZAP70 phosphotransferase activity can be stimulated through S144A, Q145A, P147A, Y597A, or Y598A mutations. NFAT can be induced independent of T cell Receptor (TCR) signalling with an Y292F mutation. ZAP70 phosphotransferase activity can also be increased with a Y492F mutation, and decreased with D461N or D479N mutations.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.11 % in 25346 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is a modest 1.4-fold higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.6 % in 589 stomach cancers tested; 0.55 % in 1270 large intestine cancers tested; 0.28 % in 864 skin cancers tested; 0.27 % in 603 endometrium cancers tested; 0.18 % in 548 urinary tract cancers tested; 0.18 % in 273 cervix cancers tested; 0.15 % in 1956 lung cancers tested; 0.11 % in 710 oesophagus cancers tested; 0.09 % in 942 upper aerodigestive tract cancers tested; 0.09 % in 939 prostate cancers tested; 0.07 % in 2082 central nervous system cancers tested; 0.07 % in 1490 breast cancers tested; 0.06 % in 1512 liver cancers tested; 0.06 % in 1467 pancreas cancers tested; 0.05 % in 1276 kidney cancers tested; 0.04 % in 891 ovary cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: R360H (4); E553K (4); R119* (3); T156M (3); P191L (3).
Comments:
Only 2 deletions, and no insertions or complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

