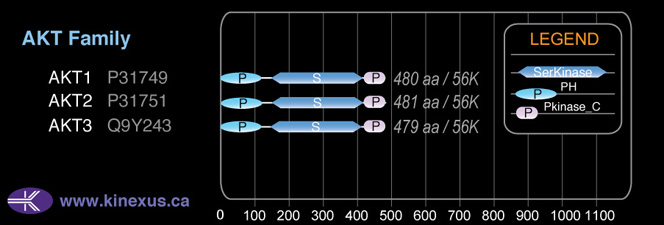
Nomenclature
Short Name:
AKT3
Full Name:
RAC-gamma serine-threonine-protein kinase
Alias:
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
AGC
Family:
AKT
SubFamily:
NA
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
55,775
# Amino Acids:
479
# mRNA Isoforms:
2
mRNA Isoforms:
55,775 Da (479 AA; Q9Y243); 54,032 Da (465 AA; Q9Y243-2)
4D Structure:
Interacts (via PH domain) with TCL1A; this enhances AKT3 phosphorylation and activation. Interacts with TRAF6
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Serine phosphorylated:
S120, S123, S197, S472+, S474, S476.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T298, T302+, T305+, T309+, T432, T440, T447.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y38, Y312-, Y323, Y434, Y473.
Ubiquitinated:
K273.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 96
96
1219
63
1029
 6
6
77
21
87
 27
27
346
15
186
 34
34
430
208
513
 55
55
703
63
568
 29
29
366
150
1527
 8
8
104
73
315
 47
47
604
61
828
 36
36
460
24
330
 8
8
107
188
92
 4
4
57
44
47
 55
55
704
257
633
 10
10
133
48
100
 10
10
125
15
163
 6
6
74
35
68
 8
8
100
37
124
 25
25
316
155
2429
 6
6
80
24
60
 7
7
83
188
60
 46
46
583
246
536
 13
13
167
34
138
 10
10
131
39
121
 7
7
94
26
69
 15
15
185
25
145
 7
7
86
32
77
 57
57
720
128
627
 6
6
79
51
63
 6
6
78
24
62
 21
21
272
25
207
 9
9
116
84
94
 38
38
478
42
302
 100
100
1272
66
2960
 13
13
164
120
420
 72
72
921
161
773
 39
39
501
105
708
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 77.8
77.8
88.8
100 78.6
78.6
79.1
100 -
-
-
100 -
-
-
- 99.6
99.6
100
100 -
-
-
- 99.6
99.6
99.8
100 99.2
99.2
99.4
100 -
-
-
- 86.1
86.1
87.3
- 40.3
40.3
55.3
100 83
83
90.8
- 41.5
41.5
56.8
96 -
-
-
- 51.4
51.4
62.7
64 -
-
-
- 51.9
51.9
67.7
54 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 21
21
30
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Regulation
Activation:
Two specific sites, one in the kinase domain (Thr-305) and the other in the C-terminal regulatory region (Ser-472), need to be phosphorylated for its full activation
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
When fully phosphorylated and translocated into the nucleus, undergoes 'Lys-48'-polyubiquitination catalyzed by TTC3, leading to its degradation by the proteasome.
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| 14-3-3 zeta (YWHAZ) | P63104 | S58 | VVGARRSSWRVVSSI | |
| ACLY | P53396 | S455 | PAPSRTASFSESRAD | |
| Akt1S1 | Q96B36 | T246 | LPRPRLNTSDFQKLK | |
| Arfaptin 2 | P53365 | S260 | GTRGRLESAQATFQA | |
| AS160 (TBC1D4) | O60343 | S588 | RMRGRLGSVDSFERS | - |
| AS160 (TBC1D4) | O60343 | T642 | QFRRRAHTFSHPPSS | - |
| ASK1 (MAP3K5) | Q99683 | S83 | ATRGRGSSVGGGSRR | - |
| Bad | Q92934 | S75 | EIRSRHSSYPAGTED | - |
| Bad | Q92934 | S99 | PFRGRSRSAPPNLWA | - |
| Caspase 9 | P55211 | S196 | KLRRRFSSLHFMVEV | - |
| Cip1 (p21, CDKN1A) | P38936 | S145 | GRKRRQTSMTDFYHS | |
| Cip1 (p21, CDKN1A) | P38936 | T144 | QGRKRRQTSMTDFYH | - |
| Csdc2 | Q9Y534 | S58 | TKRTRTYSATARASA | |
| Ezrin | P15311 | T566 | QGRDKYKTLRQIRQG | |
| FOXO1A | Q12778 | S256 | SPRRRAASMDNNSKF | - |
| FOXO1A | Q12778 | S319 | TFRPRTSSNASTISG | + |
| FOXO1A | Q12778 | T24 | LPRPRSCTWPLPRPE | |
| GABRB1 | P18505 | S409 | IQYRKPLSSREAYGR | |
| GSK3b | P49841 | S9 | SGRPRTTSFAESCKP | - |
| HAND2 | P61296 | S114 | KERRRTQSINSAFAE | |
| HMOX-1 | P09601 | S188 | LYRSRMNSLEMTPAV | |
| Huntingtin | P42858 | S421 | GGRSRSGSIVELIAG | |
| IKKa (CHUK) | O15111 | T23 | EMRERLGTGGFGNVC | + |
| IRS1 | P35568 | S270 | EFRPRSKSQSSSNCS | |
| IRS1 | P35568 | S307 | TRRSRTESITATSPA | - |
| IRS1 | P35568 | S330 | SFRVRASSDGEGTMS | |
| IRS1 | P35568 | S527 | RFRKRTHSAGTSPTI | ? |
| METTL1 | Q9UBP6 | S27 | YYRQRAHSNPMADHT | - |
| MKK4 (MAP2K4, MEK4) | P45985 | S80 | IERLRTHSIESSGKL | - |
| NuaK1 (ARK5) | O60285 | S600 | PARQRIRSCVSAENF | + |
| p27Kip1 | P46527 | T157 | GIRKRPATDDSSTQN | - |
| p47phox | P14598 | S304 | GAPPRRSSIRNAHSI | + |
| p47phox | P14598 | S328 | QDAYRRNSVRFLQQR | + |
| PAK1 | Q13153 | S21 | APPMRNTSTMIGAGS | - |
| PFKFB2 | O60825 | S466 | PVRMRRNSFTPLSSS | |
| PFKFB2 | O60825 | S483 | IRRPRNYSVGSRPLK | |
| PTP1B | P18031 | S50 | RNRYRDVSPFDHSRI | + |
| Raf1 | P04049 | S259 | SQRQRSTSTPNVHMV | - |
| SORBS2 | O94875 | S186 | PLRPRDRSSTEKHDW | |
| SORBS2 | O94875 | T188 | RPRDRSSTEKHDWDP | |
| Tau | P10636 | S214 | GGKERPGSKEEVDED | |
| TSC2 | P49815 | S939 | SFRARSTSLNERPKS | |
| Wnk1 (PRKWNK1) | Q9H4A3 | T60 | EYRRRRHTMDKDSRG | + |
| YBX1 | P67809 | S102 | NPRKYLRSVGDGETV | |
| Zyxin | Q15942 | S142 | PQPREKVSSIDLEID |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
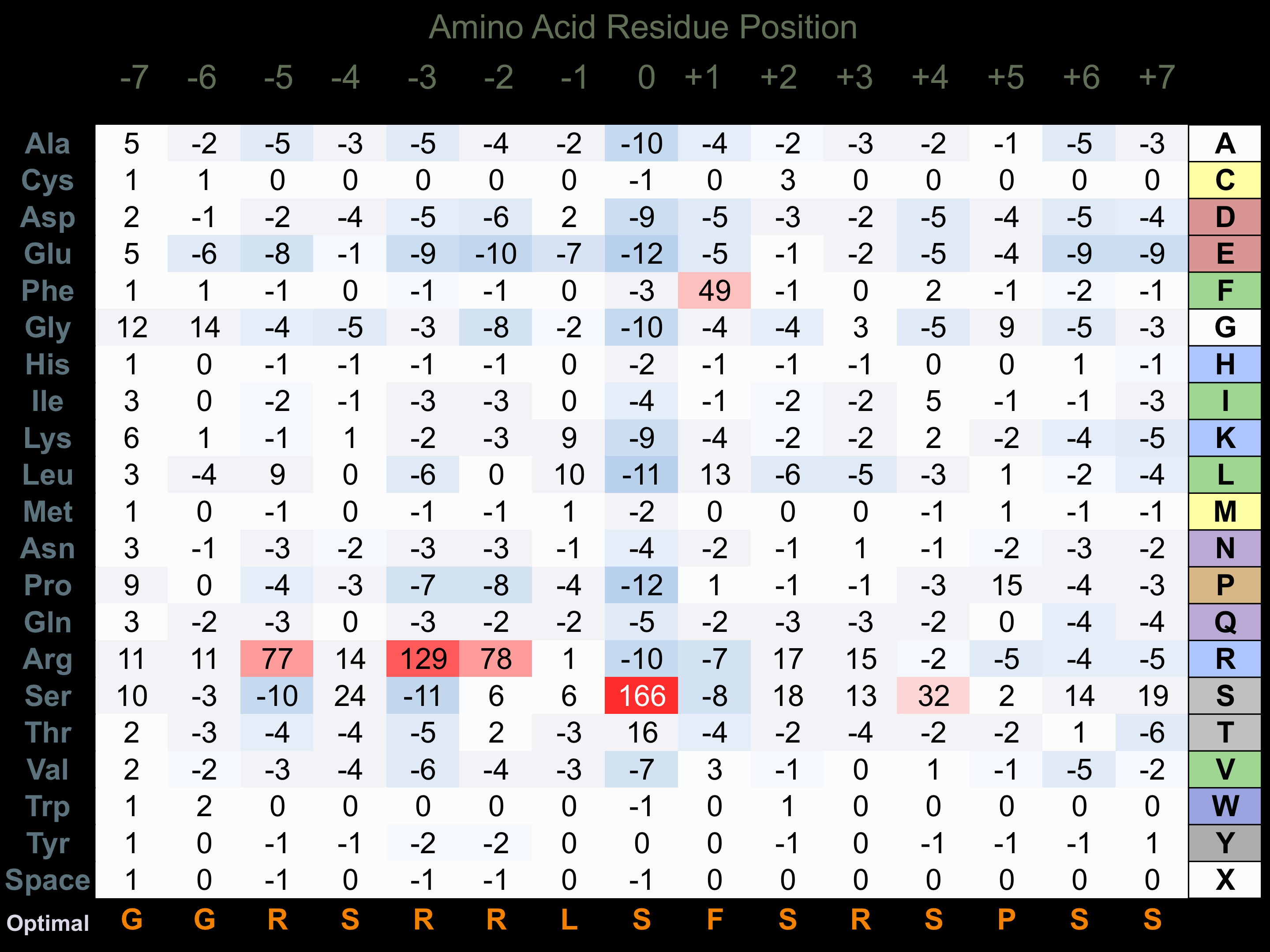
Matrix Type:
Predicted from the application of the Kinexus Kinase Substrate Predictor Version 2.0 algorithm, which was trained with over 10,000 kinase-protein substrate pairs and 8,000 kinase-peptide substrate pairs.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, developmental disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Megalencephaly-polymicrogyria-polydactyly-hydrocephalus syndrome (MPPH); Megalencephaly; Hemimegalencephaly; Megalencephaly-polymicrogyria-polydactyly-hydrocephalus syndrome (MPPH), somatic; Corpus callosum agenesis
Comments:
Megalencephaly-polymicrogyria-polydactyly-hydrocephalus syndrome (MPPH) is a rare developmental disorder characterized by polydactyly, high forebrain and ventricular septal defects, and defective inter-ventricular communication. Megalencephaly is a rare growth and developmental disorder characterized by an abnormally large brain thought to result from a disturbance in the regulation of cell proliferation during brain development. Hemimegalencephaly is an extremely rare developmental disorder characterized by the unilateral enlargement of the cerebral hemispheres. Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a disease characterized by the partial or complete absence of the corpus callosum, the brain structure connecting the two hemispheres. The effects of MPPH can range from mild to severe, depending on other brain defects associated with the disease. Deletion mutations of the 1q42-q44 chromosomal region have been linked to various developmental disorders of the brain, including agenesis of the corpus callosum and microcephaly, and have been suggested as a contributor factor in the pathogenesis of MPPH. A known breakpoint for this deletion is located 20 kb upstream of the Akt3 gene, which indicates effects on gene function/regulation by the deletion. During human development, Akt3 expression is elevated in the cortex at 9-weeks gestation, a period characterized by active neurogenesis. In addition, several substitution mutations in the Akt3 gene have been reported in patients with MPPH, including R465W, N229S, and E17K. Interestingly, the E17K mutation has also been observed in breast cancer and is thought to cause a gain-of-function of protein activity. In animal studies, mice lacking brain specific Akt3 expression during neural development display a 20% smaller brain size compared to wildtype as well as abnormal development of the corpus callosum. These abnormalities are attributed to reduced cell proliferation and closely resembled the pathological phenotype of corpus callosum agenesis as seen in humans. Brain tissue samples from Akt3 deficient mice displayed reduced levels of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) activation. Furthermore, the mouse Nmf350 mutation phenotype was attributed to a D219 substitution mutation in the kinase catalytic domain of the Akt3 gene. Enzymatic analysis of the mutant kinase in HEK293 cells revealed significantly increased kinase catalytic activity as compared to wildtype protein. The Nmf350 mouse model, characterized by low seizure threshold, brain enlargement, and ectopic neuronal development in the dentate hilus and molecular layer of the hippocampus, was identified from a phenotype-driven mutagenesis screen and is used as a model for neurological disorders. This demonstration further supports a role for abnormal Akt3 activity as a contributor in the pathology of neurological development disorders, such as MPPH.
Specific Cancer Types:
Thymoma
Comments:
AKT3 appears to be an oncoprotein (OP) based on its similarity to Akt1 and Akt2, although it does not display a higher than normal rate of mutation in human tumours. The active form of the protein kinase normally acts to promote tumour cell proliferation. AKT3 has been implicated as a key modulator in several human cancer types, including melanomas, gliomas, ovarian cancer, and breast cancer. AKT3 promotes cancer progression through a gain-of-function in the apoptosis suppressive activity of the enzyme, leading to aberrant cell growth. Expression levels of AKT3 have been shown to increase throughout the course of melanoma tumor progression, peaking in advanced-stage metastatic melanomas. Mutations in the AKT3 gene have been observed in several melanoma cell lines, including an activating E17K substitution mutation similar to that seen in the AKT1 gene in human colorectal cancers. However, the E17K mutation is relatively rare in AKT3 in human tumours. Moreover, like AKT2, there are no predominent mutations in AKT3 in human cancers, with a relatively dispersed pattern of low level mutations through out the full length of the protein. AKT3 is also known to play a pivotal role in the development of ovarian cancer through its role in the regulation of the G2/M phase transition of the cell cycle. Along with AKT2, AKT3 is also important in the formation and progression of glioblastomas. In addition, a fusion gene involving AKT3 has been identified in breast cancer tissue samples. The MAGI3/AKT3 fusion gene was recurrently identified in triple-negative breast cancer specimens, which lack estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, and ERBB2 expression. The fusion gene results in constitutive activation of the AKT3, and suppresses apoptosis and stimulates aberrant cell growth and enhanced survival.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Bladder carcinomas (%CFC= -46, p<0.052); Colorectal adenocarcinomas (early onset) (%CFC= +136, p<0.001); Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) (%CFC= +175, p<0.005); Ovary adenocarcinomas (%CFC= -64, p<0.0007); Skin melanomas - malignant (%CFC= +64, p<0.002); The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for AKT3 in diverse human cancers of 612, which is 1.3-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 16 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 0.3-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice support a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.09 % in 26137 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only 24 % higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.4 % in 1241 large intestine cancers tested; 0.39 % in 648 endometrium cancers tested; 0.35 % in 589 stomach cancers tested; 0.28 % in 910 skin cancers tested; 0.23 % in 1941 lung cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
None >3 in 21235 cancer specimens
Comments:
Only 1 deletion, and no insertions or complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

