Nomenclature
Short Name:
BRAF
Full Name:
B-Raf proto-oncogene serine-threonine-protein kinase
Alias:
- B-RAF
- P94
- RAFB1
- RMIL
- RMIL serine/threonine-protein kinase
- V-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1
- B-RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase
- BRAF1
- C-RMIL
- Kinase B-Raf
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
TKL
Family:
RAF
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
84,437
# Amino Acids:
766
# mRNA Isoforms:
1
mRNA Isoforms:
84,437 Da (766 AA; P15056)
4D Structure:
Interacts with RIT1
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
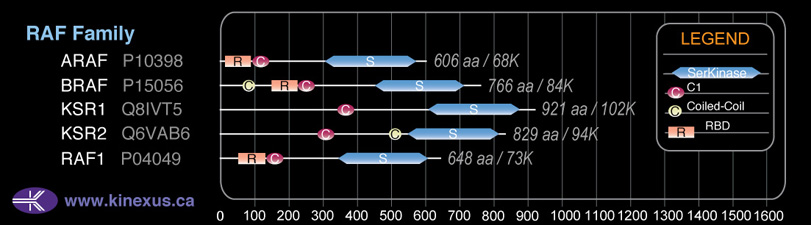
Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 82 | 102 | Coiled-coil |
| 155 | 227 | RBD |
| 235 | 283 | C1 |
| 457 | 717 | Pkinase |
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
A2, K253, K418.
Other:
K578 (Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in ubiquitin));R671 (Omega-N-methylarginine).
Serine phosphorylated:
S147, S151, S319, S333, S335, S363, S364, S365-, S394, S399, S405, S419, S428, S429-, S430, S432, S446+, S447, S465-, S467-, S579+, S602+, S605+, S607+, S614+, S729+, S732, S750.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T119, T244, T373, T396, T401-, T440-, T470, T599+, T753-.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y85, Y566, Y746, Y760.
Ubiquitinated:
K578, K601, K687.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 100
100
1465
9
1121
 0.8
0.8
11
4
9
 17
17
245
14
178
 19
19
282
46
541
 41
41
604
13
542
 11
11
165
16
179
 1.1
1.1
16
13
8
 20
20
291
22
668
 0.7
0.7
10
3
3
 4
4
53
29
28
 8
8
118
19
132
 22
22
328
36
438
 15
15
217
14
154
 1
1
15
3
3
 14
14
200
19
221
 2
2
24
5
5
 61
61
899
26
2623
 12
12
169
17
160
 8
8
120
35
89
 57
57
834
31
567
 10
10
141
19
134
 14
14
209
19
202
 18
18
258
14
188
 42
42
620
17
467
 11
11
156
19
185
 30
30
433
36
493
 14
14
209
17
171
 11
11
160
17
142
 14
14
205
17
171
 7
7
100
14
47
 49
49
724
12
76
 2
2
36
11
42
 3
3
49
51
100
 49
49
717
26
614
 40
40
591
22
578
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 99.3
99.3
99.3
100 -
-
-
97 -
-
-
99 -
-
-
99 93
93
93.5
99 -
-
-
- 88.8
88.8
89.3
97 50.3
50.3
62.3
97 -
-
-
- 85.7
85.7
86.7
- 89.8
89.8
90.9
95 49.4
49.4
61.4
89 83.5
83.5
87.5
88 82.9
82.9
87.2
- 42.8
42.8
57.9
49 50.6
50.6
65
- 30.8
30.8
46.6
51 49.4
49.4
62.7
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
42 24
24
41.5
33 -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | HRAS - P01112 |
| 2 | MAP2K1 - Q02750 |
| 3 | YWHAB - P31946 |
| 4 | RAP1GAP - P47736 |
| 5 | RAF1 - P04049 |
| 6 | RAP1A - P62834 |
| 7 | AKT1 - P31749 |
| 8 | YWHAZ - P63104 |
| 9 | MAP2K2 - P36507 |
| 10 | YWHAQ - P27348 |
| 11 | YWHAH - Q04917 |
| 12 | MRAS - O14807 |
| 13 | PRKACA - P17612 |
| 14 | MAPK1 - P28482 |
| 15 | SGK1 - O00141 |
Regulation
Activation:
Phosphorylation of Ser-446 increases phosphotransferase activity and induces interaction with H-Ras-1. Phosphorylation of Ser-579, Thr-599, Ser-602, increases phosphotransferase activity. Phosphorylation of Ser-729 increases phosphotransferase activity and induces interaction with 14-3-3 beta.
Inhibition:
Phosphorylation of Ser-365, Ser-429, and Thr-440 inhibits phosphotransferase activity. Phosphorylation of Thr-753 inhibits interaction with Raf1.
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| SGK | O00141 | S365 | GQRDRSSSAPNVHIN | - |
| Akt1 | P31749 | S365 | GQRDRSSSAPNVHIN | - |
| BRAF | P15056 | T373 | APNVHINTIEPVNID | |
| PKACa | P17612 | S429 | PQRERKSSSSSEDRN | - |
| Akt1 | P31749 | S429 | PQRERKSSSSSEDRN | - |
| PKACa | P17612 | S446 | KTLGRRDSSDDWEIP | + |
| PAK1 | Q13153 | S446 | KTLGRRDSSDDWEIP | + |
| ERK1 | P27361 | T753 | YACASPKTPIQAGGY | - |
| ERK2 | P28482 | T753 | YACASPKTPIQAGGY | - |
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| B-Raf | P15056 | T373 | APNVHINTIEPVNID | |
| MEK1 (MAP2K1) | Q02750 | S218 | VSGQLIDSMANSFVG | + |
| MEK1 (MAP2K1) | Q02750 | S222 | LIDSMANSFVGTRSY | + |
| MEK2 (MAP2K2) | P36507 | S222 | VSGQLIDSMANSFVG | + |
| MEK2 (MAP2K2) | P36507 | S226 | LIDSMANSFVGTRSY | + |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
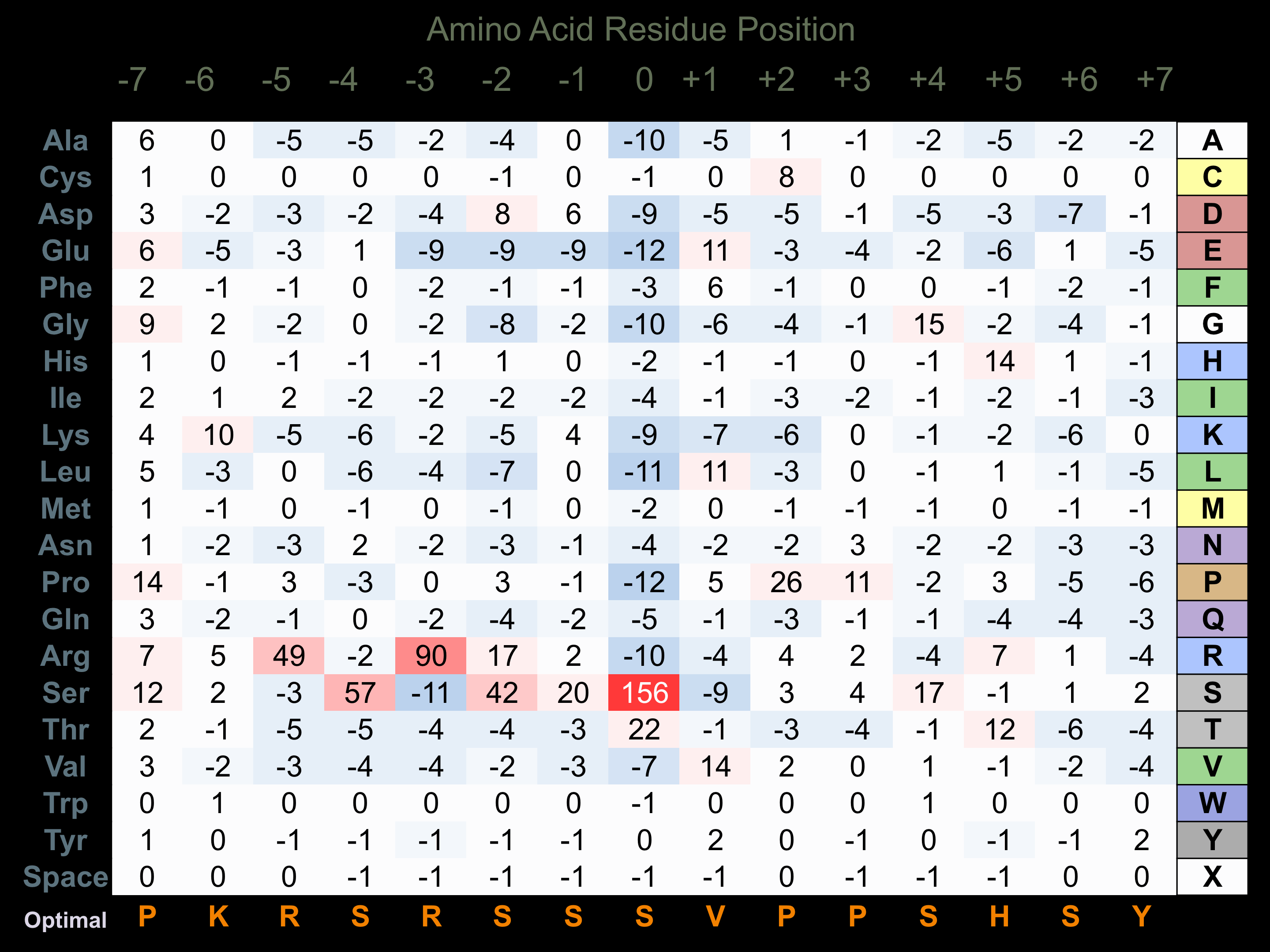
Matrix Type:
Predicted from the application of the Kinexus Kinase Substrate Predictor Version 2.0 algorithm, which was trained with over 10,000 kinase-protein substrate pairs and 8,000 kinase-peptide substrate pairs.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, developmental disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
B-Raf-related Noonan syndrome; B-Raf-related Leopard syndrome; B-Raf-related cardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome; Cardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome; Leopard syndrome; Noonan syndrome; Leopard syndrome 3; Noonan syndrome 7; Spitz nevus; Erdheim-Chester disease; Struma ovarii; Hyperplastic polyposis syndrome; Atypical mole syndrome; Nephrotic syndrome Type 3; Pulmonic stenosis; Noonan syndrome 1; Leopard syndrome 1; Hashimoto-Pritzker syndrome; Thyroiditis
Comments:
Mutations at many sites in B-Raf are associated with cardio-facio-cutaneous (CFC) syndrome 1, which is a multiple congenital disorder characterized by a distinctive facial appearance, heart defects, and mental retardation. B-Raf-related CFC syndrome often includes developmental delay, and intellectual disability. This multiple congenital disorder can affect the face, skin, heart, and testes tissues. Mutations in B-Raf have been reported in patients with CFC syndrome, including 11 distinct missense mutations localized in two main cluster regions. A Q257R substitution mutation was observed in the cysteine-rich domain of the conserved region 1 (CR1) of the B-Raf gene. The other mutational cluster was localized in the protein kinase domain of the protein, including exons 11, 12, 14, and 15 of the coding sequence. These mutations included various substitution mutations (A246P, Q257R, G469E, L485F, K499E, E501K, E501G, N581D, G534R, D638E, and T241P). No frameshift, nonsense, or splice-site mutations were observed in the patients. In vitro analysis of the T241P mutant B-Raf protein revealed absence of transforming ability of the kinase and an increased MEK phosphorylation, supporting an activation of MAPK signalling. Several mutations in B-Raf have also been found in patients with Noonan syndrome, which is a disease with typical short stature, facial dysmorphic features (e.g. webbed neck, flat nose bridge), and a high incidence of congenital heart defects, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and impaired blood clotting ability. Similar to CFC syndrome, these mutations clustered in the cysteine-rich domain and in the kinase catalytic domain. B-Raf mutations associated with Noonan syndrome also include several substitution mutations (T241M, T241R, T241P, W531C, and L597V). In vitro enzymatic analysis of the mutated proteins associated with Noonan syndrome revealed increased kinase catalytic activity, but significantly less than V600E mutated proteins found in B-Raf mutated cancers and even less than the mutated proteins associated with CFC syndrome. Additionally, the Noonan syndrome associated mutated proteins did not display any tranforming ability. Interestingly, there was no observed overlap between B-Raf mutations linked to cancer and those associated with CFC syndrome or Noonan syndrome. T241P substitution is linked to Leopard syndrome 3. The typical symptoms of this rare, inherited disease are lentigines, electrocardiographic conduction abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonic stenosis, abnormalities of genitalia, retardation of growth, and sensorineural deafness from abnormal formation of the inner ear. Spitz Nevus is a non-cancerous skin lesion affecting skin, lymph node, and tongue. Erdheim-Chester Disease is a rare disease characterized by over-production and accumulation of histiocytes and it will affect bone, lung, and skin tissue. Pulmonic stenosis is the blockage of blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary aorta. Pulmonic stenosis links to congenital heart disease, and pulmonary valve stenosis and it affects heart, liver, and lung tissues. Hashimoto-Pritzker Syndrome is associated with Langerhans-cell histiocytosis and histiocytoma, and affiliated tissue includes bone, liver, and bone marrow.
Specific Cancer Types:
B-Raf-related Noonan syndrome; B-Raf-related Leopard syndrome; B-Raf-related cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome; Colorectal cancer (CRC); Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome; Adenocarcinomas; Non-Hodgkin lymphomas; Lung cancer (LC); Thyroid cancer; Sarcomas; Pilocytic astrocytoma; Non-small cell lung carcinomas; Colorectal cancer, somatic; lymphomas, non-Hodgkin, somatic; Colon cancer, somatic; Colonic adenoma recurrence, Reduced risk of; Colon cancer; Papillary thyroid carcinomas; Cystadenomas; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), somatic; Adenocarcinomas of lung, Somatic; Hairy cell leukemias; Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas; Metanephric adenomas; Familial melanomas; Struma ovarii; Glomus tumours; Perineurioma; melanomas of soft parts; Hyperplastic polyposis syndrome; Atypical mole syndrome; Mature B-cell neoplasm; Craniopharyngioma; Posterior uveal melanomas; Intestinal neoplasms; Villous adenomas; Lung adenomas; Lung cancer (LC), somatic; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); Adenocarcinomas of lung, familial non-Hodgkin lymphomas; Thyroiditis; melanomas
Comments:
B-RAF is a known oncoprotein (OP). Cancer-related mutations in human tumours point to a gain of function of the protein kinase. The active form of the protein kinase normally acts to promote tumour cell proliferation. Gain-of-function mutations in B-Raf are estimated to be present in ~15-19% of all human cancers, and 66% of malignant melanomas have been identified with a B-Raf somatic missense mutation. B-Raf and K-Ras mutations are functionally similar and mutually exclusive in cancers. A single point mutation (V600E), located in the kinase catalytic domain in the activation loop between Subdomains VII and VIII. It has been reported to account for ~80% of the B-Raf mutations in human cancers. Mutated B-Raf proteins display constitutive elevated levels of phosphotransferase activity, resulting in the aberrant promotion of cell division, differentiation, and cytokine secretion. In addition, mutant B-Raf proteins with the V600E mutation do not require RAS function for the growth of the cancer cells, revealing a gain-of-function mechanism resulting in aberrant B-Raf activity. Suppression of this mutation in melanoma causes growth arrest and promotes apoptosis. Mutations in the B-Raf gene were identified in 43 cell lines of various human cancer types including melanoma (59%), colorectal cancer (18%), glioma (11%), lung cancer (3%), sarcoma (9%), ovarian carcinoma (4%), breast cancer (2%), and liver cancer (14%). In contrast, B-Raf mutations were not observed in cancer cell lines of neuroblastomas, bladder cancer, leukemia/lymphomas, cervical carcinomas, renal cell carcinomas, pancreatic carcinomas, prostate carcinomas, gastric carcinomas, testicular carcinomas, uterine carcinomas, or 29 other cancer types. In addition to substitution mutations, B-Raf can obtain oncogenic activity through the creation of fusion proteins. For example, the paracentic inversion of chromosome 7q results in the fusion between exons 1-8 of the AKAP9 gene and exons 9-18 of the B-Raf gene. This fusion protein contains the B-Raf kinase catalytic domain, but lacks the auto-inhibitory domain found at the N-terminus of the wild-type B-Raf protein. Therefore the fusion protein has elevated kinase activity leading to constitutive stimulation of downstream MAPK signalling and transforming abilities in certain cell types (e. g. NIH-3T3 cells). This chromosomal inversion mutation is hypothesized to result primarily from radiation and be a major causal factor of thyroid cancers. Due to the wide-spread occurrence of activating B-Raf mutations in numerous human cancer types, B-Raf represents a major target for novel cancer therapeutics. In animal studies, mice with the V600E mutant B-Raf protein developed benign melanocyte hyperplasia, which did not progress to melanoma. However when this mutation was combined with PTEN knockout (a known tumour suppressor) the mice developed melanoma with metastases reported in the lymph nodes and lungs, which indicates a requirement in certain cell types for combinatorial cancer-promoting mutations and the insufficiency of B-Raf mutations for cancer development. Non-Hodgkin lymphomas are a cancer beginning in the lymphatic system, and will arise from B- or T- cells. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma spreads in an unpredictable way (separating it from Hodgkin Lymphoma), has at least 30 forms of cancer, and has an important protein, perforin 1 (PRF1), associated with it. Pilocytic Astrocytoma is typically a benign, slow-growing tumour of the brain or spinal cord, and the cause is unknown. Cystadenoma will affect the pancreas, appendix, and ovaries. Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma will affect the brain, spinal cord, and parietal lobe, and is related to ganglioma and giant cell glioblastoma. Struma Ovarii has a role in thyroiditis and hyperthyroidism, and affects thyroid, ovary, and liver tissue. Perineurioma affects colon, tongue, and kidney and has similarities to granular cell tumour, and neurofibromatosis. Hyperplastic Polyposis Syndrome is associated with colorectal and colon cancer. Atypical Mole Syndrome is associated with melanoma and intraocular melanoma. Craniopharyngioma is a rare disease that manifests as a slow-growing benign tumour with a link to obesity, and pituitary adenoma. It affects the pituitary gland, brain, and hypothalamus.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in human Brain oligodendrogliomas (%CFC= +193, p<0.015). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for B-RAF in diverse human cancers of 572, which is 1.2-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 20 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 0.3-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice support a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 2.51 % in 216332 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is 33.5-fold higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 5.39 % in 47062 thyroid cancers tested; 5.39 % in 19812 skin cancers tested; 2.33 % in 320 pituitary cancers tested; 1.64 % in 74924 large intestine cancers tested; 1.33 % in 8297 haematopoietic and lymphoid cancers tested; 1.04 % in 6049 central nervous system cancers tested; 1.01 % in 696 bone cancers tested; 0.92 % in 4487 ovary cancers tested; 0.72 % in 959 biliary tract cancers tested; 0.29 % in 14611 lung cancers tested; 0.29 % in 1076 urinary tract cancers tested; 0.27 % in 1790 kidney cancers tested; 0.24 % in 2681 soft tissue cancers tested; 0.19 % in 2036 pancreas cancers tested; 0.19 % in 1858 prostate cancers tested; 0.19 % in 1755 liver cancers tested; 0.18 % in 2908 endometrium cancers tested; 0.16 % in 3767 breast cancers tested; 0.15 % in 2626 stomach cancers tested; 0.13 % in 2543 upper aerodigestive tract cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: V600E (38,621); V600K (685).
Comments:
In human tumours, the mutations are primaily around amino acid residue V600, which includes point mutations, complex mutations, insertions and deletions.

