Nomenclature
Short Name:
KDR
Full Name:
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2
Alias:
- A type III receptor tyrosine kinase
- CD309
- Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2
- VEGFR
- VEGFR2
- VGR2
- EC 2.7.10.1
- FLK1
- Kinase insert domain receptor
- Protein-tyrosine kinase receptor Flk-1
Classification
Type:
Protein-tyrosine kinase
Group:
TK
Family:
VEGFR
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
151,527
# Amino Acids:
1356
# mRNA Isoforms:
3
mRNA Isoforms:
151,527 Da (1356 AA; P35968); 79,634 Da (712 AA; P35968-3); 75,896 Da (678 AA; P35968-2)
4D Structure:
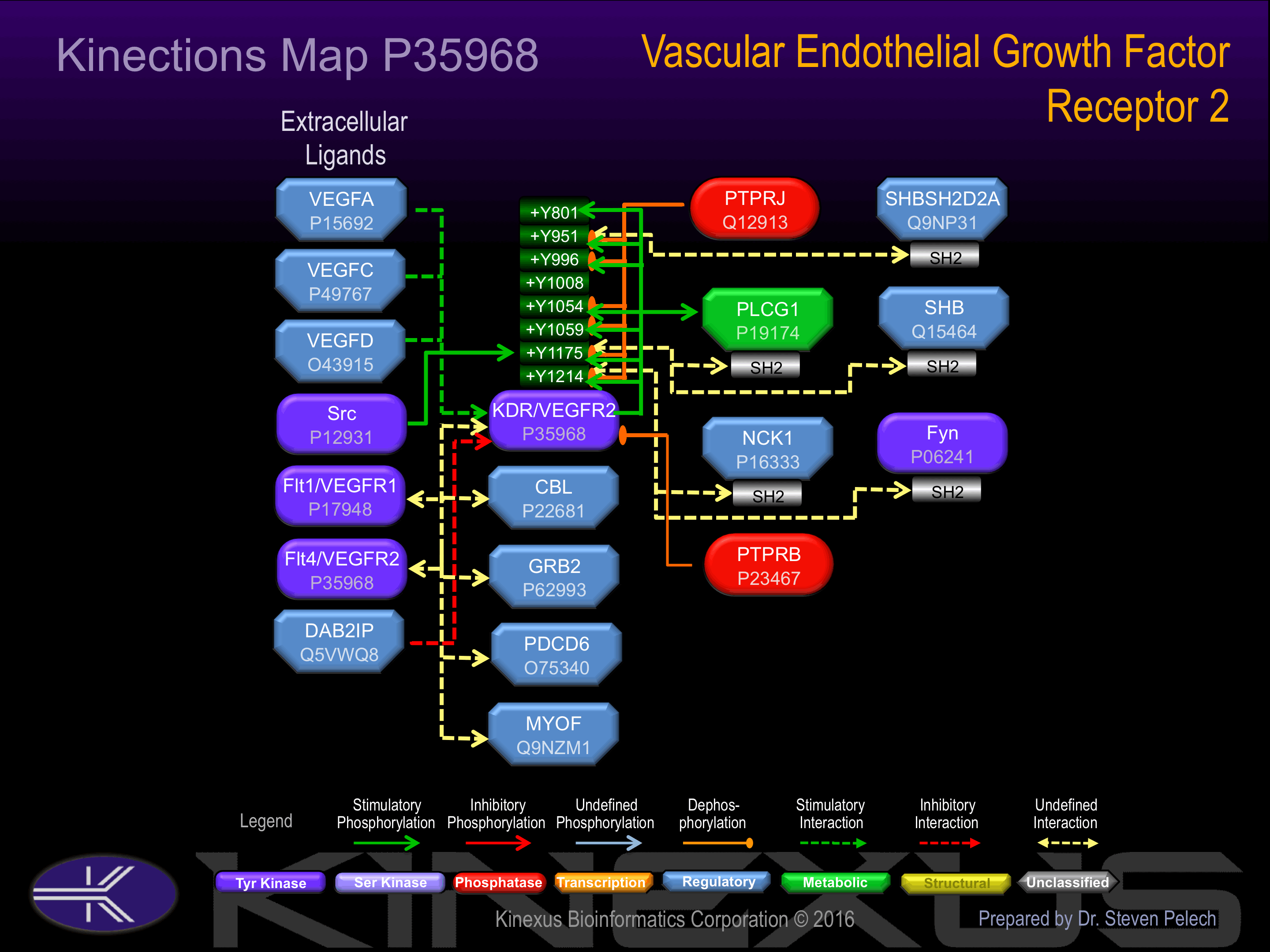
Interacts with MYOF By similarity. Interacts with SHB; upon VEGF activation. Interacts with HIV-1 Tat
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
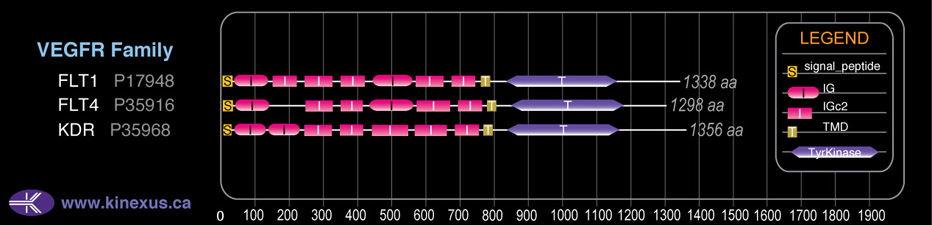
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K960.
N-GlcNAcylated:
N46, N66, N96, N143, N158, N245, N318, N374, N395, N511, N523, N580, N613, N619, N631, N675, N704, N721.
Serine phosphorylated:
S711, S982, S984, S1235, S1279, S1281, S1288, S1290.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T1217, T1238.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y801+, Y951+, Y996+, Y1008+, Y1054+, Y1059+, Y1175+, Y1214+, Y1223.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 90
90
824
16
889
 11
11
100
12
48
 13
13
122
29
143
 100
100
911
84
1984
 75
75
687
14
677
 7
7
63
42
144
 41
41
369
23
472
 44
44
401
61
1114
 36
36
332
10
293
 13
13
117
87
133
 8
8
69
46
67
 56
56
512
156
613
 12
12
112
40
136
 5
5
43
12
19
 11
11
100
43
154
 13
13
115
9
43
 6
6
51
216
91
 9
9
78
38
99
 7
7
64
77
60
 62
62
568
56
597
 13
13
117
42
147
 10
10
88
44
129
 13
13
114
38
165
 7
7
66
38
225
 8
8
75
42
167
 49
49
450
66
600
 7
7
61
43
105
 11
11
103
38
132
 32
32
292
38
402
 10
10
89
14
55
 54
54
496
18
358
 46
46
418
21
457
 18
18
168
44
470
 64
64
581
31
604
 11
11
96
22
95
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 92.3
92.3
92.3
100 91.5
91.5
92.1
98.5 -
-
-
91 -
-
-
97 43.2
43.2
59.6
93 -
-
-
- 84.8
84.8
90.3
87 85.7
85.7
91.7
86 -
-
-
- 58.6
58.6
65.2
- 44.3
44.3
60.2
74 25.8
25.8
41.7
63 50.1
50.1
65.4
53 27.9
27.9
43.3
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Regulation
Activation:
Activated by binding vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which induces dimerization and autophosphorylation. Autophosphorylation of Tyr-801increases phosphotransferase activity and induces interaction with PIK3R1. Autophosphorylation of Tyr-951 and Tyr-1008 induces interaction with PLCg1. Autophosphorylation of Tyr-1054, Tyr-996 and Tyr-1059 increases phosphotransferase activity and induces interaction with PLCg1. Autophosphorylation of Tyr-1175 increases phosphotransferase activity and induces interaction with PLCg1, Shb, Shc1 and Shc2.
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| PFN1 | P07737 | Y129 | GLINkkCYEMASHLR | |
| KDR (VEGFR2) | P35968 | Y1054 | FGLARDIYKDPDYVR | + |
| KDR (VEGFR2) | P35968 | Y1059 | DIYKDPDYVRKGDAR | + |
| KDR (VEGFR2) | P35968 | Y1175 | AQQDGKDYIVLPISE | + |
| KDR (VEGFR2) | P35968 | Y1214 | VCDPKFHYDNTAGIS | + |
| KDR (VEGFR2) | P35968 | Y951 | RFRQGKDYVGAIPVD | + |
| KDR (VEGFR2) | P35968 | Y996 | EEAPEDLYKDFLTLE | + |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
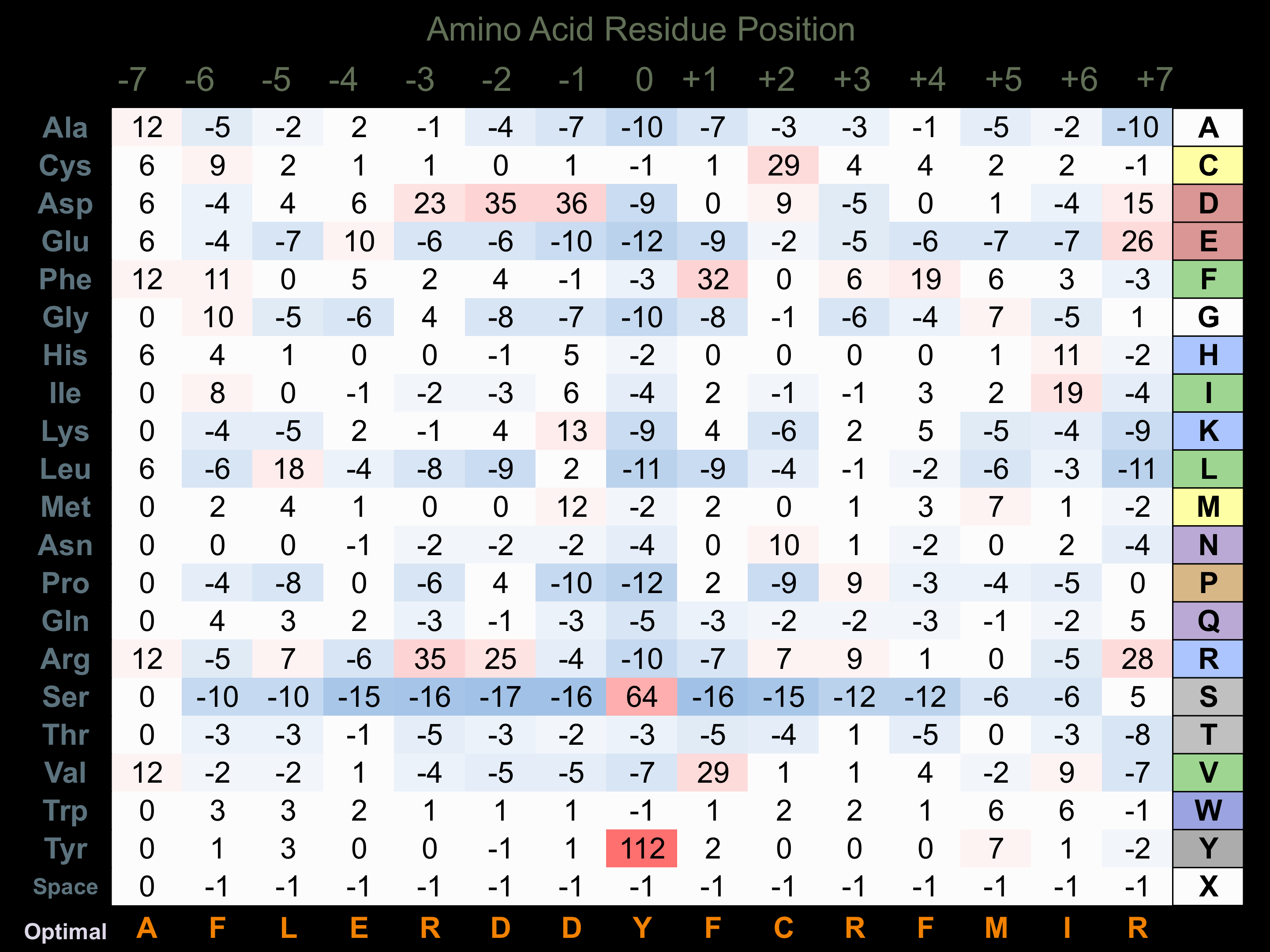
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 13 known protein substrate phosphosites and 37 peptides phosphorylated by recombinant KDR in vitro tested in-house by Kinexus.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, immune disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Bursitis; Leukostasis; Olecranon bursitis; Endotheliitis
Comments:
Bursitis is characterized by the inflammation of a bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that functions as a cushion between moving parts of the body (e.g. muscles, bones, tendons). Leukostasis is a condition characterized by a white blood cell count in the blood stream in excess of 100,000 cells/uL of fluid. This condition is often observed in leukemia patients and typically involves abnormal intravascular leukocyte aggregation. Occluded blood vessels cause local hypoxemia and hemorrhage, mainly affecting the brain and lungs. In addition, KDR mediates the activation of the MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1, and the MAP kinase intracellular signalling pathways. Leukostasis is often seen as a manifestation of diabetic retinopathy, along with leukocyte adhesion, hyperpermeability and retinal neovascularization. In a mouse model of diabetes, retinal tissue samples displayed increased vascular permeability, leukocye adhesion, and blood vessel formation correlated with increased levels of phosphorylated KDR protein. In addition, VEGF signalling, as it promotes angiogenesis, plays an important role in the inflammation of synovial joints. For example, VEGF expression was observed in the subacromial bursa in 39 out of 41 patients with motion pain due to rotator cuff disease (including a subset with subacromial bursitis) compared to only 1 out of 9 with no motion pain. Additionally, 31 out of 33 patients with synovial proliferation showed VEGF mRNA expression in tissue samples correlated with higher blood vessel counts and VEGF+ subacromial bursa area, indicating a role for VEGF signalling (and possibly KDR expression) in the pathogenic inflammation of the subacromial bursa (i.e. bursitis).
Specific Cancer Types:
Hemangiomas; Hemangioma, capillary infantile; Angiosarcomas; Colorectal cancer; Kaposi's sarcomas; Fibrosarcomas of bone; Thyroid cancer; Oligodendrogliomas; Renal cell carcinomas; Epithelioid hemangioendotheliomas; Capillary hemangiomas; Adenosquamous carcinomas; Thoracic cancer; Cervical adenosquamous carcinomas; Hemangioma, capillary infantile, somatic; Gastrointestinal stromal tumours
Comments:
KDR appears to be an oncoprotein (OP). Capillary hemangioma is the most common tumour type found in infants, being observed in ~10 % of births. The enlargement of these tumours is due to the hyperplasia of vascular endothelial cells and associated pericytes and is thought to be caused by a mutation in the vascular growth-regulatory mechanisms. Mutations in the KDR gene have been observed in patients with hemangioma, including a missense mutation in the kinase catalytic domain (P1147S) and a substitution mutation (C482R) in the extracellular domain of the KDR protein. The C482R mutant KDR protein displayed increased kinase catalytic activity in vitro as compared to the control protein, indicating a role for the oncogenic activity of KDR in tumorigenesis. In addition, KDR functions as an inhibitor of neovascularization as it disrupts vascular smooth muscle cell function. During PDGF-mediated angiogenesis, activation of KDR by VEGF inhibits PDGFRB activation in vascular smooth muscle cells through the formation of a dimer between KDR and PDGFRB. Therefore, inhibition of KDR allows for angiogenesis in response to both VEGF and PDGF. This has implications for cancer, as the deletion of VEGF in tumour cells increases angiogenesis and blood vessel maturation, a critical step in tumorigenesis. Significantly higher KDR expression was observed in metastatic as compared to non-metastatic human colon cancer cell lines, and higher expression was directly correlated with increased neovascularization and tumour cell proliferation. In addition, KDR expression was correlated with blood vessel count in human intestinal-type gastric cancer specimens. Elevated KDR expression has also been reported in tumour cells in primary and metastatic ovarian carcinoma. Furthermore, various animal studies have confirmed the importance of VEGF signalling in cancer progression. For example, VEGF signalling is vital to the early stages of tumour progression in mouse models of squamous skin tumours. In addition, inhibition of KDR resulted in tumour regression through decreased microvasculature and impaired ability to maintain the stem-like characteristic of the tumour cells. Whereas, over-expression of VEGFA accelerated the growth of tumour epithelial cells by promoting the stem-like characteristic, causing elevated cellular proliferation and renewal. Deletion of the VEGF co-receptor neuropilin-1 (Nrp1) in cancer cells compromised their stem-like characteristic.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Bladder carcinomas (%CFC= +97, p<0.065); Brain glioblastomas (%CFC= -57, p<0.0004); Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (cRCC) (%CFC= +171, p<0.022); Lung adenocarcinomas (%CFC= -61, p<0.0001); Malignant pleural mesotheliomas (MPM) tumours (%CFC= +82, p<0.064); Ovary adenocarcinomas (%CFC= -72, p<0.0002); Skin melanomas (%CFC= -61, p<0.067); Skin melanomas - malignant (%CFC= -68, p<0.003); and Uterine leiomyomas from fibroids (%CFC= -61, p<0.017). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for KDR in diverse human cancers of 348, which is 0.8-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 0 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 100% lower than the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.15 % in 26488 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is 2-fold higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.59 % in 1155 large intestine cancers tested; 0.34 % in 1964 lung cancers tested; 0.2 % in 603 endometrium cancers tested; 0.13 % in 607 oesophagus cancers tested; 0.13 % in 1336 liver cancers tested; 0.09 % in 917 ovary cancers tested; 0.09 % in 1963 central nervous system cancers tested; 0.09 % in 1319 kidney cancers tested; 0.07 % in 2037 haematopoietic and lymphoid cancers tested; 0.05 % in 1597 breast cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: Q472H (12); V297I (10).
Comments:
Only 5 deletions, 3 insertions and no complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.