Nomenclature
Short Name:
JNK3
Full Name:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 10
Alias:
- C-Jun N-terminal kinase 3
- EC 2.7.11.24
- MAPK10
- MK10
- P493F12
- FLJ12099; FLJ33785; P493F12; PRKM10; p54bSAPK; Stress-activated protein kinase JNK3
- JNK3A
- JNK3-alpha-2
- Kinase JNK3
- MAP kinase p49 3F12
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
CMGC
Family:
MAPK
SubFamily:
JNK
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
52,585
# Amino Acids:
464
# mRNA Isoforms:
4
mRNA Isoforms:
52,585 Da (464 AA; P53779); 48,554 Da (422 AA; P53779-2); 48,128 Da (426 AA; P53779-3); 31,933 Da (277 AA; P53779-4)
4D Structure:
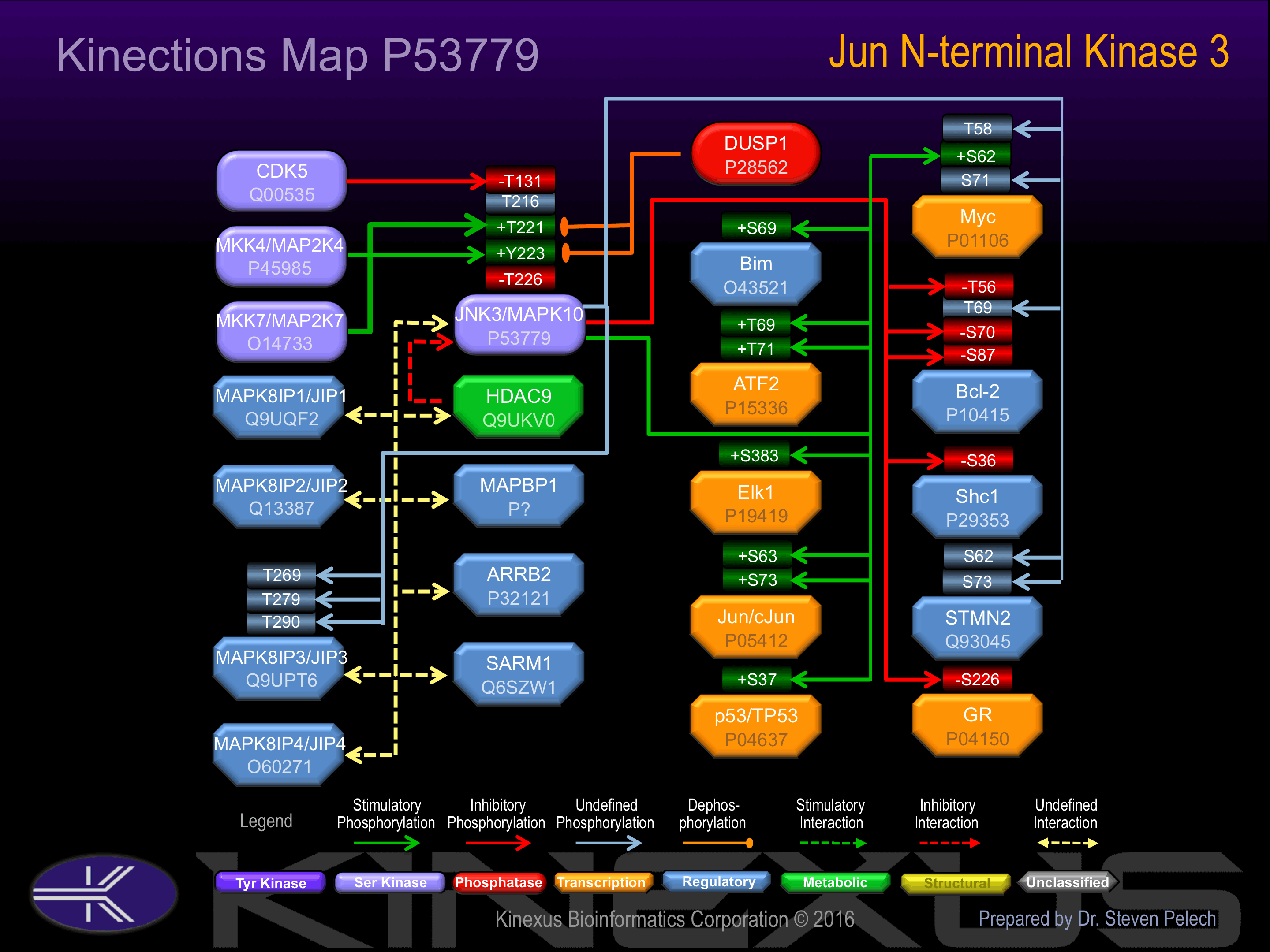
Interacts with MAPKBP1 By similarity. Binds to at least four scaffolding proteins, MAPK8IP1/JIP-1, MAPK8IP2/JIP-2, MAPK8IP3/JIP-3/JSAP1 and SPAG9/MAPK8IP4/JIP-4. These proteins also bind other components of the JNK signaling pathway. Interacts with HDAC9. Interacts with ARRB2; the interaction enhances MAPK10 activation by MAP3K5.
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 64 | 359 | Pkinase |
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Palmitoylated:
C462, C463.
Serine phosphorylated:
S193, S217-, S330, S417.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T131-, T216+, T221+, T226-, T281.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y223+.
Ubiquitinated:
K204.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 97
97
1071
22
811
 10
10
115
13
84
 19
19
212
6
201
 56
56
616
90
614
 47
47
521
23
432
 7
7
83
52
120
 25
25
282
33
455
 26
26
283
35
476
 18
18
204
10
151
 16
16
172
92
174
 6
6
71
24
83
 45
45
502
143
652
 8
8
92
17
50
 9
9
102
11
69
 6
6
63
23
78
 13
13
142
14
116
 9
9
105
338
102
 8
8
91
12
114
 7
7
73
72
76
 31
31
349
84
311
 33
33
371
23
411
 8
8
93
23
98
 9
9
95
15
121
 25
25
282
15
570
 6
6
67
23
92
 46
46
514
59
632
 8
8
86
20
63
 11
11
122
15
131
 29
29
322
15
421
 15
15
165
28
143
 42
42
461
42
186
 100
100
1108
26
2127
 19
19
208
83
442
 63
63
697
57
663
 13
13
146
62
214
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 39
39
52.6
100 90.1
90.1
91.2
100 -
-
-
100 -
-
-
- 99.8
99.8
99.8
98 -
-
-
- 98.7
98.7
98.9
100 98.7
98.7
98.9
99 -
-
-
- 72.3
72.3
75.5
- 70.5
70.5
76.5
98 79.7
79.7
84.9
98 70.3
70.3
77.2
95.5 -
-
-
- 62.7
62.7
70.9
78 -
-
-
- 59
59
70.9
70 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 35.3
35.3
55.2
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | MAPK8IP3 - Q9UPT6 |
| 2 | CDK5 - Q00535 |
| 3 | STMN2 - Q93045 |
| 4 | MAP2K4 - P45985 |
| 5 | SH3BP5 - O60239 |
| 6 | TP53 - P04637 |
| 7 | MAPKBP1 - O60336 |
| 8 | DUSP16 - Q9BY84 |
| 9 | DUSP1 - P28562 |
| 10 | PLIN2 - Q99541 |
Regulation
Activation:
Phosphorylation at Thr-221 and Tyr-223, by MAP2K4 and MAP2K7. MAP2K7, increases phosphotransferase activity. MAP2K7 phosphorylates JNK3 on Thr-221 causing a conformational change and a large increase in Vmax. MAP2K4 then phosphorylates Tyr-223 resulting in a further increase in Vmax.
Inhibition:
Phosphorylation at Thr-131 inhibits phosphotransferase activity. Inhibited by dual specificity phosphatases, such as DUSP1. Inhibited by HDAC9.
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| APLP2 | Q06481 | T736 | VEVDPMLTPEERHLN | |
| APP | P05067 | T743 | VEVDAAVTPEERHLS | |
| ATF2 | P15336 | T69 | SVIVADQTPTPTRFL | + |
| ATF2 | P15336 | T71 | IVADQTPTPTRFLKN | + |
| Bcl-2 | P10415 | S70 | RDPVARTSPLQTPAA | |
| Bcl-2 | P10415 | S87 | AAAGPALSPVPPVVH | + |
| Bcl-2 | P10415 | T56 | FSSQPGHTPHPAASR | + |
| Bcl-2 | P10415 | T74 | ARTSPLQTPAAPGAA | |
| Bim | O43521 | S69 | GPLAPPASPGPFATR | |
| DRPLA | P54259 | S734 | EEYETPESPVPPARS | |
| Elk-1 | P19419 | S383 | IHFWSTLSPIAPRSP | + |
| GR | P04150 | S226 | IDENCLLSPLAGEDD | - |
| JIP3 | Q9UPT6 | T269 | GQSSAAATPSTTGTK | |
| JIP3 | Q9UPT6 | T279 | TTGTKSNTPTSSVPS | |
| JIP3 | Q9UPT6 | T290 | SVPSAAVTPLNESLQ | |
| Jun (c-Jun) | P05412 | S63 | KNSDLLTSPDVGLLK | + |
| Jun (c-Jun) | P05412 | S73 | VGLLKLASPELERLI | + |
| MCL1 | Q07820 | S121 | PAADAIMSPEEELDG | |
| MCL1 | Q07820 | T163 | TDGSLPSTPPPAEEE | |
| Myc | P01106 | S62 | LLPTPPLSPSRRSGL | |
| Myc | P01106 | S71 | SRRSGLCSPSYVAVT | |
| Myc | P01106 | T58 | KKFELLPTPPLSPSR | |
| NFAT2 | O95644 | S172 | YRDPSCLSPASSLSS | |
| p53 | P04637 | S37 | NVLSPLPSQAMDDLM | + |
| Shc1 | P29353 | S36 | TPPEELPSPSASSLG | - |
| STMN2 | Q93045 | S62 | ELILKPPSPISEAPR | |
| STMN2 | Q93045 | S73 | EAPRTLASPKKKDLS |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
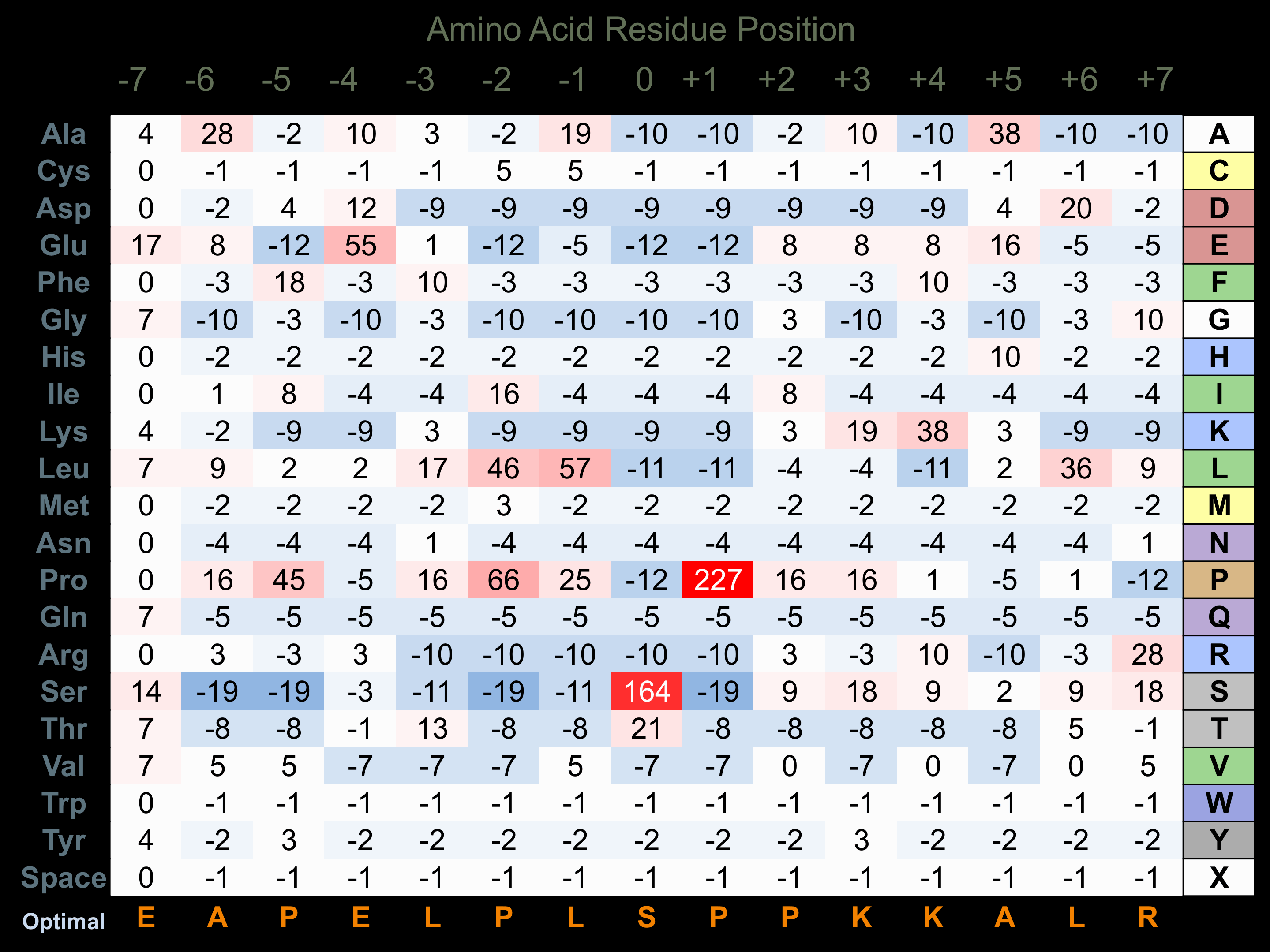
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 22 known protein substrate phosphosites. Note that additional binding sites on JNK substrates with D motifs (consensus=R-P-t-s/r/t-L-p-L or K/r-x-s-L-s-L/i/v-s-l/p) facilitate higher selectivity for phosphorylation by this protein kinase.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Neurological disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Coffin-Lowry syndrome; Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis; Anhidrosis; Lennox-Gastaut syndrome; Opioid abuse
Comments:
A single patient with pharmacoresistant epileptic encephalopathy has been found to have chromosomal aberration, translocation t(Y;4)(q11.2;q21) that leads to JNK3 truncation, involving this gene. A 13-year-old boy with delayed psychomotor development and mild intellectual disability without seizures who had a de novo heterozygous balanced translocation, 46,X,t(Y;4)(q12;q21.3), where the breakpoint is at JNK3 gene, and leads to elimination of JNK3 functions.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Cervical cancer (%CFC= +97, p<0.0001); Cervical cancer stage 2A (%CFC= -71, p<0.064); Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (cRCC) (%CFC= -45, p<0.007); Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (cRCC) stage I (%CFC= -56, p<0.0001); Malignant pleural mesotheliomas (MPM) tumours (%CFC= -48, p<0.001); T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia (%CFC= +83, p<0.066); and Uterine leiomyomas (%CFC= -73, p<0.003).
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.1 % in 24434 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only 31 % higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
None > 1 in 20,654 cancer specimens
Comments:
No deletions, insertions or complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.