Nomenclature
Short Name:
LKB1
Full Name:
Serine-threonine-protein kinase 11
Alias:
- AMPKK
- EC 2.7.11.1
- KPM
- PJS
- Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-19
- STK11
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
CAMK
Family:
CAMKL
SubFamily:
LKB
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
48,636
# Amino Acids:
433
# mRNA Isoforms:
2
mRNA Isoforms:
48,636 Da (433 AA; Q15831); 45,387 Da (404 AA; Q15831-2)
4D Structure:
Found in a ternary complex composed of SMAD4, STK11 and STK11IP. Interacts with SMAD4, STK11IP and WDR6.
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
Domain Distribution:
| Start | End | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 49 | 309 | Pkinase |
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K44 (N6), K48 (N6), K96 (N6), K97 (N6), K296 (N6), K311 (N6), K416 (N6), K423 (N6), K431 (N6).
Methylated:
C430 (predicted).
Other:
C430 (S-farnesyl cysteine, predicted).
Palmitoylated:
C418 (predicted).
Serine phosphorylated:
S31, S240, S307, S334, S401, S428+.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T32, T185+, T189, T336-, T363+, T402+.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y36, Y60, Y156, Y166.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 55
55
969
41
1077
 5
5
89
16
102
 34
34
597
11
454
 17
17
307
134
472
 43
43
770
44
550
 6
6
110
100
287
 9
9
158
51
409
 39
39
688
38
652
 10
10
182
17
149
 7
7
129
132
183
 14
14
252
32
299
 44
44
783
174
634
 15
15
270
33
362
 3
3
51
9
74
 20
20
353
25
529
 5
5
90
25
76
 8
8
151
125
176
 17
17
303
19
309
 11
11
199
122
241
 29
29
510
165
473
 16
16
280
24
314
 16
16
286
28
290
 32
32
561
13
416
 31
31
549
20
441
 20
20
356
22
378
 48
48
855
84
588
 10
10
174
36
238
 20
20
364
20
450
 21
21
379
20
411
 28
28
501
56
604
 41
41
732
24
677
 100
100
1777
46
3580
 15
15
265
95
718
 45
45
798
104
665
 11
11
188
61
289
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 99.3
99.3
99.3
99 99.3
99.3
99.5
99 -
-
-
98 -
-
-
93 92.5
92.5
94.5
93.5 -
-
-
- 90.1
90.1
93.3
91 90.6
90.6
93.1
91 -
-
-
- 57.7
57.7
63.3
- 89.3
89.3
93.2
90.5 81.3
81.3
87.5
84 82.3
82.3
87.3
83 -
-
-
- 41.5
41.5
54.9
53 54.6
54.6
71.9
- 29.8
29.8
43.8
43 57.7
57.7
72.3
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 27.5
27.5
43.7
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | STRADA - Q7RTN6 |
| 2 | CAB39 - Q9Y376 |
| 3 | PRKAA2 - P54646 |
| 4 | PTEN - P60484 |
| 5 | TP53 - P04637 |
| 6 | WDR6 - Q9NNW5 |
| 7 | HSP90AA2 - Q14568 |
| 8 | TNIP2 - Q8NFZ5 |
| 9 | CDC37 - Q16543 |
| 10 | SMARCA4 - P51532 |
| 11 | MARK2 - Q7KZI7 |
| 12 | HSP90AA1 - P07900 |
| 13 | MARK1 - Q9P0L2 |
| 14 | RPS6KB1 - P23443 |
| 15 | RPS6KA3 - P51812 |
Regulation
Activation:
Activated by binding of a complex consisting of CAB39 and STRAD or CAB39 and ALS2CR2. Phosphorylation at Ser-307 induces interaction with AMPK1, STLK5 and exportin 1. Phosphorylation at Ser-428 increases phosphotransferase activity.
Inhibition:
Phosphorylation at Thr-336 inhibits LKB1.
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| LKB1 | Q15831 | T189 | LLLTTGGTLKISDLG | ? |
| PKCz | Q05513 | S307 | IRQIRQHSWFRKKHP | ? |
| LKB1 | Q15831 | T336 | KDRWRSMTVVPYLED | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | T363 | IEDDIIYTQDFTVPG | + |
| LKB1 | Q15831 | T363 | IEDDIIYTQDFTVPG | + |
| DNAPK | P78527 | T363 | IEDGIIYTQDFTVPG | + |
| PKACa | P17612 | S428 | SSKIRRLSACKQQ__ | + |
| MSK1 | O75582 | S428 | SSKIRRLSACKQQ__ | + |
| p70S6K | P23443 | S428 | SSKIRRLSACKQQ__ | + |
| PKCz | Q05513 | S428 | SSKIRRLSACKQQ__ | + |
| LKB1 | Q15831 | S428 | SSKIRRLSACKQQ__ | + |
| RSK1 | Q15418 | S428 | SSKIRRLSACKQQ__ | + |
| DNAPK | P78527 | S428 | SSKIRRLSACKQQ__ | + |
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| AMPKa1 (PRKAA1) | Q13131 | S496 | ATPQRSGSVSNYRSC | |
| AMPKa1 (PRKAA1) | Q13131 | T183 | SDGEFLRTSCGSPNY | + |
| AMPKa1 (PRKAA1) | Q13131 | T269 | VDPMKRATIKDIREH | + |
| AMPKa2 (PRKAA2) | P54646 | S491 | STPQRSCSAAGLHRP | |
| AMPKa2 (PRKAA2) | P54646 | T172 | SDGEFLRTSCGSPNY | + |
| AMPKa2 (PRKAA2) | P54646 | T258 | VDPLKRATIKDIREH | |
| BRSK1 | Q8TDC3 | T189 | VGDSLLETSCGSPHY | + |
| BRSK2 | Q8IWQ3 | T174 | VGDSLLETSCGSPHY | + |
| LKB1 (STK11) | Q15831 | S428 | SSKIRRLSACKQQ__ | + |
| LKB1 (STK11) | Q15831 | T189 | LLLTTGGTLKISDLG | ? |
| LKB1 (STK11) | Q15831 | T336 | KDRWRSMTVVPYLED | + |
| LKB1 (STK11) | Q15831 | T363 | IEDDIIYTQDFTVPG | + |
| MARK1 | Q9P0L2 | T215 | TVGNKLDTFCGSPPY | + |
| MARK2 | Q7KZI7 | T208 | TFGNKLDTFCGSPPY | + |
| MARK3 | P27448 | S215 | KLDTFCGSPPYAAPE | - |
| MARK3 | P27448 | S238 | KLDTFCGSPPYAAPE | - |
| MARK3 | P27448 | T211 | TVGGKLDTFCGSPPY | + |
| MARK3 | P27448 | T234 | TVGGKLDTFCGSPPY | + |
| MARK4 | Q96L34 | T214 | TLGSKLDTFCGSPPY | + |
| MELK | Q14680 | T167 | NKDYHLQTCCGSLAY | + |
| NuaK1 (ARK5) | O60285 | T211 | QKDKFLQTFCGSPLY | + |
| Nuak2 | Q9H093 | S573 | PPLRGCVSVDNLTGL | |
| Nuak2 | Q9H093 | T208 | HQGKFLQTFCGSPLY | + |
| Nuak2 | Q9H093 | Y131 | KIVIVMEYASRGDLY | |
| p53 | P04637 | S15 | PSVEPPLSQETFSDL | + |
| p53 | P04637 | S392 | FKTEGPDSD______ | + |
| PTEN | P60484 | S380 | EPDHYRYSDTTDSDP | - |
| PTEN | P60484 | T382 | DHYRYSDTTDSDPEN | - |
| PTEN | P60484 | T383 | HYRYSDTTDSDPENE | - |
| QIK (SIK2) | Q9H0K1 | T175 | KSGELLATWCGSPPY | + |
| QSK | Q9Y2K2 | T163 | TPGQLLKTWCGSPPY | + |
| SIK | P57059 | T182 | KSGEPLSTWCGSPPY | + |
| SNRK | Q9NRH2 | T173 | QPGKKLTTSCGSLAY | + |
| STRADA (STRAD) | Q7RTN6 | T329 | GLSDSLTTSTPRPSN | |
| STRADA (STRAD) | Q7RTN6 | T419 | SGIFGLVTNLEELEV |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
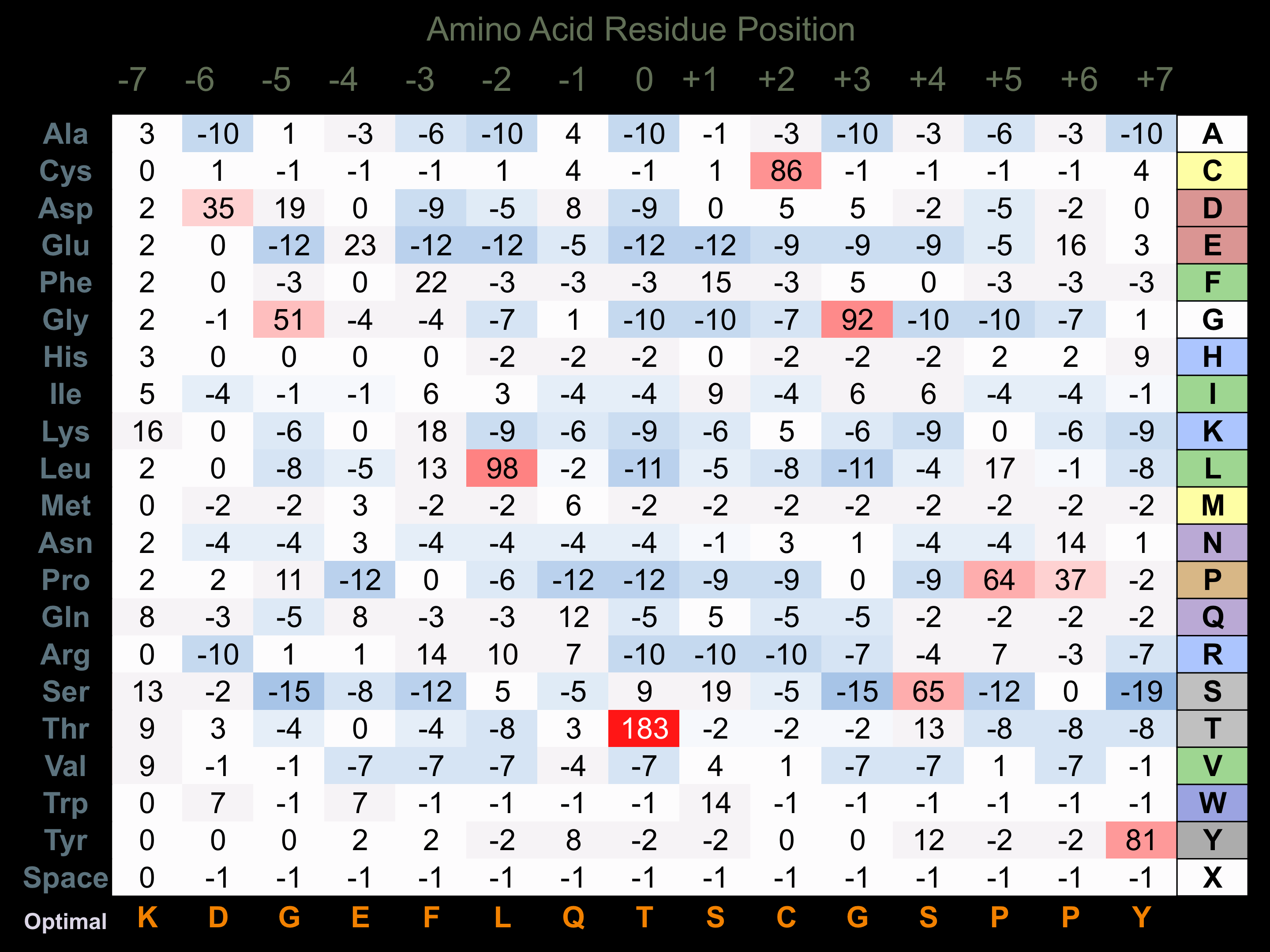
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 51 known protein substrate phosphosites.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, gastrointestinal disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; Intussusception; Tuberous sclerosis; Cowden disease; Juvenile polyposis syndrome; Polyhydramnios; Megalencephaly
Comments:
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS) is an autosomal-dominant disease characterized by polyp formation in the gastrointestinal tract and abnormal pigment deposition on the lips, buccal muccosa, and digits. PJS is associated with an increased risk for gastrointestinal and pancreatic cancer. Intussusception is a gastrointestinal disease realted to PJS. Cowden syndrome is a genetic disease characterized by the formation of numerous non-cancerous growths (hamartomas) on various areas of the body, which is associated with an increased risk of developing breast, thyroid, or endometrial cancer. Several mutations in the LKB1 gene have been observed in patients with PJS, including a deletion mutation of exons 4 and 5, an inversion of exons 6 and 7, terminal mutations (Y253X, K84X, E57X, Y246X), a 1-bp deletion at 843G resulting in a frameshift, a 4-bp deletion (716delGGTC) causing a frameshift, a splice site mutation causing a frameshift, substitution mutations (L67P, G135R, W239C, F354L), and a 9-bp deletion mutation converting the 4 codons from 303-309 from ile-arg-gln-his to a single asn. All of the mutations associated with the disease lead to inactivation of the LKB1 protein. For example, the substitution mutations are located in highly conserved residues in the kinase catalytic domain. It has been estimated that germline inactivating mutations in the LKB1 gene account for 60% of familial and 50% of sporadic cases of PJS. In addition, ~42% of patients with PJS do not display mutations in LKB1, indicating the involvement of other genes in the disease pathology. Several of the observed mutations in the LKB1 gene are predicted to disrupt the interation between LKB1 and PTEN. PTEN is a dual phosphatase that is routinely mutated in autosomal disorders with similar phenotypes as PJS (e.g. Cowden syndrome), indicating a role for LKB1/PTEN interaction in the disease pathogenesis and confirming LKB1 as a key tumour suppressor in intestinal cells.
Specific Cancer Types:
Pancreatic cancer; Lung cancer; Carney complex; Acinar cell carcinomas; Large cell carcinomas; Germ cell tumours; Testicular tumours, somatic; Melanomas, malignant, somatic; Male germ cell tumours, somatic; Spermatocytic seminomas, somatic
Comments:
LKB1 appears to be a tumour suppressor protein (TSP). Cancer-related mutations in human tumours point to a loss of function of the protein kinase. The active form of the protein kinase normally acts to promote tumour cell proliferation. Mutations in the LKB1 gene have been observed in cancer patients. In particularly, cancer-associated mutations are found in the substrate recognition domain of the protein or result in protein truncation. Whereas, mutations affecting ATP binding and catalysis are rarely observed in human cancer. Significantly reduced LKB1 expression has been observed in benign intestinal polyps, correlated with reduced apoptosis. This is thought to be the cause of the aberrant growth and may potentially contribute to the development of malignant intestinal tumours. Additionally, LKB1 protein in tumour cells is restricted to the nucleus, compared to the normal distribution of the protein in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. The introduction of LKB1 protein into LKB1-deficient cancer cell lines results in G1 phase cell cycle arrest. This effect is still seen for LKB1 proteins that lack nuclear localization signals, indicating that the tumour suppressive effects of the kinase are mediated in the cytoplasm. The proposed mechanism of LKB1-mediated cell cycle arrest is a p53-dependent induction of p21. In animal studies, LKB1-deficient tumours displyed shorter latency, an expanded histological prolife (including adeno-, squamous-, and large cell carcinoma), as well as more frequent metastasis when compared to tumours lacking p53 or Arf (other tumour suppressor genes). In addition, LKB1 inactivation was observed in 34% of adenocarcinomas and 19% of squamous cell carcinomas in 144 human lung cancer specimens. Analysis of gene expression in human lung cancer cell lines and mouse lung tumours revealed that repression of LKB1 results in the activation of various metastasis-promoting genes, such as NEDD9, VEGFC, and CD24. Therefore, it has been concluded that LKB1 is a key cellular component in the prevention of pulmonary tumorigenesis and in the control of initiation, differentiation, and metastasis of lung cancer cells.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Breast epithelial cell carcinomas (%CFC= +65, p<0.003); and Skin melanomas - malignant (%CFC= +83, p<0.004). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for LKB1 in diverse human cancers of 391, which is 0.9-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 196 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 3.3-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice support a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.33 % in 31881 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is 4.5-fold higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 1.45 % in 460 cervix cancers tested; 1.38 % in 4085 lung cancers tested; 0.83 % in 1771 large intestine cancers tested; 0.63 % in 1083 skin cancers tested; 0.32 % in 999 stomach cancers tested; 0.2 % in 1491 pancreas cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: F354L (36); D194Y (12); P281L (11).
Comments:
Over 50 deletions, 20 insertions and 6 complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

