Nomenclature
Short Name:
smMLCK
Full Name:
Myosin light chain kinase, smooth muscle and non-muscle isozymes
Alias:
- EC 2.7.11.18
- DKFZp686I10125
- smMLCK
- MLCK108
- MLCK210
- MSTP083; MYLK; MYLK1; Myosin light chain kinase; Myosin light polypeptide kinase; Telokin
- FLJ12216
- KMLS
- KRP
- MLCK
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
CAMK
Family:
MLCK
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
210,774
# Amino Acids:
1914
# mRNA Isoforms:
11
mRNA Isoforms:
210,715 Da (1914 AA; Q15746); 210,586 Da (1913 AA; Q15746-6); 205,059 Da (1863 AA; Q15746-3); 203,055 Da (1845 AA; Q15746-2); 202,350 Da (1841 AA; Q15746-5); 197,399 Da (1794 AA; Q15746-4); 110,205 Da (992 AA; Q15746-7); 110,076 Da (991 AA; Q15746-11); 80,410 Da (714 AA; Q15746-9); 16,970 Da (154 AA; Q15746-8); 16,840 Da (153 AA; Q15746-10)
4D Structure:
All isoforms including Telokin bind calmodulin. Interacts with SVIL
1D Structure:
Subfamily Alignment
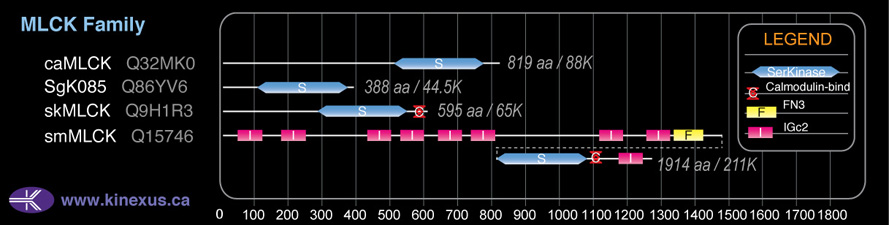
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K608, K1042, K1113, K1496, K1744, K1747.
Methylated:
K603.
Serine phosphorylated:
S145, S305, S324, S328, S343, S367, S515+, S804+, S815-, S827, S947, S1005, S1093, S1208, S1388, S1438, S1759, S1760, S1768, S1772, S1773, S1776, S1779, S1788, S1812.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T88, T109, T118, T151, T331, T335, T488, T978, T1748, T1774, T1778, T1814.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y104, Y231, Y464+, Y471+, Y556, Y611, Y792, Y846, Y1410, Y1449, Y1575, Y1635, Y1835.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 32
32
1346
43
1031
 6
6
263
14
206
 100
100
4156
1
0
 7
7
298
148
466
 29
29
1216
45
847
 9
9
367
85
467
 13
13
530
59
851
 12
12
494
29
853
 41
41
1719
10
528
 14
14
594
71
349
 8
8
331
16
229
 27
27
1123
131
688
 10
10
434
12
267
 25
25
1052
9
633
 3
3
137
12
165
 3
3
107
28
140
 75
75
3101
179
2803
 10
10
429
8
210
 2
2
79
61
57
 23
23
975
153
730
 18
18
736
12
730
 13
13
550
14
468
 7
7
311
10
539
 10
10
415
8
58
 3
3
124
12
178
 19
19
807
99
979
 3
3
128
15
64
 15
15
642
8
330
 72
72
2995
8
817
 1.4
1.4
57
28
34
 0.1
0.1
4
6
1
 22
22
920
41
2230
 8
8
343
118
823
 16
16
656
135
586
 3
3
135
74
115
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 99
99
99.4
99 97.3
97.3
98.4
97 -
-
-
- -
-
-
100 87.8
87.8
91.9
89 -
-
-
- 84.4
84.4
89.4
85.5 -
-
-
86 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 69
69
79.2
71 -
-
-
48 33.9
33.9
40.5
64 -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
41 26.6
26.6
40.7
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
-
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | ACTC1 - P68032 |
| 2 | PRKG2 - Q13237 |
| 3 | PRKCA - P17252 |
| 4 | CAMK2G - Q13555 |
| 5 | PAK1 - Q13153 |
| 6 | PAK2 - Q13177 |
| 7 | CALM1 - P62158 |
| 8 | MLC1 - Q15049 |
| 9 | MAPK3 - P27361 |
| 10 | NCK1 - P16333 |
| 11 | PIK3R1 - P27986 |
| 12 | RNF10 - Q8N5U6 |
| 13 | CDT1 - Q9H211 |
Regulation
Activation:
Binding to calcium and calmodulin is required for activation. Phosphorylation at Ser-804 increases the calmodulin-independent phosphotransferase activity. Isoform 1 is activated by phosphorylation on Tyr-464 and Tyr-471.Phosphorylation at Tyr-464 and Tyr-471 induces interaction with cortactin.
Inhibition:
Phosphorylation of Ser-815 inhibits the calmodulin-dependent activity due to a decrease in the affinity for calmodulin
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| ABL | P00519 | Y231 | NQDDVGVYTCLVVNG | |
| ABL | P00519 | Y464 | QEGSIEVYEDAGSHY | + |
| SRC | P12931 | Y464 | QEGSIEVYEDAGSHY | + |
| SRC | P12931 | Y471 | YEDAGSHYLCLLKAR | + |
| ABL | P00519 | Y556 | LNGQPIQYARSTCEA | |
| ABL | P00519 | Y611 | KSSRkSEYLLPVAPS | |
| ABL | P00519 | Y792 | QPWHAGQYEILLKNR | |
| smMLCK | Q15746 | S804 | KNRVGECSCQVSLML | + |
| smMLCK | Q15746 | S815 | SLMLQNSSARALPRG | - |
| PKACa | P17612 | S815 | SLMLQNSSARALPRG | - |
| CaMK2a | Q9UQM7 | S815 | SLMLQNSSARALPRG | - |
| ABL | P00519 | Y846 | DGGGSDRYGSLRPGW | |
| PKG1 | Q13976 | S1005 | GLSGRKSSTGSPTSP | |
| ERK2 | P28482 | S1005 | GLSGRKSSTGSPTSP | |
| PAK2 | Q13177 | S1208 | MKSRRPKSSLPPVLG | |
| PKACa | P17612 | S1388 | LATCRSTSFNVQDLL | |
| PKACa | P17612 | S1388 | LATCRSTSFNVQDLL | |
| ABL | P00519 | Y1449 | EKEPEVDYRTVTINT | |
| ABL | P00519 | Y1575 | QISEGVEYIHKQGIV | |
| ABL | P00519 | Y1635 | VAPEVINYEPIGYAT | |
| smMLCK | Q15746 | T1748 | ARRKWQKTGNAVRAI | |
| PAK2 | Q13177 | S1759 | VRAIGRLSSMAMISG | |
| smMLCK | Q15746 | S1760 | RAIGRLSSMAMISGL | |
| PKACa | P17612 | S1760 | RAIGRLSSMAMISGL | |
| CaMK2a | Q9UQM7 | S1760 | RAIGRLSSMAMISGL | |
| smMLCK | Q15746 | S1768 | MAMISGLSGRKSSTG | |
| PAK1 | Q13153 | S1772 | SGLSGRKSSTGSPTS | |
| PKG1 | Q13976 | S1773 | GLSGRKSSTGSPTSP | |
| PKACa | P17612 | S1773 | GLSGRKSSTGSPTSP | |
| CaMK2a | Q9UQM7 | S1773 | GLSGRKSSTGSPTSP | |
| smMLCK | Q15746 | S1776 | GRKSSTGSPTSPLNA | |
| PKACa | P17612 | S1776 | GRKSSTGSPTSPINA | |
| GSK3B | P49841 | S1776 | GRKSSTGSPTSPLNA | |
| PKG1 | Q13976 | S1779 | SSTGSPTSPLNAEKL | |
| ERK1 | P27361 | S1779 | SSTGSPTSPLNAEKL | |
| PKACa | P17612 | S1779 | SSTGSPTSPLNAEKL | |
| ERK2 | P28482 | S1779 | SSTGSPTSPLNAEKL | |
| smMLCK | Q15746 | S1812 | PHVKPYFSKTIRDLE | |
| smMLCK | Q15746 | T1814 | VKPYFSKTIRDLEVV |
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| MRLC1 (MYL9) | P24844 | S20 | KRPQRATSNVFAMFD | |
| MRLC1 (MYL9) | P24844 | T19 | KKRPQRATSNVFAMF | |
| MRLC2 (MYL12B) | P19105 | S2 | _______SSKRTKTK | + |
| MRLC2 (MYL12B) | P19105 | S20 | KRPQRATSNVFAMFD | |
| MRLC2 (MYL12B) | P19105 | S3 | ______SSKRTKTKT | + |
| MRLC2 (MYL12B) | P19105 | T135 | TTMGDRFTDEEVDEL | |
| MRLC2 (MYL12B) | P19105 | T19 | KKRPQRATSNVFAMF | + |
| MRLC2 (MYL12B) | P19105 | Y156 | DKKGNFNYIEFTRIL | |
| MYLK1 (smMLCK) | Q15746 | S1760 | RAIGRLSSMAMISGL | |
| MYLK1 (smMLCK) | Q15746 | S1768 | MAMISGLSGRKSSTG | |
| MYLK1 (smMLCK) | Q15746 | S1776 | GRKSSTGSPTSPLNA | |
| MYLK1 (smMLCK) | Q15746 | S1812 | PHVKPYFSKTIRDLE | |
| MYLK1 (smMLCK) | Q15746 | S804 | KNRVGECSCQVSLML | + |
| MYLK1 (smMLCK) | Q15746 | S815 | SLMLQNSSARALPRG | - |
| MYLK1 (smMLCK) | Q15746 | T1748 | ARRKWQKTGNAVRAI | |
| MYLK1 (smMLCK) | Q15746 | T1814 | VKPYFSKTIRDLEVV | |
| TNNI3 | P19429 | S41 | AKKKSKISASRKLQL | |
| TNNI3 | P19429 | S43 | KKSKISASRKLQLKT | |
| TNNI3 | P19429 | T142 | RGKFKRPTLRRVRIS |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
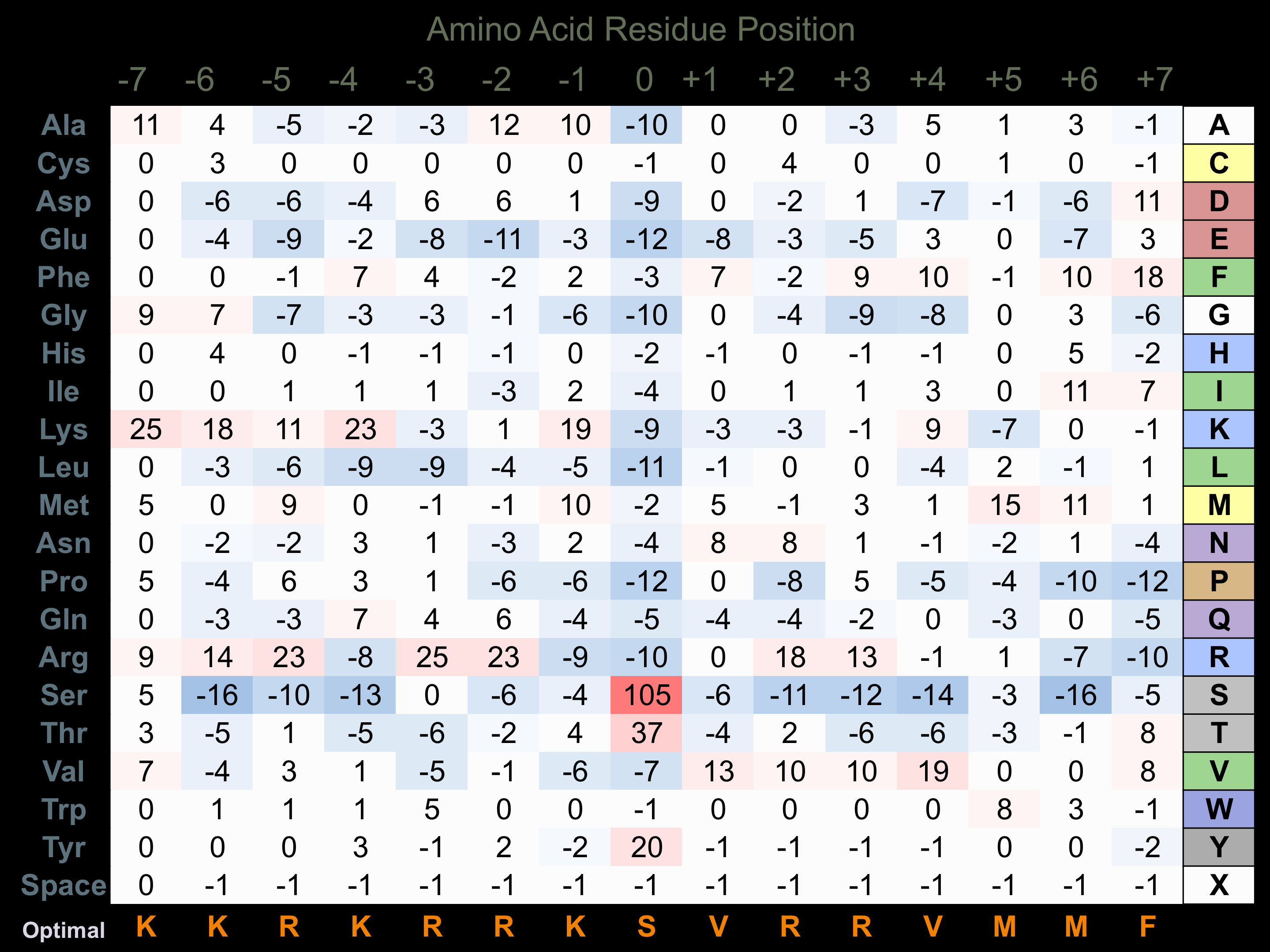
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 37 known protein substrate phosphosites and 27 peptides phosphorylated by recombinant MYLK1 in vitro tested in-house by Kinexus.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cardiovascular disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
MYLK-related thoracic aortic aneurysms and aortic dissections; Aortic aneurysm; Aortic aneurysm, familial thoracic 7; Thoracic aortic aneurysms and aortic dissections; Giardiasis; Intracranial vasospasm; Aortic aneurysm, Familial thoracic 4
Comments:
Aortic aneurysm is a bulging or 'ballooning' in the wall of the aorta, posing a risk of bursting and causing internal bleeding and death. Aortic aneurysm may occur in either the thoracic aorta or the abdominal aorta. Giardiasis is a diarrheal condition caused by infection with Giardia, a microscopic parasite found on surfaces or in soil, food, or water that has been contaminated with feces from an affected individual. Intracranial vasospasm is a condition characterized by the spasm of the muscle in the walls of blood vessels leading to vasoconstriction of the vessel. This vasoconstriction can lead to tissue ischemia and death (necrosis). Mutations in the MLCK1 gene have been observed in patients with aortic aneuryms, including a S1759P substitution mutation and a R1480X termination mutation. The S1759P mutation was located in the alpha-helix of the calmodulin-binding domain of the protein and is predicted to result in the loss of MLCK1 catalytic activity due to altered binding affinity of calmodulin. In vitro enzymatic analysis of the S1759P mutant protein revealed a 6-fold decrease in catalytic activity compared to the wild-type protein. In animal studies, mice lacking MLCK1 displayed increased accumulation of proteoglycans in aortic tissues, combined with elevated expression of lumican, decorin and collagen in the adventitial layer and an overall increase in aortic type III collagen expression as compared to controls. In addition, the expression of elastin-degrading metalloproteinase MMP2 was elevated in the aortic tissue of mice lacking MLCK1, although the elastic fibres were not degraded in the corresponding aortic media. Therefore, loss-of-function of the MLCK1 is associated with extensive changes in the extracellular matrix and connective tissue profile of aortic tissue, potentially predisposing the patient to a higher risk of aortic aneurysm.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Bladder carcinomas (%CFC= -78, p<0.015); Breast epithelial carcinomas (%CFC= -66, p<0.006); Breast epithelial cell carcinomas (%CFC= -45, p<0.017); Cervical cancer stage 2B (%CFC= -46, p<0.077); Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (cRCC) stage I (%CFC= +107, p<0.019); Colon mucosal cell adenomas (%CFC= -78, p<0.0001); Colorectal adenocarcinomas (early onset) (%CFC= +311, p<0.013); Lung adenocarcinomas (%CFC= -62, p<0.0001); Malignant pleural mesotheliomas (MPM) tumours (%CFC= +203, p<0.0008); Pituitary adenomas (ACTH-secreting) (%CFC= +124); Prostate cancer - metastatic (%CFC= -81, p<0.0001); Skin fibrosarcomas (%CFC= -84); Skin melanomas - malignant (%CFC= -90, p<0.005); Skin squamous cell carcinomas (%CFC= -62, p<0.04); Uterine leiomyomas from fibroids (%CFC= +73, p<0.009); and Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (%CFC= -73, p<0.002). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for MLCK1 in diverse human cancers of 303, which is 0.7-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 2 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 97% lower than the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.09 % in 24770 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is only 14 % higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.51 % in 864 skin cancers tested; 0.28 % in 603 endometrium cancers tested; 0.27 % in 589 stomach cancers tested; 0.26 % in 1270 large intestine cancers tested; 0.14 % in 1822 lung cancers tested; 0.13 % in 548 urinary tract cancers tested; 0.11 % in 238 bone cancers tested; 0.08 % in 65 Meninges cancers tested; 0.08 % in 273 cervix cancers tested; 0.07 % in 881 prostate cancers tested; 0.07 % in 833 ovary cancers tested; 0.07 % in 1512 liver cancers tested; 0.07 % in 1316 breast cancers tested; 0.06 % in 942 upper aerodigestive tract cancers tested; 0.06 % in 710 oesophagus cancers tested; 0.06 % in 558 thyroid cancers tested; 0.04 % in 127 biliary tract cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: A1099T (9); A350T (4).
Comments:
Only 5 deletions, 1 insertion and no complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.

