Nomenclature
Short Name:
CHK2
Full Name:
Check point kinase 2
Alias:
- Cds1
- CHEK2
- CHK2 checkpoint homologue (S. pombe)
- EC 2.7.11.1
- RAD53
Classification
Type:
Protein-serine/threonine kinase
Group:
CAMK
Family:
RAD53
SubFamily:
NA
Specific Links
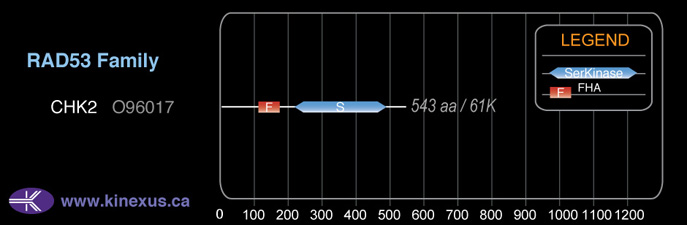
Structure
Mol. Mass (Da):
60,915
# Amino Acids:
543
# mRNA Isoforms:
13
mRNA Isoforms:
65,419 Da (586 AA; O96017-9); 60,915 Da (543 AA; O96017); 57,526 Da (514 AA; O96017-12); 50,203 Da (452 AA; O96017-4); 38,125 Da (339 AA; O96017-7); 36,157 Da (322 AA; O96017-13); 32,142 Da (289 AA; O96017-8); 26,084 Da (234 AA; O96017-2); 24,396 Da (225 AA; O96017-11); 22,594 Da (203 AA; O96017-5); 18,706 Da (165 AA; O96017-6); 17,370 Da (162 AA; O96017-3); 15,420 Da (140 AA; O96017-10)
4D Structure:
NA
1D Structure:
3D Image (rendered using PV Viewer):
PDB ID
Subfamily Alignment
Domain Distribution:
Kinexus Products
Click on entries below for direct links to relevant products from Kinexus for this protein kinase.
hiddentext
Post-translation Modifications
For detailed information on phosphorylation of this kinase go to PhosphoNET
Acetylated:
K235.
Serine phosphorylated:
S12, S15, S19+, S24, S28+, S33+, S35+, S39, S40, S41, S42, S44, S50, S52, S55, S62, S67, S73+, S120, S140, S164-, S210-, S260, S372-, S379+, S435, S456, S516+.
Threonine phosphorylated:
T26+, T43, T45, T65, T68+, T205-, T225, T378-, T383+, T387-, T389-, T432, T517.
Tyrosine phosphorylated:
Y390+.
Distribution
Based on gene microarray analysis from the NCBI
Human Tissue Distribution
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
% Max Expression:
Mean Expression:
Number of Samples:
Standard Deviation:
 74
74
992
16
1295
 4
4
60
8
61
 4
4
51
13
80
 16
16
208
57
443
 35
35
470
14
467
 6
6
78
42
118
 18
18
240
19
421
 90
90
1205
32
2782
 14
14
185
10
163
 4
4
57
42
42
 2
2
33
25
38
 39
39
521
106
609
 4
4
50
25
47
 2
2
32
7
29
 3
3
46
22
86
 3
3
39
7
15
 1
1
14
108
28
 3
3
38
19
46
 3
3
36
56
31
 24
24
321
56
348
 2
2
30
21
42
 3
3
42
23
39
 4
4
49
15
50
 3
3
43
19
50
 4
4
47
21
59
 100
100
1340
39
2883
 4
4
49
28
32
 4
4
52
19
63
 3
3
40
19
41
 11
11
145
14
96
 38
38
513
30
284
 37
37
492
21
590
 51
51
689
51
1003
 63
63
839
26
679
 3
3
34
31
45
Evolution
Species Conservation
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
PhosphoNET % Identity:
PhosphoNET % Similarity:
Homologene %
Identity:
 100
100
100
100 99.8
99.8
99.8
100 99.1
99.1
99.1
98.5 -
-
-
86 -
-
-
94 89.3
89.3
93
88 -
-
-
- 83.2
83.2
89.7
88 83.5
83.5
89.9
87 -
-
-
- 74.4
74.4
82.1
- 67.6
67.6
77.9
71.5 59.7
59.7
73.1
66 28.2
28.2
42
56 -
-
-
- 34.1
34.1
51.6
42 37.2
37.2
54.5
- 30.2
30.2
49.5
36 43.3
43.3
58.4
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- 28.4
28.4
47.1
41 -
-
-
39
For a wider analysis go to PhosphoNET Evolution in PhosphoNET
Binding Proteins
Examples of known interacting proteins
hiddentext
| No. | Name – UniProt ID |
|---|---|
| 1 | TP53 - P04637 |
| 2 | CDC25A - P30304 |
| 3 | MUS81 - Q96NY9 |
| 4 | MSH2 - P43246 |
| 5 | PLK1 - P53350 |
| 6 | NBN - O60934 |
| 7 | MDM2 - Q00987 |
| 8 | STRAP - Q9Y3F4 |
| 9 | DBF4 - Q9UBU7 |
| 10 | MRC1 - P22897 |
| 11 | ASF1A - Q9Y294 |
| 12 | RAD9A - Q99638 |
| 13 | CDC25C - P30307 |
| 14 | RB1 - P06400 |
| 15 | PPP2R5B - Q15173 |
Regulation
Activation:
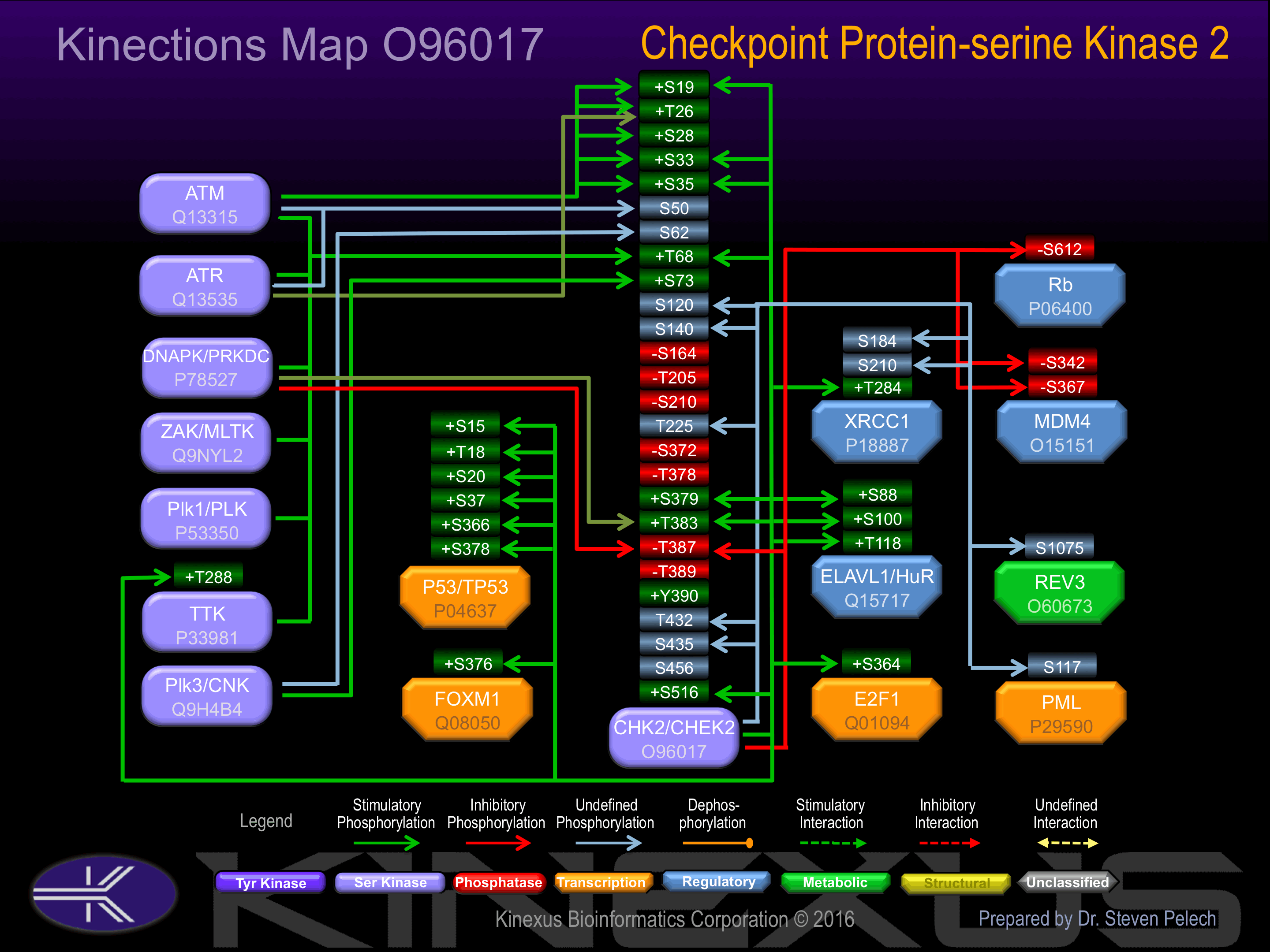
Rapidly phosphorylated on Thr-68 by MLTK in response to DNA damage and to replication block. Also activated by phosphorylation at Ser-19, Thr-26, Ser-28, Ser-33, Ser-35, Thr-383, Thr-387 and Ser-516,
Inhibition:
NA
Synthesis:
NA
Degradation:
NA
Known Upstream Kinases
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Kinase Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| CHK2 | O96017 | S19 | SHGSSACSQPHGSVT | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | S19 | SHGSSACSQPHGSVT | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | T26 | SQPHGSVTQSQGSSS | + |
| ATR | Q13535 | T26 | SQPHGSVTQSQGSSS | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | S28 | PHGSVTQSQGSSSQS | + |
| CHK2 | O96017 | S33 | TQSQGSSSQSQGISS | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | S33 | TQSQGSSSQSQGISS | + |
| CHK2 | O96017 | S35 | SQGSSSQSQGISSSS | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | S35 | SQGSSSQSQGISSSS | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | S50 | TSTMPNSSQSSHSSS | |
| ATR | Q13535 | S50 | TSTMPNSSQSSHSSS | |
| PLK3 | Q9H4B4 | S62 | SSSGTLSSLETVSTQ | |
| PLK1 | P53350 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| TTK | P33981 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| ZAK | Q9NYL2 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| CHK2 | O96017 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| ATM | Q13315 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| ATR | Q13535 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| DNAPK | P78527 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| PLK3 | Q9H4B4 | S73 | VSTQELYSIPEDQEP | + |
| CHK2 | O96017 | S120 | YWFGRDKSCEYCFDE | |
| CHK2 | O96017 | S140 | TDKYRTYSKKHFRIF | ? |
| CHK2 | O96017 | T225 | DEYIMSKTLGSGACG | |
| CHK2 | O96017 | S379 | SKILGETSLMRTLCG | + |
| CHK2 | O96017 | T383 | GETSLMRTLCGTPTY | + |
| DNAPK | P78527 | T383 | GETSLMRTLCGTPTY | + |
| CHK2 | O96017 | T387 | LMRTLCGTPTYLAPE | - |
| DNAPK | P78527 | T387 | LMRTLCGTPTYLAPE | - |
| CHK2 | O96017 | T432 | PPFSEHRTQVSLKDQ | |
| CHK2 | O96017 | S435 | SEHRTQVSLKDQITS | |
| CHK2 | O96017 | S516 | PQVLAQPSTSRKRPR | + |
Known Downstream Substrates
For further details on these substrates click on the Substrate Short Name or UniProt ID. Phosphosite Location is hyperlinked to PhosphoNET
predictions.
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Substrate Short Name | UniProt ID (Human) | Phosphosite Location | Phosphosite Sequence | Effect of Phosphorylation |
|---|
| AATF | Q9NY61 | S143 | SKKSRSHSAKTPGFS | |
| AATF | Q9NY61 | S477 | ELIERKTSSLDPNDQ | |
| AATF | Q9NY61 | S510 | KKVDRKASKGRKLRF | |
| BRCA1 | P38398 | S988 | PPLFPIKSFVKTKCK | |
| Cdc25A | P30304 | S124 | PALKRSHSDSLDHDI | |
| Cdc25A | P30304 | S178 | LFTQRQNSAPARMLS | - |
| Cdc25A | P30304 | S279 | VLKRPERSQEESPPG | |
| Cdc25A | P30304 | S293 | GSTKRRKSMSGASPK | |
| Cdc25C | P30307 | S216 | SGLYRSPSMPENLNR | ? |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S120 | YWFGRDKSCEYCFDE | |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S140 | TDKYRTYSKKHFRIF | ? |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S19 | SHGSSACSQPHGSVT | + |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S33 | TQSQGSSSQSQGISS | + |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S35 | SQGSSSQSQGISSSS | + |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S379 | SKILGETSLMRTLCG | + |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S435 | SEHRTQVSLKDQITS | |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | S516 | PQVLAQPSTSRKRPR | + |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | T225 | DEYIMSKTLGSGACG | |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | T383 | GETSLMRTLCGTPTY | + |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | T387 | LMRTLCGTPTYLAPE | - |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | T432 | PPFSEHRTQVSLKDQ | |
| Chk2 (CHEK2) | O96017 | T68 | SSLETVSTQELYSIP | + |
| E2F1 | Q01094 | S364 | PLLSRMGSLRAPVDE | + |
| ELAVL1 | Q15717 | S100 | VSYARPSSEVIKDAN | + |
| ELAVL1 | Q15717 | S88 | LNGLRLQSKTIKVSY | + |
| ELAVL1 | Q15717 | T118 | SGLPRTMTQKDVEDM | + |
| FOXM1 | Q08050 | S376 | PLLPRVSSYLVPIQF | + |
| LATS2 | Q9NRM7 | S408 | PVPSRTNSFNSHQPR | ? |
| MDM4 | O15151 | S342 | SKLTHSLSTSDITAI | - |
| MDM4 | O15151 | S367 | PDCRRTISAPVVRPK | - |
| p53 | P04637 | S15 | PSVEPPLSQETFSDL | + |
| p53 | P04637 | S20 | PLSQETFSDLWKLLP | + |
| p53 | P04637 | S366 | PGGSRAHSSHLKSKK | + |
| p53 | P04637 | S37 | NVLSPLPSQAMDDLM | + |
| p53 | P04637 | S378 | SKKGQSTSRHKKLMF | + |
| p53 | P04637 | T18 | EPPLSQETFSDLWKL | + |
| PML | P29590 | S117 | ESLQRRLSVYRQIVD | ? |
| Rb | P06400 | S612 | MYLSPVRSPKKKGST | - |
| REV3 | O60673 | S1075 | ENIKRTLSFRKKRSH | |
| TTK | P33981 | T288 | SPDCDVKTDDSVVPC | + |
| XRCC1 | P18887 | S184 | EEDESANSLRPGALF | |
| XRCC1 | P18887 | S210 | ASDPAGPSYAAATLQ | |
| XRCC1 | P18887 | T284 | APTRTPATAPVPARA | + |
Protein Kinase Specificity
Matrix of observed frequency (%) of amino acids in aligned protein substrate phosphosites
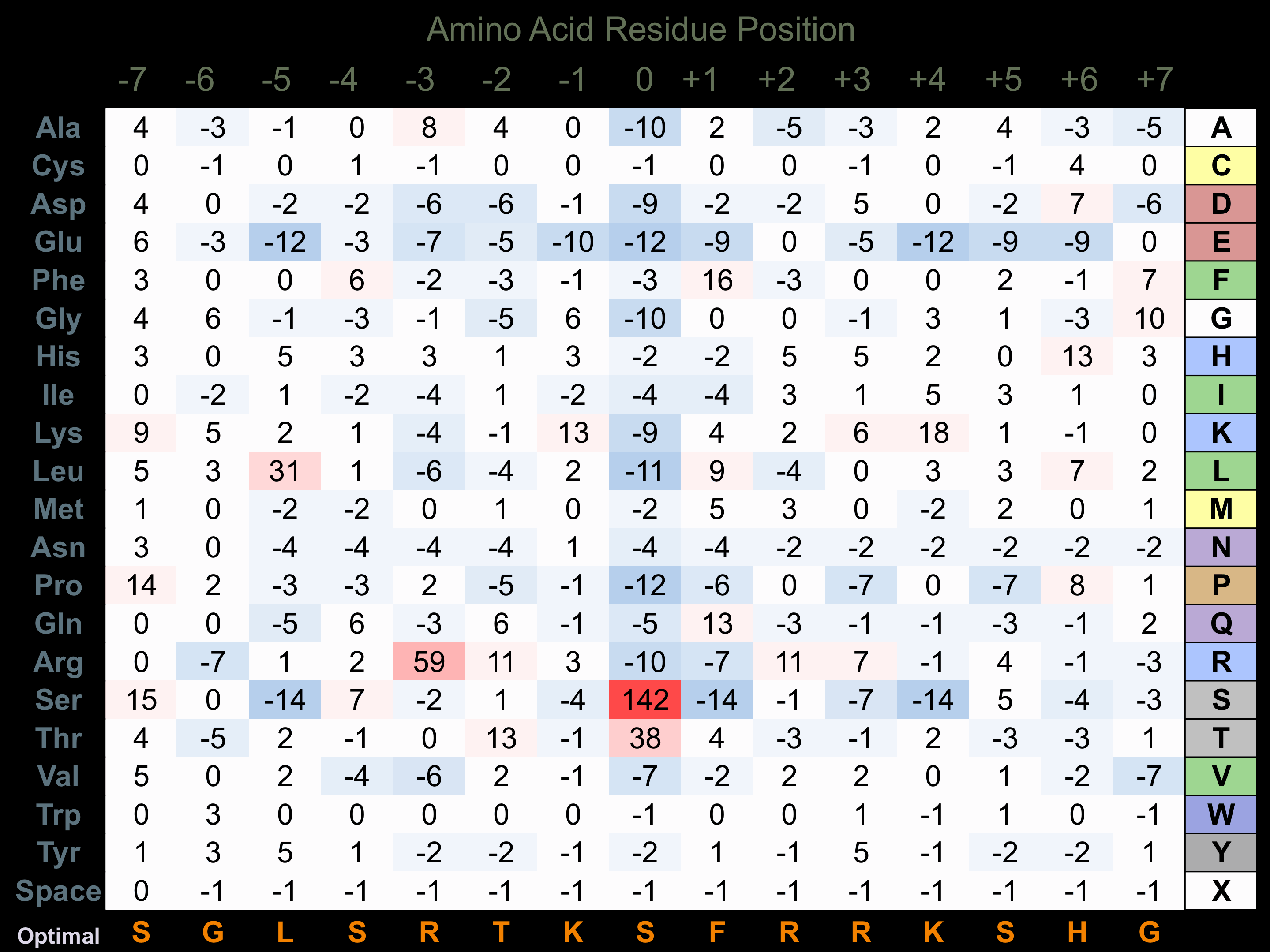
Matrix Type:
Experimentally derived from alignment of 66 known protein substrate phosphosites and 7 peptides phosphorylated by recombinant CHK2 in vitro tested in-house by Kinexus.
Domain #:
1
Inhibitors
For further details on these inhibitors click on the Compound Name and enter it into DrugKiNET or click on the ID's
Based on in vitro and/or in vivo phosphorylation data
| Compound Name | KD, Ki or IC50 (nM) | PubChem ID | ChEMBL ID | PubMed ID |
|---|
Disease Linkage
General Disease Association:
Cancer, neurological disorders
Specific Diseases (Non-cancerous):
Ataxia telangiectasia; Hypoxia
Comments:
Ataxia telangiectasia is a rare neurological disease characterized by the degeneration of motor-control and speech centres of the brain. The disease does not appear to affect cognition or intellectual ability of those affected. Symptoms of this disease generally include progressive difficulty with movement coordination (ataxia), walking difficulty, problems with balance and hand coordination, involuntary movements (chorea), muscle twitches (myoclonus), defective nerve function (neuropathy), and clusters of enlarged blood vessels (telangiectases) in the eyes or on the skin. Affected individuals have increased risk for the development of diabetes and certain cancers (35% increased risk), particularly leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer, and are more sensitize to ionizing radiation. Ataxia telangiectasia can also be caused by mutations in the ATM gene, which phosphorylates and activates CHK2, and functioning in the monitoring and repair of double-stranded DNA breaks. Females that are heterozygous for mutations in the ATM gene displayed a 2-5 fold higher risk of developing breast cancer. ATM-mediated phosphorylation and activation of CHK2 can be lost through a S73A mutation in CHK2.
Specific Cancer Types:
Familial prostate cancer (FPC); Breast cancer; Li-Fraumeni syndrome; Prostate cancer 3; Prostate cancer 4; Prostate cancer, somatic; Prostate cancer, progression of; Prostate cancer, hereditary, 5; Prostate cancer; Osteosarcoma; Bilateral breast cancer; Breast and colorectal cancer; Colorectal cancer; Breast cancer susceptibility; Ovarian cancer; Male breast cancer; Pancreas adenocarcinomas; T-cell prolymphocytic leukemias; Breast-ovarian cancer, familial, 2; Prostate cancer, progression and metastasis of; Osteosarcoma, somatic; CHEK2-related susceptibility to breast cancer; Li-Fraumeni syndrome, CHEK2-related; CHEK2-related susceptibility to breast and colorectal cancer
Comments:
CHK2 appears to be a tumour suppressor protein (TSP). Cancer-related mutations in human tumours point to a loss of function of the protein kinase. The active form of the protein kinase normally acts to inhibit tumour cell proliferation. Early in tumorigenesis (prior to genomic instability and malignancy) human cells activate the ATR/ATM-mediated DNA damage checkpoint, of which CHK2 is a key regulator, to prevent tumour progression and promote apoptosis. Activated CHK2 phosphorylates and inhibits CDC25 a dual-specificity phosphatase required for progression through the cell cycle. CHK2 further causes cell cycle arrest through activation of a DNA repair protein BRCA1 and apoptosis factor PML. The role of CHK2 in the development of cancer is in a primarily tumour suppressor role through causing cell cycle arrest. Loss-of-function mutations in CHK2, are thought to allow for aberrant cell proliferation, cell survival, genomic instability, and tumorigenesis, which is consistent with CHK2 as a tumour suppressor protein. In animal studies, embryonic stem cells isolated from a CHK2 deficient mouse failed to maintain radiation-induced cell cycle arrest in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. In addition, thymocytes from the same mice did not undergo apoptosis in the presence of DNA damage. This phenotype was rescued by the introduction of CHK2 protein into the cells, which restored normal ability to arrest the cell cycle in response to DNA damage, resulting in increased levels of p53-dependent transcription in response to DNA damage and increased p53 stabilization. Several mutations in the CHK2 gene have been observed in certain human cancer types (including Li-Fraumeni syndrome 2 (LFS2), prostate cancer (PC), osteogenic sarcoma (OSRC), and breast cancer (BC)). These mutations include substitution mutations (P85L, A17S, R180H, R181C, R181H, E239K, S428F), termination mutations (E239X), deletions/insertions, and mutations in splice-sites resulting in abnormal splice variants. It has been observed that inhibition of CHK2 through mutations in the regulatory FHA domain has been observed in low frequency in osteosarcomas and cancers of the ovary, lung and vulva. An R145W substitution is found in colon cancer and LFS2, which leads to CDC25A degradation in response to ionizing radiation. The substitution mutations at many sites lead to loss of phosphorylation and activation (e. g. T68A, S73A, T383A and T387A), phosphotransferase activity (e. g. D347A, D368N) or increased ubiquitination (e. g. S456A) are associated with many types of cancer. Such mutations in CHK2 lead to impairment of cell cycle arrest and aberrant cell proliferation and growth. In addition, 5% of patients from high-risk families for breast cancer with negative test results for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations were observed to carry mutations in the CHK2 gene, indicating a role for the CHK2 protein in breast cancer tumorigenesis. In addition, inherited loss-of-function mutations in the CHK2 gene are associated with a 2-fold increased risk for breast cancer. In particular, a certain deletion mutation (1100delC) has been commonly observed in individuals from families with a high risk for breast cancer development. This mutation was predicted to produce a truncated CHK2 protein completely lacking kinase catalytic activity. Furthermore, breast cancer tissue from patients with the 1100delC mutations in the CHK2 gene also display significantly reduced expression levels of the CHK2 protein. Li-Fraumeni Syndrome is linked to breast cancer and sarcoma, with the Plk3 signalling, and transcriptional activation of cell cycle inhibitor p21 associated pathways. LFS2 is characterized by development of a sarcoma-affected proband before the age of 45. Associated tissues include breast, adrenal gland, and brain tissues. Osteocarcinoma is a bone-forming cell carcinoma that can also affect bone, lung, and breast tissues. Ataxia Telangiectasia is characterized by neurodegeneration of motor-control and speech centres of the brain. Sufferers have a 35% of developing cancer in their lifetime, with sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Hypoxia is related to breast and prostate cancer, and is the deprivation of oxygen in tissues. Oxygen deprivation, and evasion, can be very important in solid tumour formation. Somatic Osteosarcoma is related to Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
Gene Expression in Cancers:
TranscriptoNET (www.transcriptonet.ca) analysis with mRNA expression data retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was normalized against 60 abundantly and commonly found proteins, indicated altered expression for this protein kinase as shown here as the percent change from normal tissue controls (%CFC) as supported with the Student T-test in the following types of human cancers: Breast epithelial carcinomas (%CFC= -49, p<0.037); and Colon mucosal cell adenomas (%CFC= +90, p<0.0001). The COSMIC website notes an up-regulated expression score for CHK2 in diverse human cancers of 551, which is 1.2-fold of the average score of 462 for the human protein kinases. The down-regulated expression score of 28 for this protein kinase in human cancers was 0.5-fold of the average score of 60 for the human protein kinases.
Mutagenesis Experiments:
Insertional mutagenesis studies in mice have not yet revealed a role for this protein kinase in mouse cancer oncogenesis.
Mutation Rate in All Cancers:
Percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.18 % in 25863 diverse cancer specimens. This rate is 2.4-fold higher than the average rate of 0.075 % calculated for human protein kinases in general.
Mutation Rate in Specific Cancers:
Highest percent mutation rates per 100 amino acids length in human cancers: 0.84 % in 1963 central nervous system cancers tested; 0.56 % in 1187 large intestine cancers tested; 0.37 % in 602 endometrium cancers tested; 0.37 % in 500 urinary tract cancers tested; 0.28 % in 905 ovary cancers tested; 0.26 % in 1945 lung cancers tested; 0.23 % in 807 skin cancers tested.
Frequency of Mutated Sites:
Most frequent mutations with the number of reports indicated in brackets: A392A (46); Y390C (37); K373E (20); M381V (15). These are primarily in the kinase catalytic domain.
Comments:
Only 3 deletions, 3 insertions and 3 complex mutations are noted on the COSMIC website.